Unveiling The Earth’s Topography: A Comprehensive Exploration Of Physical Maps
Unveiling the Earth’s Topography: A Comprehensive Exploration of Physical Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling the Earth’s Topography: A Comprehensive Exploration of Physical Maps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Earth’s Topography: A Comprehensive Exploration of Physical Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Earth’s Topography: A Comprehensive Exploration of Physical Maps
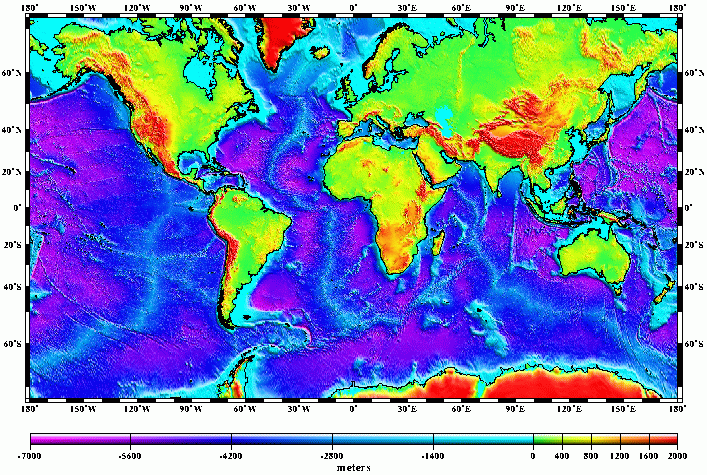
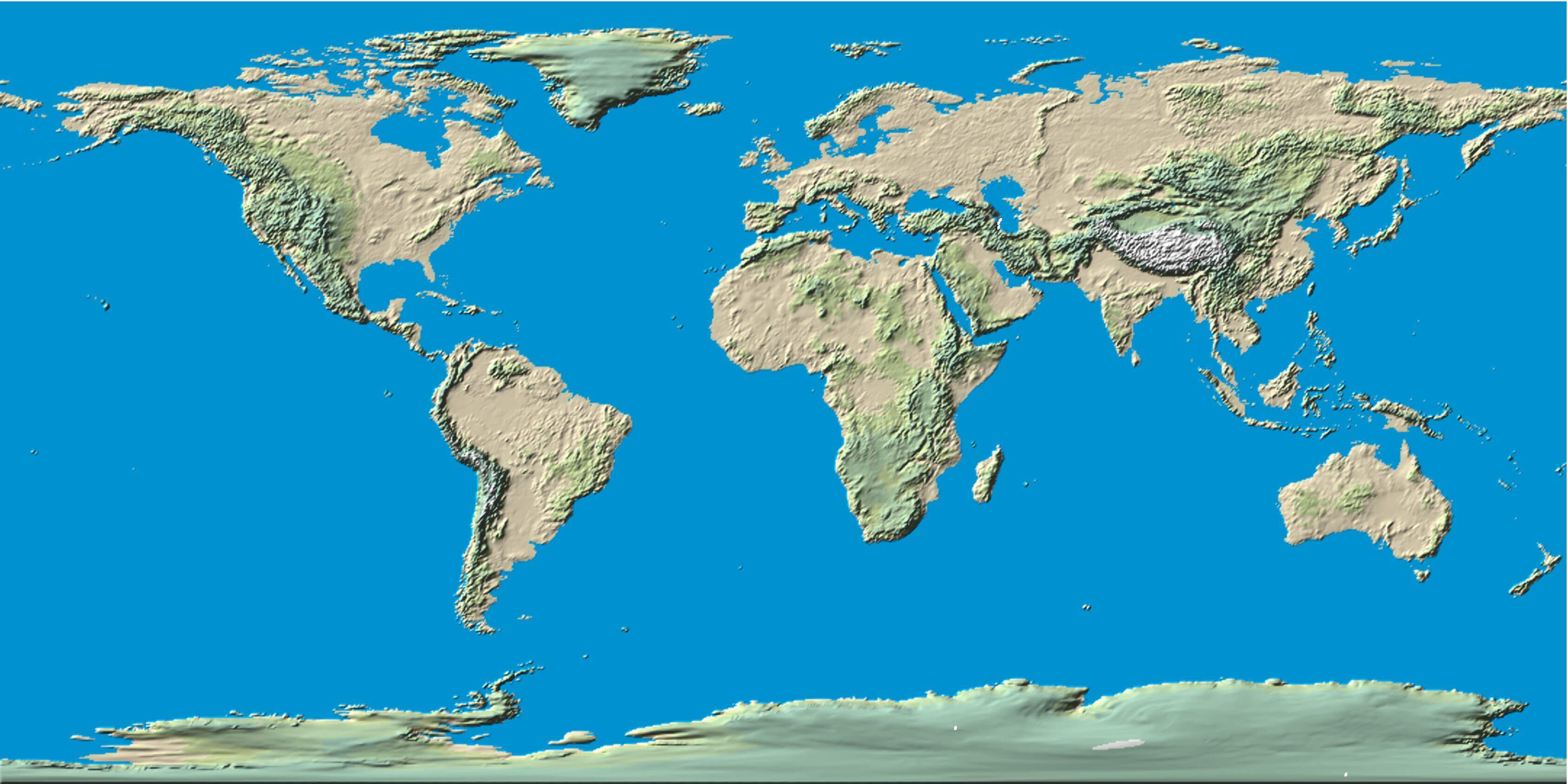
Physical maps, often referred to as relief maps, serve as visual representations of the Earth’s surface, emphasizing its physical features. They provide a detailed and comprehensive portrayal of the planet’s diverse topography, showcasing mountains, valleys, plains, rivers, and other prominent landforms. These maps are invaluable tools for understanding the Earth’s natural landscape, its geological history, and the impact of these features on human societies and ecosystems.
Understanding the Language of Physical Maps:
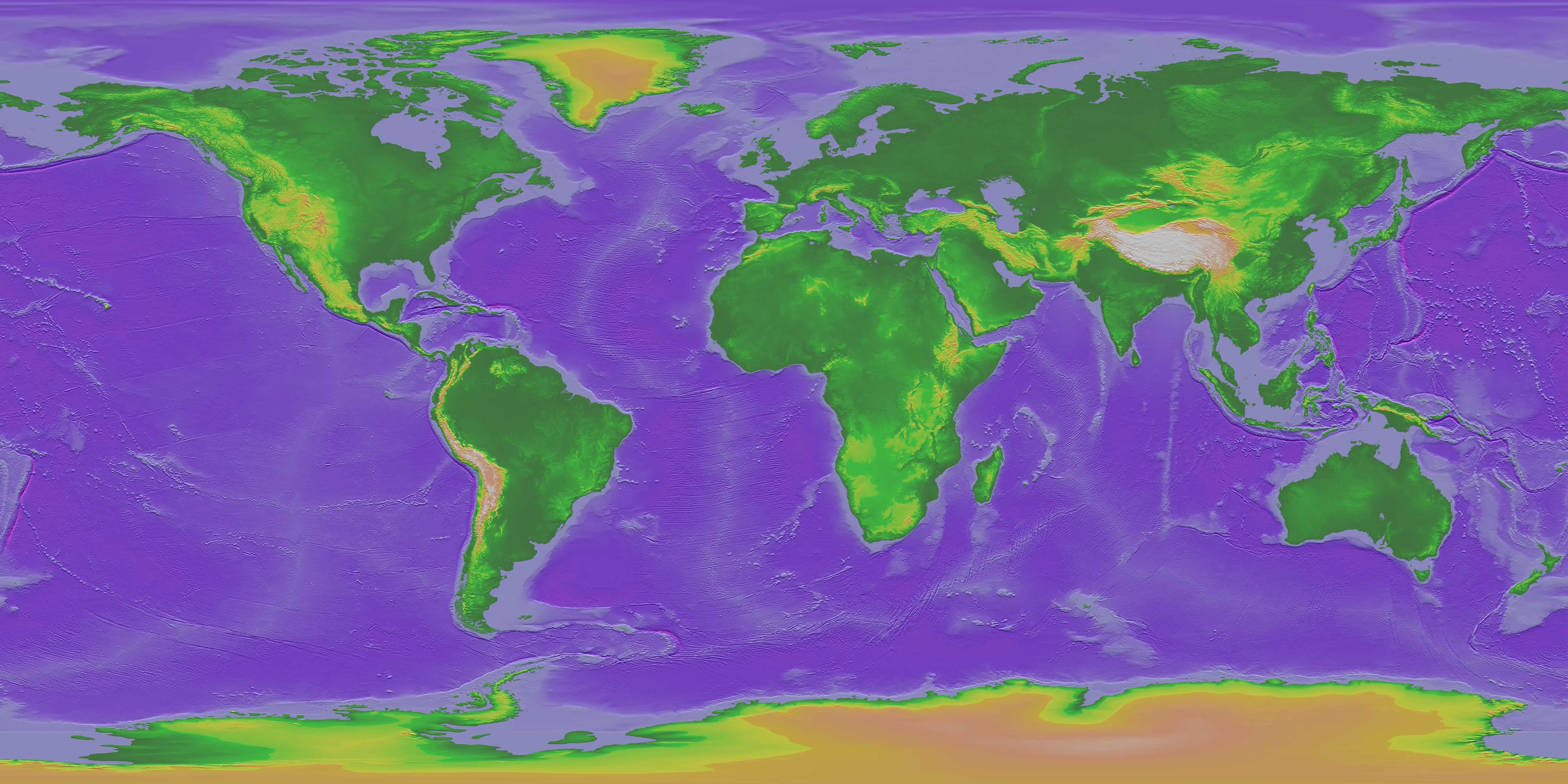
Physical maps utilize various techniques to represent the Earth’s topography. The most common method is through the use of contour lines, which connect points of equal elevation. These lines create a visual representation of the terrain’s undulation, providing a clear understanding of the steepness and gentleness of slopes.
Color and Shading:
