Unveiling The Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide To Topographic Map Vectors
Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Topographic Map Vectors
Related Articles: Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Topographic Map Vectors
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Topographic Map Vectors. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Topographic Map Vectors

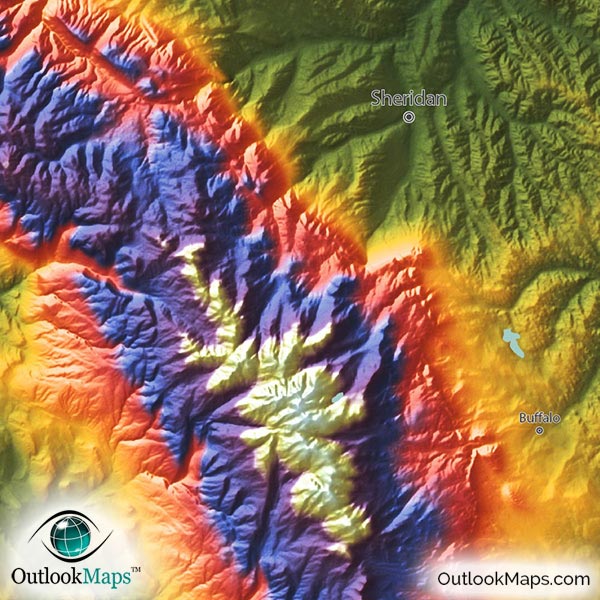
Topographic maps are essential tools for visualizing and understanding the Earth’s surface. They provide a detailed representation of terrain, elevation, and other features, offering invaluable insights for diverse applications ranging from navigation and land management to environmental studies and disaster preparedness. While traditional topographic maps are printed on paper, the advent of digital technology has ushered in a new era of map representation: topographic map vectors.
Understanding the Essence of Vector Data:
Before delving into the specifics of topographic map vectors, it is crucial to grasp the fundamental concept of vector data. Unlike raster data, which represents images as a grid of pixels, vector data uses points, lines, and polygons to define geographic features. Each feature is defined by its geometry (shape and location) and attributes (descriptive information). This approach offers several advantages:
- Scalability: Vector data can be scaled without losing detail, making it ideal for large-scale projects or when zooming in on specific areas.
- Precision: The use of points, lines, and polygons allows for accurate representation of features, eliminating the pixelation inherent in raster data.
- Flexibility: Vector data is easily edited and manipulated, facilitating analysis, visualization, and integration with other datasets.
Topographic Map Vectors: A Digital Revolution:
Topographic map vectors are essentially digitized versions of traditional topographic maps, leveraging the power of vector data to represent terrain features with remarkable accuracy and versatility. These maps are created by converting the contours, elevation points, and other elements of a paper map into digital coordinates, forming a database of geographic information. This process allows for seamless integration with Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and other spatial analysis tools.
Key Components of a Topographic Map Vector:
A topographic map vector typically includes the following components:
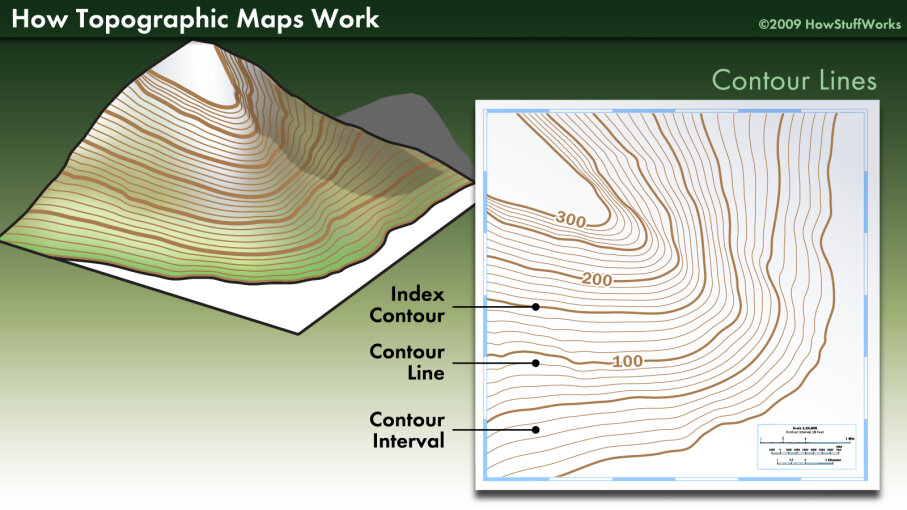
- Contours: Lines connecting points of equal elevation, providing a visual representation of terrain slopes and changes in altitude.
- Elevation Points: Discrete points on the map representing specific elevations, often used in conjunction with contours to refine the elevation model.
- Hydrographic Features: Rivers, lakes, streams, and other water bodies are represented by lines or polygons, capturing their location and shape.
- Land Cover: Different land cover types, such as forests, grasslands, and urban areas, are depicted using polygons, providing insights into the composition of the landscape.
- Cultural Features: Roads, railroads, buildings, and other man-made structures are represented by lines or polygons, offering valuable context for navigation and planning.
