Unveiling The Power Of Sandpoint Maps: A Comprehensive Guide To Spatial Analysis And Visualization
Unveiling the Power of Sandpoint Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Spatial Analysis and Visualization
Related Articles: Unveiling the Power of Sandpoint Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Spatial Analysis and Visualization
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Power of Sandpoint Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Spatial Analysis and Visualization. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Power of Sandpoint Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Spatial Analysis and Visualization
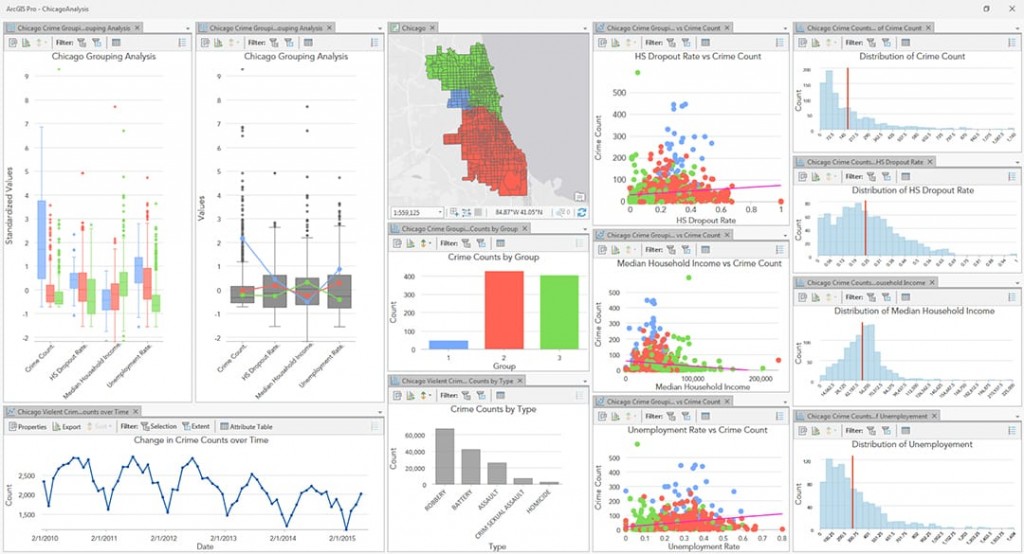
The field of spatial analysis relies heavily on the ability to visualize and interpret data tied to specific locations. This is where sandpoint maps, also known as dot density maps, emerge as powerful tools. These maps offer a unique perspective on spatial patterns, revealing insights that might otherwise remain hidden within raw data.
Understanding the Essence of Sandpoint Maps
Sandpoint maps are a type of thematic map that uses dots to represent the frequency or density of a particular phenomenon across a geographical area. Each dot represents a specific unit of data, such as a population count, crime incident, or disease case. The density of dots, therefore, visually communicates the concentration of the phenomenon in different parts of the map.
Key Components of a Sandpoint Map
A well-constructed sandpoint map comprises several key components:
- Base Map: This provides the underlying geographical framework, typically a map of a region, city, or country.
- Data Points: These are the dots representing the occurrences of the phenomenon being mapped.
- Legend: This clarifies the relationship between the dots and the data they represent. It specifies the number of units each dot signifies.
- Color Scheme: This can be used to differentiate between various categories of data, adding another layer of information to the map.
Benefits of Using Sandpoint Maps
Sandpoint maps offer numerous advantages in spatial analysis and visualization:
- Clear Visual Representation: They provide a straightforward and intuitive way to understand spatial patterns and distributions.
- Data Density Visualization: The density of dots effectively conveys the concentration of the phenomenon in different areas.
- Easy Interpretation: Even without extensive statistical knowledge, viewers can readily grasp the spatial trends illustrated by the map.
- Effective Communication: Sandpoint maps are a powerful tool for communicating complex spatial data to diverse audiences, including policymakers, researchers, and the general public.
- Identification of Hotspots and Outliers: They help identify areas with high concentrations of the phenomenon, revealing potential hotspots or outliers that require further investigation.
Applications of Sandpoint Maps
The versatility of sandpoint maps makes them valuable in a wide range of fields:
- Urban Planning: Analyzing population density, crime rates, and access to services.
