Understanding The Structure Of The Federal Reserve System: A Geographical Perspective
Understanding the Structure of the Federal Reserve System: A Geographical Perspective
Related Articles: Understanding the Structure of the Federal Reserve System: A Geographical Perspective
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Structure of the Federal Reserve System: A Geographical Perspective. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Understanding the Structure of the Federal Reserve System: A Geographical Perspective
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Understanding the Structure of the Federal Reserve System: A Geographical Perspective
- 3.1 The Twelve Federal Reserve Districts
- 3.2 The Importance of Geographical Distribution
- 3.3 Functions of the Federal Reserve Banks
- 3.4 The Federal Reserve Map: A Visual Representation of the System
- 3.5 FAQs:
- 3.6 Tips:
- 3.7 Conclusion:
- 4 Closure
Understanding the Structure of the Federal Reserve System: A Geographical Perspective
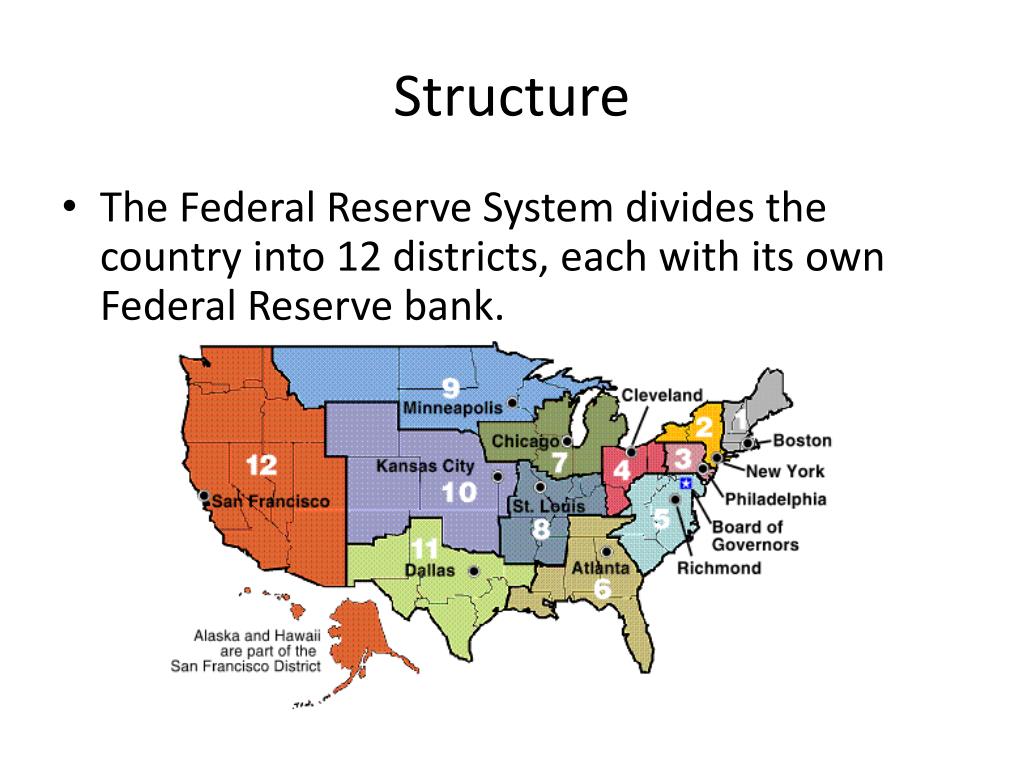
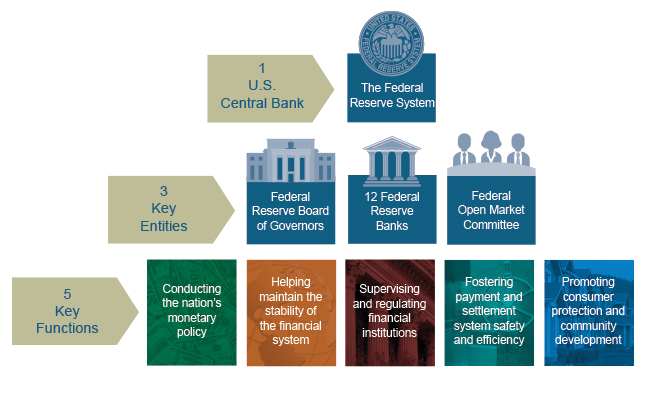
The Federal Reserve System, commonly known as the Fed, is the central bank of the United States. Its primary responsibility is to ensure the stability of the nation’s financial system and to foster economic growth. The Fed’s structure is not centralized but rather decentralized, with 12 regional Federal Reserve Banks strategically located across the country. This geographical distribution plays a crucial role in the Fed’s effectiveness and reflects the diverse economic landscape of the United States.