Physical maps often incorporate color and shading to further enhance the visual representation of elevation. Higher elevations are typically represented by darker shades or warmer colors, while lower elevations are depicted in lighter shades or cooler colors. This color gradient provides a visually intuitive understanding of the landscape’s overall form.
Symbols and Labels:
Physical maps also employ symbols and labels to depict specific geographical features. Mountains, rivers, lakes, and other prominent landforms are often marked with distinct symbols. Labels provide additional information, identifying the names of these features and their locations.
Beyond the Surface:
Physical maps extend beyond the depiction of surface features. They can incorporate information about geological formations, such as rock types and fault lines, as well as hydrological features like drainage patterns and water bodies. These details offer valuable insights into the Earth’s geological history and the processes that have shaped its present landscape.
The Importance of Physical Maps:
Physical maps play a crucial role in various fields, offering a wealth of information and serving as essential tools for:
- Geography and Geology: Physical maps are indispensable for understanding the Earth’s topography, geological formations, and the processes that have shaped its surface. They are essential for research, teaching, and planning in these fields.
- Environmental Studies: Physical maps are crucial for studying the distribution of natural resources, the impact of human activities on the environment, and the potential for natural disasters.
- Urban Planning and Development: Physical maps provide essential information for urban planning, infrastructure development, and the assessment of environmental impact.
- Military and Defense: Physical maps are critical for military operations, providing information on terrain, elevation, and potential obstacles.
- Navigation and Recreation: Physical maps are used for hiking, camping, and other outdoor activities, providing essential information about routes, elevation changes, and points of interest.
- Education: Physical maps are valuable tools for teaching geography, geology, and environmental science, providing a visual and engaging way to understand the Earth’s diverse landscape.
FAQs about Physical Maps:
Q: What are the different types of physical maps?
A: Physical maps can be categorized based on their scale and focus. Some common types include:
- World Maps: Depicting the entire Earth’s surface, often focusing on major landmasses and oceans.
- Regional Maps: Focusing on specific continents, countries, or regions, providing detailed information about their topography.
- Topographic Maps: Highly detailed maps focusing on specific areas, often used for hiking, navigation, and other outdoor activities.
Q: How are physical maps created?
A: Physical maps are created using a combination of data sources, including:
- Aerial Photography and Satellite Imagery: Providing high-resolution images of the Earth’s surface.
- Ground Surveys: Using instruments like GPS and surveying equipment to measure elevations and distances.
- Digital Elevation Models (DEMs): Representing the Earth’s surface as a series of data points, providing detailed elevation information.
Q: What are the limitations of physical maps?
