Unraveling The Terrain Of The Big Apple: A Look At Topographic Maps Of New York City
Unraveling the Terrain of the Big Apple: A Look at Topographic Maps of New York City
Related Articles: Unraveling the Terrain of the Big Apple: A Look at Topographic Maps of New York City
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Terrain of the Big Apple: A Look at Topographic Maps of New York City. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the Terrain of the Big Apple: A Look at Topographic Maps of New York City

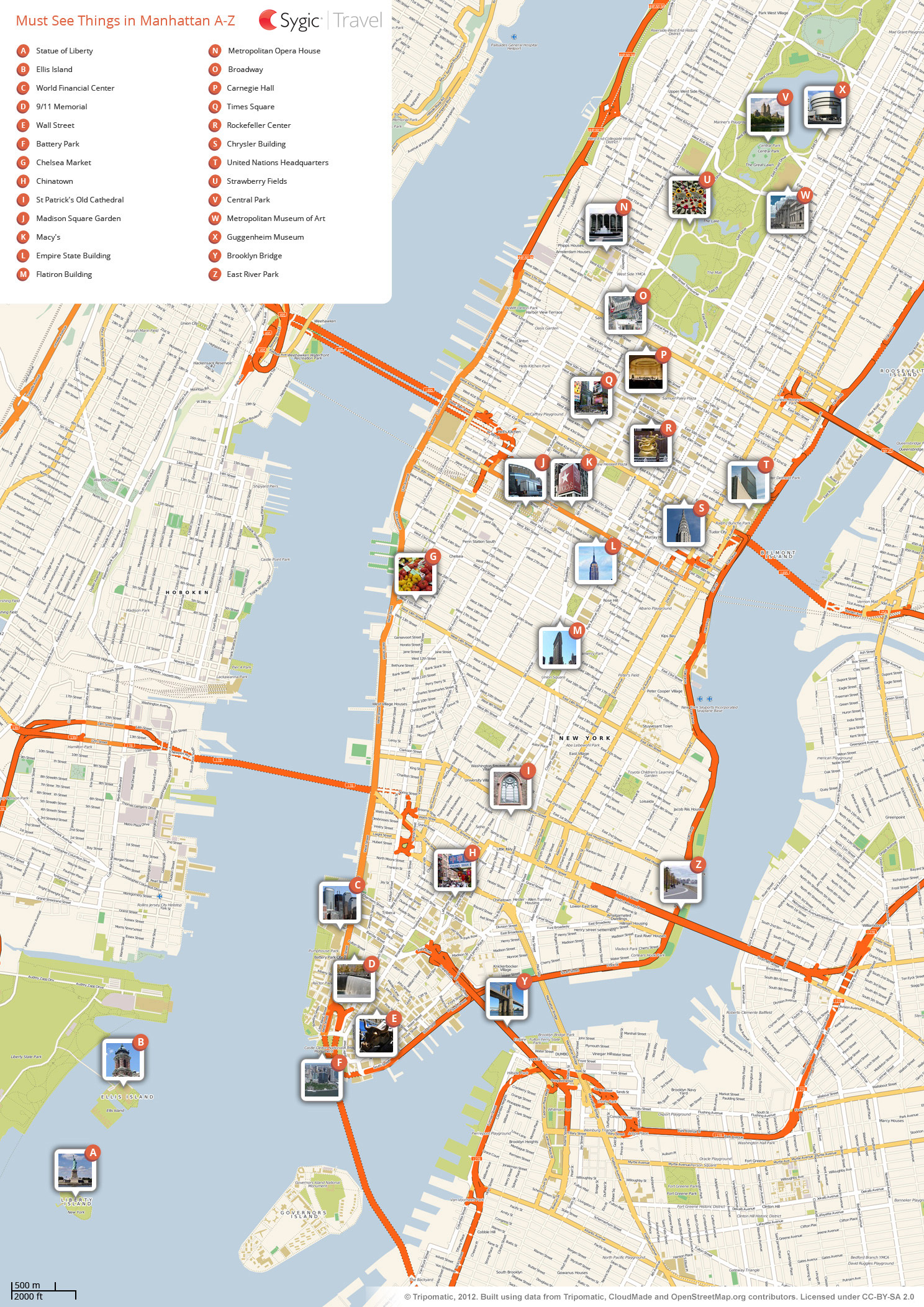
New York City, a sprawling metropolis, is not simply a flat canvas. Its landscape is a tapestry of hills, valleys, and waterways, each playing a role in shaping the city’s history, infrastructure, and urban fabric. Understanding this terrain becomes crucial when navigating the city, planning urban development, or simply appreciating the intricate relationship between the city and its natural environment. Topographic maps, with their unique ability to depict elevation and landforms, offer a vital tool for this understanding.