Benefits of Using Topographic Map Vectors:
The transition from paper maps to digital topographic map vectors has brought about a multitude of advantages:
- Accessibility: Digital maps are readily available online, eliminating the need for physical copies and providing easy access to information for anyone with an internet connection.
- Interoperability: Vector data can be seamlessly integrated with other GIS datasets, enabling complex spatial analysis and visualization of various environmental and societal factors.
- Dynamic Visualization: Digital maps allow for interactive exploration, zooming in and out, changing the viewpoint, and visualizing data in different formats.
- Data Analysis: The structured nature of vector data facilitates data analysis, allowing users to perform queries, extract information, and identify patterns within the geographic landscape.
- Customization: Digital maps can be easily customized to meet specific needs, allowing users to select relevant features, apply thematic overlays, and create tailored visualizations.
Applications of Topographic Map Vectors:
The versatility of topographic map vectors extends across diverse fields, offering valuable insights and supporting critical decision-making:
- Navigation: Hikers, climbers, and outdoor enthusiasts rely on topographic map vectors to navigate challenging terrain, identify trails, and plan routes.
- Urban Planning: City planners utilize these maps to assess land suitability for development, manage infrastructure projects, and optimize urban growth.
- Environmental Studies: Researchers and environmental agencies leverage topographic map vectors to analyze land cover changes, monitor deforestation, and assess the impact of climate change.
- Disaster Management: Emergency response teams use topographic map vectors to assess flood risks, plan evacuation routes, and coordinate relief efforts.
- Military Operations: The military relies on topographic map vectors for planning missions, navigating complex terrain, and understanding the battlefield environment.
Frequently Asked Questions about Topographic Map Vectors:
1. What are the different types of topographic map vectors available?
Topographic map vectors come in various formats, including:
- Shapefiles: A widely used geospatial data format that stores geographic information in a set of files.
- GeoTIFF: A georeferenced image file format that can store elevation data and other topographic features.
- KML: A file format used by Google Earth and other mapping software to display geographic information.
- GeoJSON: A text-based format for representing geographic data that is increasingly popular due to its flexibility and ease of use.
2. How can I obtain topographic map vectors?
There are several sources for obtaining topographic map vectors:
- Government Agencies: National mapping agencies, such as the United States Geological Survey (USGS), provide free and open-source topographic map vectors.
- Commercial Vendors: Companies specializing in geospatial data offer high-resolution topographic map vectors for purchase.
- OpenStreetMap: This collaborative project provides a free and open-source map of the world, including topographic data.
3. What software can I use to view and analyze topographic map vectors?
Several software programs are designed to work with topographic map vectors, including:
- ArcGIS: A comprehensive GIS software suite offering advanced tools for data analysis, visualization, and map creation.
- QGIS: A free and open-source GIS software that provides a user-friendly interface for working with vector data.
- Google Earth: A popular online mapping platform that allows users to view and interact with topographic map vectors.
4. What are the limitations of topographic map vectors?
While topographic map vectors offer significant advantages, it is important to acknowledge their limitations:
- Data Accuracy: The accuracy of topographic map vectors depends on the quality of the original source data and the methods used for digitization.
- Data Updating: Topographic map vectors may not always reflect the latest changes in the landscape, requiring regular updates to maintain accuracy.
- Data Complexity: Working with large and complex topographic map vectors can require specialized software and technical skills.
Tips for Using Topographic Map Vectors:
- Choose the right data source: Select a data source that provides the level of detail and accuracy required for your specific application.
- Understand data limitations: Be aware of the potential inaccuracies and limitations of the data to avoid misinterpretations.
- Utilize appropriate software: Choose a software program that is compatible with the data format and offers the functionality needed for your analysis.
- Explore data visualization techniques: Experiment with different visualization methods to present the data effectively and communicate insights clearly.
- Collaborate with experts: If needed, seek assistance from GIS professionals or other experts to ensure accurate data interpretation and analysis.
Conclusion:
Topographic map vectors represent a powerful tool for understanding and interacting with the Earth’s surface. By leveraging the advantages of vector data, they offer unparalleled accuracy, accessibility, and versatility, facilitating a wide range of applications in various fields. As technology continues to advance, the use of topographic map vectors is likely to become even more widespread, enabling deeper insights into the complexities of our planet and informing critical decisions across diverse sectors.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Topographic Map Vectors. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- A Comprehensive Guide To The Map Of Lakewood, California
- Thailand: A Jewel In The Heart Of Southeast Asia
- Navigating The Nation: A Guide To Free United States Map Vectors
- Navigating The Tapestry Of Arkansas: A Comprehensive Guide To Its Towns And Cities
- Mapping The Shifting Sands: A Look At 9th Century England
- A Journey Through Greene County, New York: Exploring The Land Of Catskill Mountains And Scenic Beauty
- The United States Of America In 1783: A Nation Forged In Boundaries
- Unraveling The Magic: A Comprehensive Guide To The Wizard Of Oz Map In User Experience Design
Leave a Reply