A: Physical maps, while valuable tools, have certain limitations:
- Distortion: Due to the Earth’s spherical shape, it is impossible to represent its surface accurately on a flat map without some distortion.
- Scale: Maps are typically scaled down, meaning that features are represented at a smaller size than in reality.
- Outdated Information: Physical maps can become outdated as the Earth’s landscape changes due to natural processes or human activities.
Tips for Using Physical Maps:
- Choose the right map: Select a map with the appropriate scale and focus for your specific needs.
- Understand the map’s symbols and legends: Familiarize yourself with the map’s symbols and labels to accurately interpret the information it presents.
- Consider the map’s date: Check the map’s publication date to ensure that the information is up-to-date.
- Use additional resources: Combine physical maps with other sources of information, such as online maps, satellite imagery, and field observations, to gain a more comprehensive understanding of the landscape.
Conclusion:
Physical maps are essential tools for understanding the Earth’s topography, its geological history, and the impact of these features on human societies and ecosystems. They provide a visual and engaging way to explore the planet’s diverse landscape, offering insights into its natural beauty, its complex processes, and its intricate relationship with human activities. By utilizing physical maps, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the Earth’s remarkable features and the importance of preserving and understanding its natural heritage.
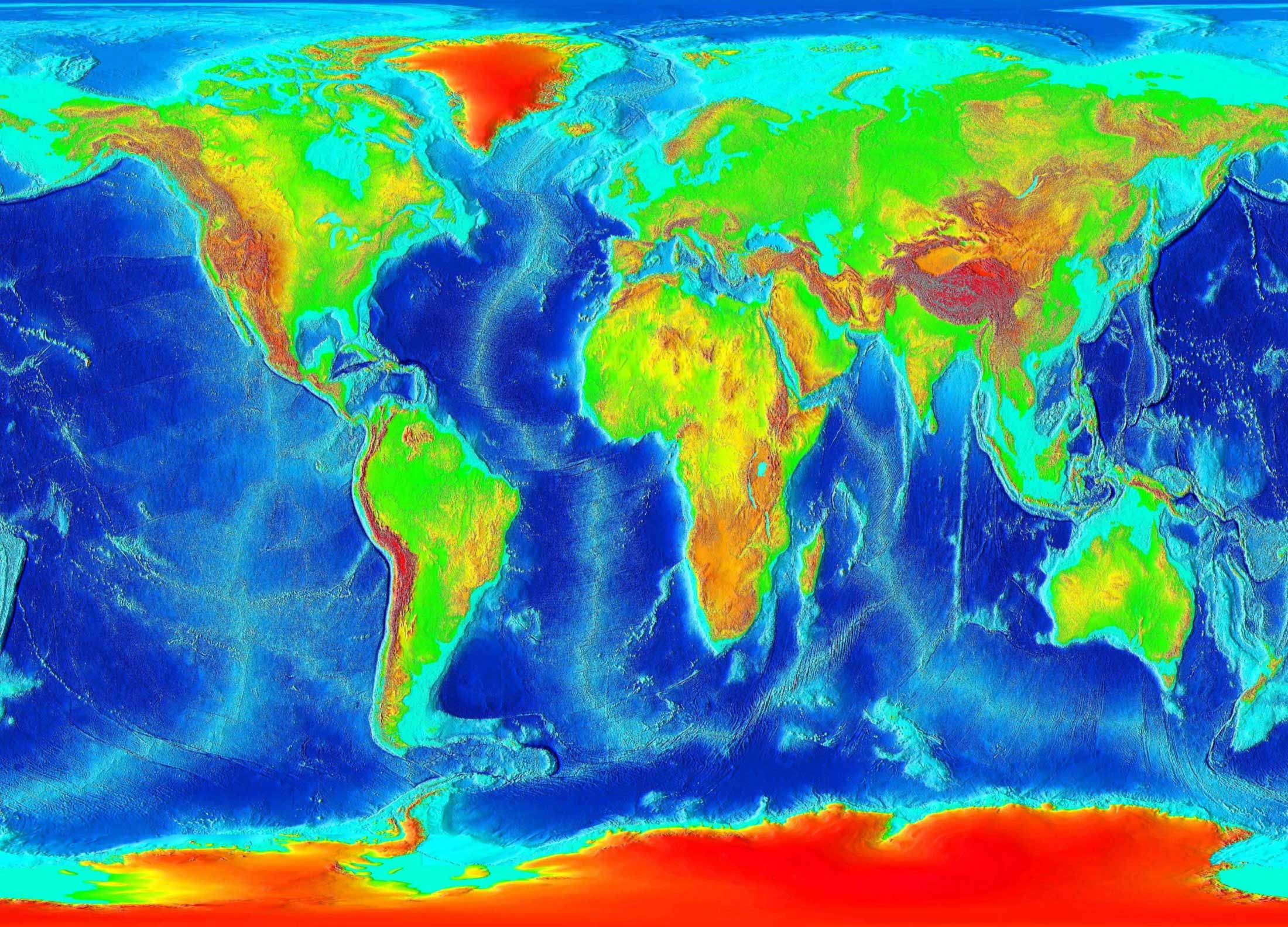