A Visual Representation of Elevation:
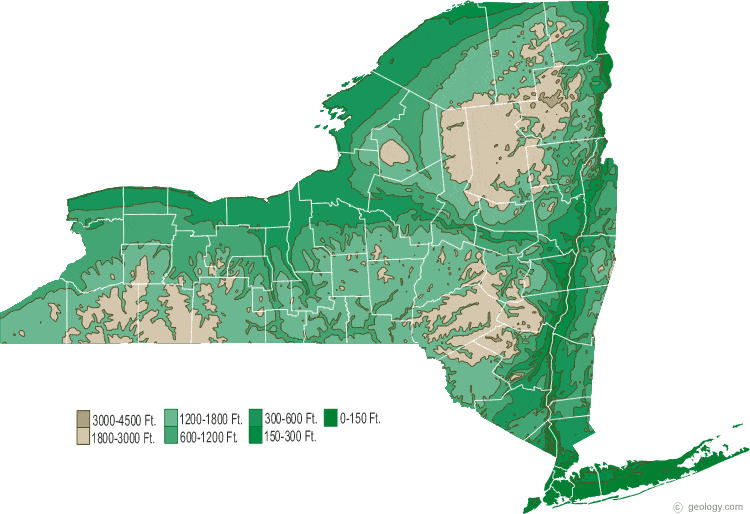
Unlike traditional maps that focus solely on geographical locations, topographic maps utilize contour lines to represent elevation. These lines connect points of equal elevation, effectively creating a three-dimensional representation of the landscape on a two-dimensional surface. The closer the contour lines, the steeper the terrain, while widely spaced lines indicate a gradual slope. This visual representation allows users to visualize the rise and fall of the land, providing a critical understanding of the city’s topography.
Decoding the Layers of New York City:
Examining a topographic map of New York City reveals several key features that shape the urban landscape:
- Manhattan’s Ridge: The island of Manhattan is not entirely flat. A prominent ridge runs along its central axis, culminating in Morningside Heights and reaching its highest point at Bennett Park. This ridge, formed by glacial activity, has historically influenced the city’s development, with its slopes accommodating housing and commercial areas.
- The East River Valley: The East River, though technically a tidal strait, acts as a valley separating Manhattan from Brooklyn and Queens. This valley, carved by glacial meltwater, is a significant geographical feature, influencing the city’s transportation infrastructure and the development of waterfront areas.
- The Brooklyn Heights: Brooklyn Heights, a prominent neighborhood overlooking the East River, is a testament to the city’s diverse topography. Its elevated location, a result of glacial deposits, offers panoramic views and has shaped the neighborhood’s historical and architectural character.
- The Staten Island Hills: Staten Island, the city’s southernmost borough, boasts a series of hills, including Todt Hill, the highest point in the city. These hills, formed by volcanic activity millions of years ago, provide a contrasting landscape to the flatter terrain of the other boroughs.
Beyond the Contour Lines: Unveiling the City’s Story:
Topographic maps of New York City are not just visual aids; they are historical documents, revealing the city’s evolution and the impact of human intervention on its landscape.
- The Impact of Urban Development: The maps reveal the significant changes in the city’s topography due to land reclamation projects, infrastructure development, and the construction of skyscrapers. The filling of wetlands, the creation of parks, and the alteration of coastlines are all evident, highlighting the dynamic relationship between the city and its natural environment.