- Epidemiology: Mapping disease outbreaks, identifying high-risk areas, and tracking disease spread.
- Environmental Science: Visualizing pollution levels, deforestation patterns, and wildlife distribution.
- Social Sciences: Studying migration patterns, poverty distribution, and access to education.
- Business Analytics: Identifying customer demographics, market trends, and competitor locations.
Construction and Interpretation of Sandpoint Maps
Creating an effective sandpoint map requires careful consideration of several factors:
- Data Selection: Choose data relevant to the research question and ensure its accuracy and reliability.
- Data Aggregation: Determine the appropriate unit of measurement for each dot (e.g., one dot represents 100 people).
- Map Projection: Select a suitable map projection that minimizes distortion and accurately represents the geographical area.
- Color Scheme: Use a color scheme that enhances visual clarity and effectively distinguishes between different categories of data.
- Legend Design: Create a clear and concise legend that explains the relationship between dots and data.
Interpreting a sandpoint map involves analyzing the spatial patterns revealed by the distribution of dots. Look for areas with high concentrations of dots, areas with few or no dots, and any clusters or trends that emerge from the map.
FAQs about Sandpoint Maps
1. What are the limitations of sandpoint maps?
While powerful, sandpoint maps have limitations. They can be challenging to create for large datasets due to the potential for overcrowding. Additionally, they do not account for the spatial distribution of the data within the area represented by each dot.
2. How do I choose the appropriate scale for my sandpoint map?
The scale should be determined based on the data and the research question. A larger scale (more detailed) is suitable for smaller areas with high data density, while a smaller scale (less detailed) is appropriate for larger areas with lower data density.
3. Can sandpoint maps be used to show multiple variables?
Yes, but it requires careful planning. Using different colors or symbols for different variables can visually represent multiple phenomena on the same map. However, it is crucial to avoid overcomplicating the map and ensure clarity in interpretation.
4. How do I determine the optimal dot size for my sandpoint map?
The dot size should be proportional to the data unit represented. Larger dots indicate higher values, while smaller dots represent lower values. It is crucial to maintain a consistent dot size throughout the map to avoid misinterpretations.
5. What software can be used to create sandpoint maps?
Several software programs can create sandpoint maps, including ArcGIS, QGIS, and Mapbox. These programs offer various features for data manipulation, map design, and visualization.
Tips for Creating Effective Sandpoint Maps
- Keep it Simple: Avoid overcrowding the map with too many dots.
- Use Clear Labels: Ensure that all labels are legible and easy to understand.
- Choose Appropriate Colors: Opt for colors that enhance visual clarity and contrast.
- Maintain Consistency: Use the same dot size and symbol throughout the map.
- Provide Context: Include a title, legend, and scale bar to provide context.
- Test for Clarity: Show the map to others to ensure it is easily interpretable.
Conclusion
Sandpoint maps offer a powerful and intuitive way to visualize spatial patterns and distributions. By understanding the principles behind their construction and interpretation, researchers, analysts, and decision-makers can leverage these maps to uncover insights, communicate complex data, and make informed decisions based on spatial patterns. As technology advances, sandpoint maps are likely to play an even greater role in various fields, providing valuable insights into the spatial dynamics of our world.