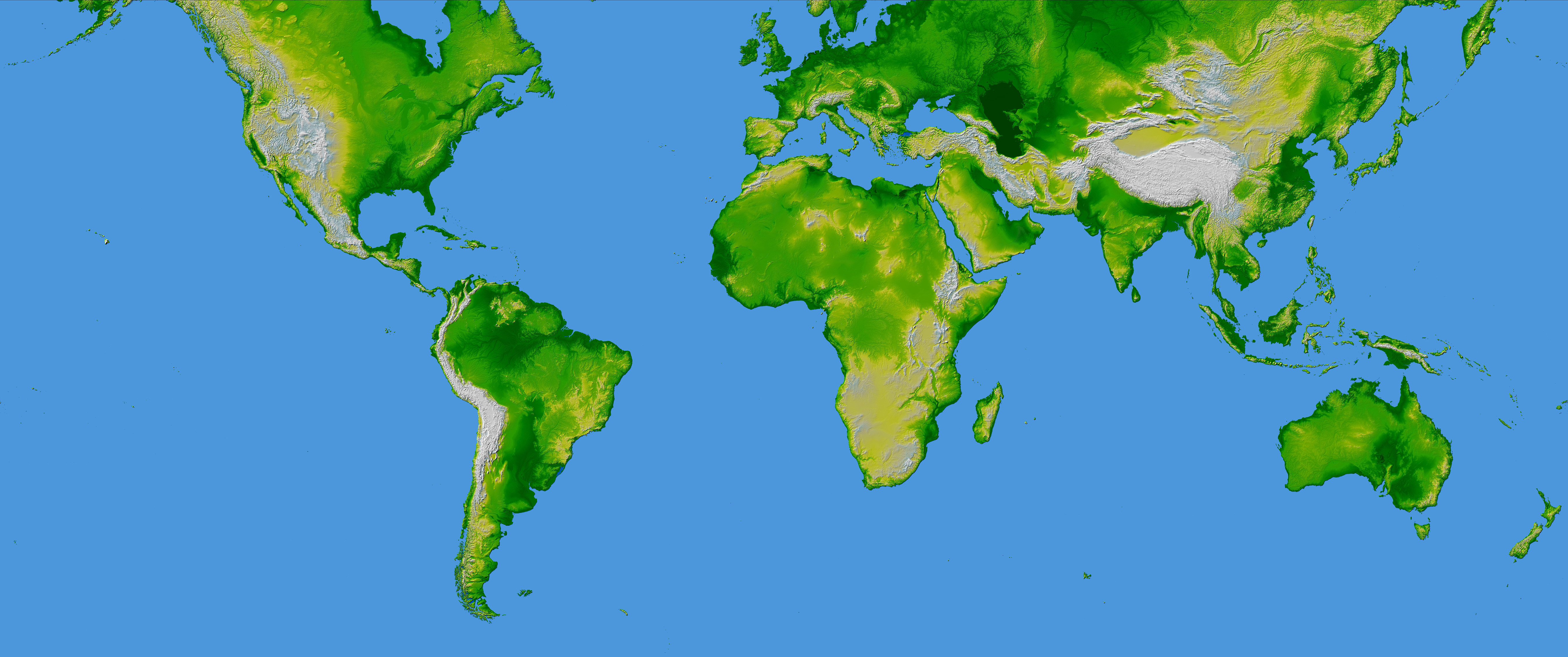
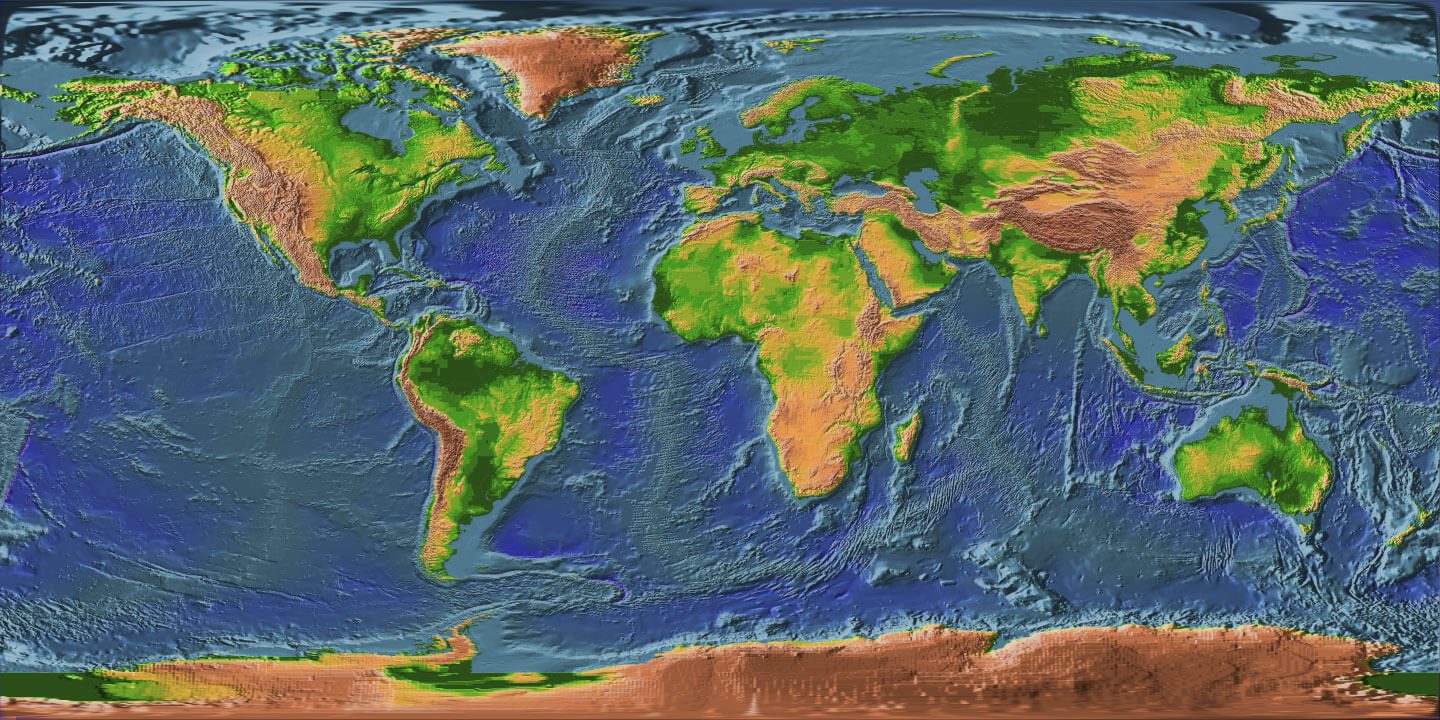

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Earth’s Topography: A Comprehensive Exploration of Physical Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- A Comprehensive Guide To The Map Of Lakewood, California
- Thailand: A Jewel In The Heart Of Southeast Asia
- Navigating The Nation: A Guide To Free United States Map Vectors
- Navigating The Tapestry Of Arkansas: A Comprehensive Guide To Its Towns And Cities
- Mapping The Shifting Sands: A Look At 9th Century England
- A Journey Through Greene County, New York: Exploring The Land Of Catskill Mountains And Scenic Beauty
- The United States Of America In 1783: A Nation Forged In Boundaries
- Unraveling The Magic: A Comprehensive Guide To The Wizard Of Oz Map In User Experience Design
Leave a Reply