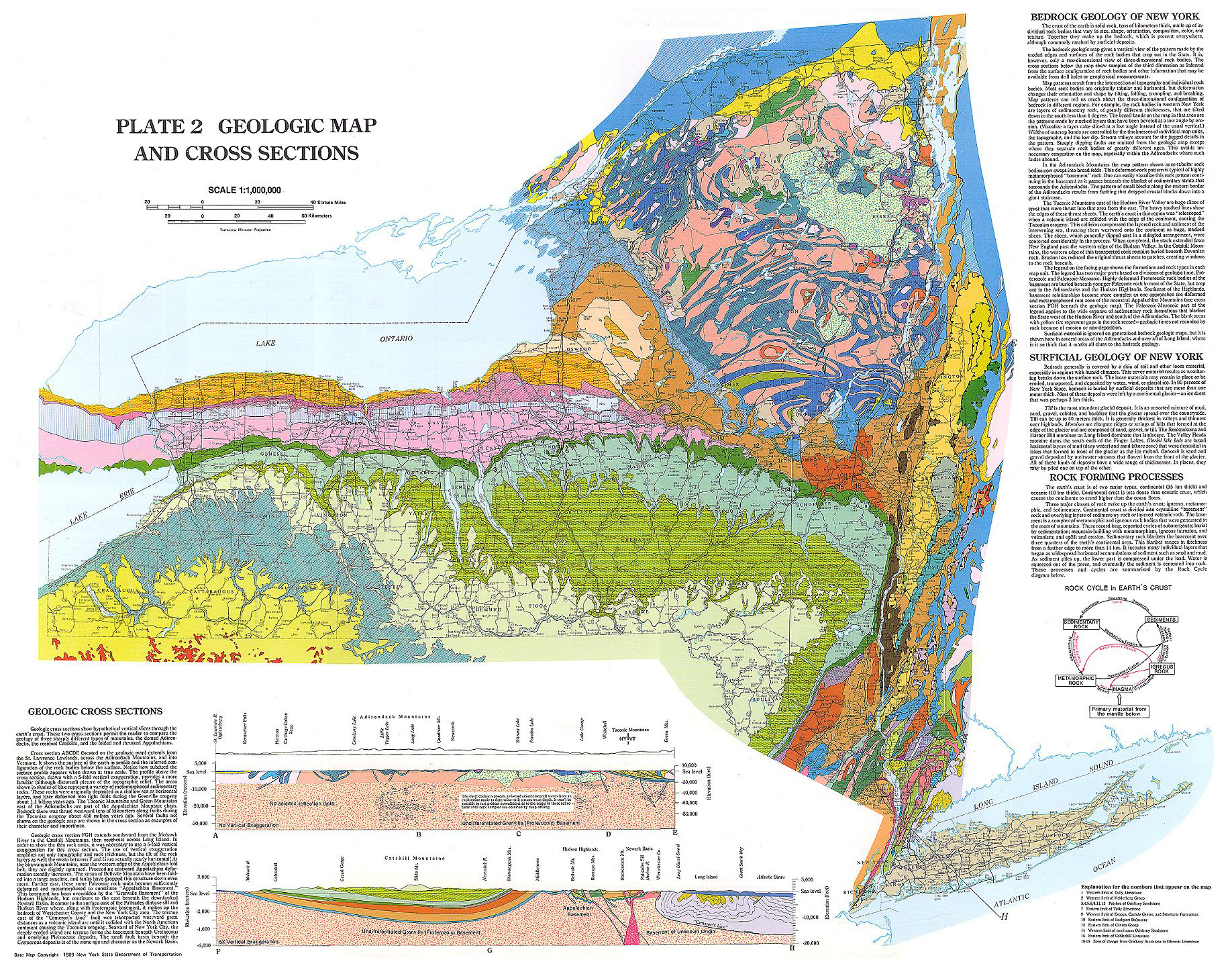
- The Influence of Geology: Topographic maps reveal the geological forces that shaped the city, from the glacial activity that carved the valleys and deposited sediment to the volcanic activity that created the hills of Staten Island. Understanding these geological origins helps explain the city’s unique terrain and the distribution of its natural resources.
- The Role of Water: The presence of rivers, bays, and the Atlantic Ocean is clearly depicted on topographic maps, highlighting the city’s dependence on water for transportation, recreation, and economic development. These waterways also reveal the city’s vulnerability to flooding and the importance of coastal management.