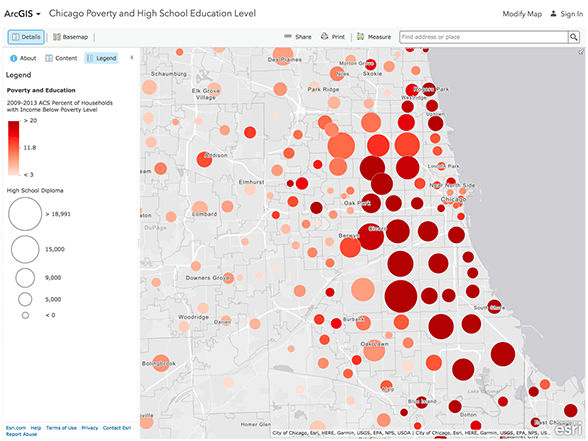



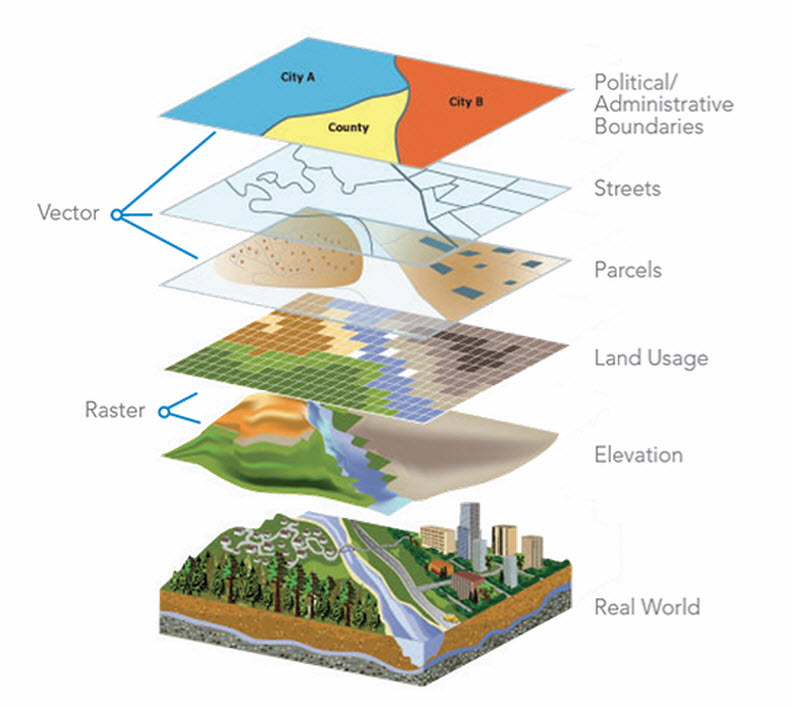
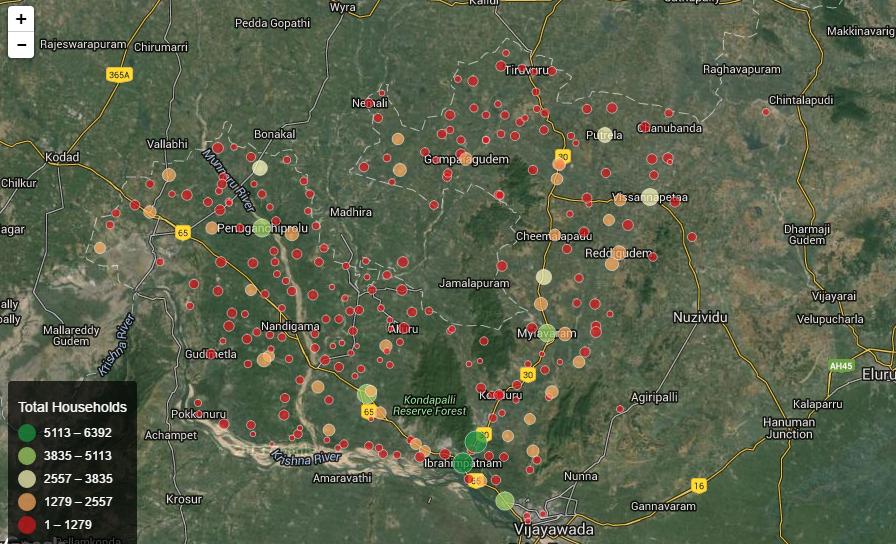
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Power of Sandpoint Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Spatial Analysis and Visualization. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- A Comprehensive Guide To The Map Of Lakewood, California
- Thailand: A Jewel In The Heart Of Southeast Asia
- Navigating The Nation: A Guide To Free United States Map Vectors
- Navigating The Tapestry Of Arkansas: A Comprehensive Guide To Its Towns And Cities
- Mapping The Shifting Sands: A Look At 9th Century England
- A Journey Through Greene County, New York: Exploring The Land Of Catskill Mountains And Scenic Beauty
- The United States Of America In 1783: A Nation Forged In Boundaries
- Unraveling The Magic: A Comprehensive Guide To The Wizard Of Oz Map In User Experience Design
Leave a Reply