Benefits of Topographic Maps for New York City:
Beyond their historical and geographical significance, topographic maps provide valuable insights for various sectors:
- Urban Planning and Development: Planners use topographic maps to assess potential development sites, analyze the feasibility of infrastructure projects, and understand the impact of construction on the surrounding environment.
- Emergency Management: Emergency responders rely on topographic maps to navigate challenging terrain during natural disasters and to assess the potential impact of flooding, landslides, and other hazards.
- Environmental Conservation: Environmentalists use topographic maps to study the distribution of natural resources, identify sensitive ecosystems, and plan conservation efforts.
- Education and Recreation: Topographic maps serve as educational tools, helping students understand the city’s geography and its relationship to the natural world. They also guide hikers, cyclists, and outdoor enthusiasts in exploring the city’s diverse terrain.
FAQs on Topographic Maps of New York City:
1. Where can I find topographic maps of New York City?
Topographic maps of New York City are available from various sources, including:
- United States Geological Survey (USGS): The USGS provides free downloadable topographic maps of the entire United States, including New York City.
- New York City Department of City Planning: The Department of City Planning offers maps and data related to the city’s topography, including contour lines and elevation data.
- Online Mapping Services: Websites like Google Maps and OpenStreetMap offer topographic layers that can be overlaid on their maps, providing elevation information.
2. What are the different types of topographic maps available?
Topographic maps of New York City are available in different scales, each offering a different level of detail:
- Large-scale maps: These maps cover smaller areas in more detail, suitable for local planning and navigation.
- Small-scale maps: These maps cover larger areas with less detail, useful for regional planning and understanding the city’s broader topography.
3. How can I interpret the contour lines on a topographic map?
Contour lines represent points of equal elevation. The closer the lines, the steeper the terrain, while widely spaced lines indicate a gradual slope. Contour lines that form a closed circle represent a hill or peak, while those that form a U-shape indicate a valley.
4. How can I use topographic maps for recreational activities?
Topographic maps are invaluable for hikers, cyclists, and outdoor enthusiasts, providing information on elevation changes, trails, and potential hazards. They can help plan routes, estimate travel time, and choose appropriate activities based on the terrain.
5. What are the limitations of topographic maps?
Topographic maps are static representations of the landscape and do not account for dynamic changes, such as vegetation growth, building construction, or natural disasters. They also do not provide information on cultural features, such as roads, buildings, or landmarks.
Tips for Using Topographic Maps of New York City:
- Choose the appropriate scale: Select a map that covers the area of interest and provides the level of detail needed for the specific purpose.
- Understand the contour lines: Familiarize yourself with the meaning of contour lines and their relationship to elevation and terrain.
- Use other resources: Combine topographic maps with other sources of information, such as street maps, satellite imagery, and online mapping services, to gain a comprehensive understanding of the city’s landscape.
- Practice navigation: Familiarize yourself with the use of compass and GPS devices to navigate using topographic maps.
Conclusion:
Topographic maps of New York City offer a unique perspective on the city’s landscape, revealing the intricate interplay between nature and urban development. By understanding the city’s terrain and the forces that shaped it, we can better appreciate its history, plan for its future, and navigate its complex urban environment. Whether for urban planning, emergency management, or simply enjoying the city’s outdoor spaces, topographic maps remain a valuable tool for understanding the multifaceted landscape of the Big Apple.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Terrain of the Big Apple: A Look at Topographic Maps of New York City. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- A Comprehensive Guide To The Map Of Lakewood, California
- Thailand: A Jewel In The Heart Of Southeast Asia
- Navigating The Nation: A Guide To Free United States Map Vectors
- Navigating The Tapestry Of Arkansas: A Comprehensive Guide To Its Towns And Cities
- Mapping The Shifting Sands: A Look At 9th Century England
- A Journey Through Greene County, New York: Exploring The Land Of Catskill Mountains And Scenic Beauty
- The United States Of America In 1783: A Nation Forged In Boundaries
- Unraveling The Magic: A Comprehensive Guide To The Wizard Of Oz Map In User Experience Design
Leave a Reply