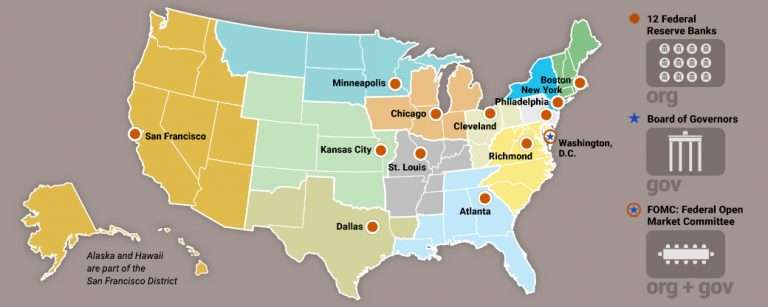
The Twelve Federal Reserve Districts
The United States is divided into twelve Federal Reserve Districts, each with its own Federal Reserve Bank. These districts are not defined by state lines but rather by economic activity and geographical proximity. The twelve districts are:
- Boston: Encompassing Maine, Vermont, New Hampshire, Massachusetts, Rhode Island, and Connecticut.
- New York: Covering New York State and northern New Jersey.
- Philadelphia: Including Pennsylvania, Delaware, southern New Jersey, and parts of eastern Ohio.
- Cleveland: Serving Ohio, western Pennsylvania, eastern Kentucky, and northern West Virginia.
- Richmond: Covering Virginia, North Carolina, South Carolina, Maryland, and the District of Columbia.
- Atlanta: Encompassing Georgia, Florida, Alabama, Mississippi, and parts of Louisiana and Tennessee.
- Chicago: Serving Illinois, Indiana, Michigan, Wisconsin, and parts of Iowa and Minnesota.
- St. Louis: Including Missouri, Arkansas, Tennessee, southern Illinois, and parts of Mississippi and Kentucky.
- Minneapolis: Covering Minnesota, North Dakota, South Dakota, Montana, and parts of Wisconsin and Iowa.
- Kansas City: Serving Kansas, Nebraska, Oklahoma, Colorado, Wyoming, and parts of Missouri and New Mexico.
- Dallas: Encompassing Texas, Louisiana, and parts of New Mexico and Oklahoma.
- San Francisco: Serving California, Nevada, Arizona, Utah, Alaska, Hawaii, and parts of Idaho and Oregon.
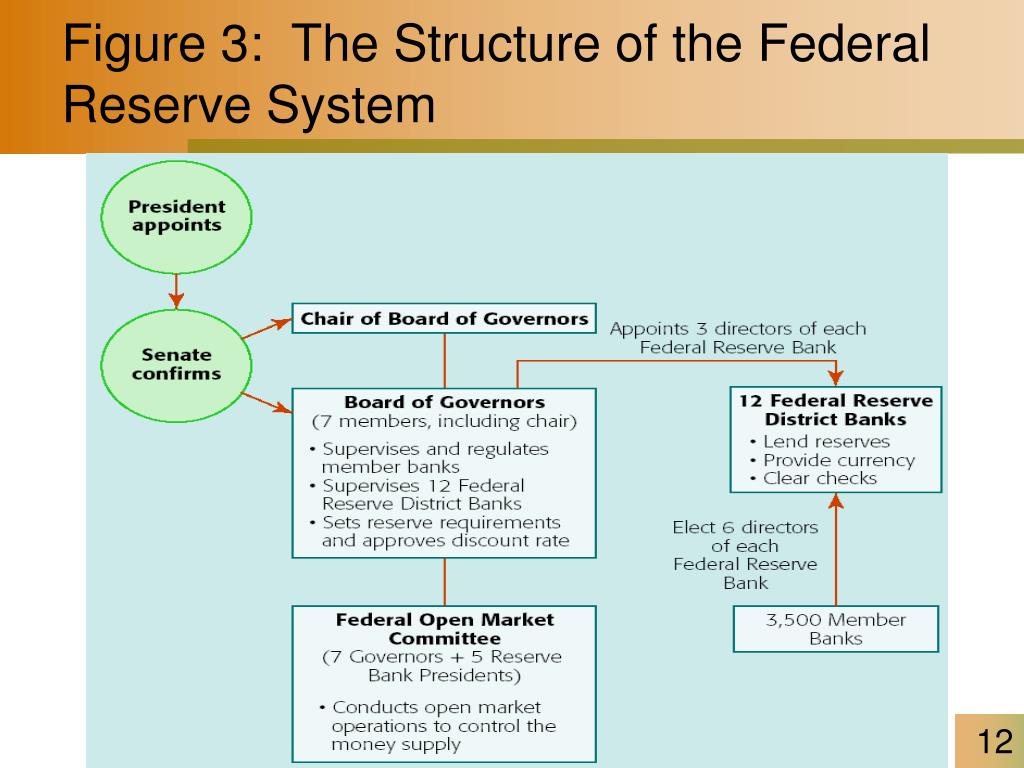
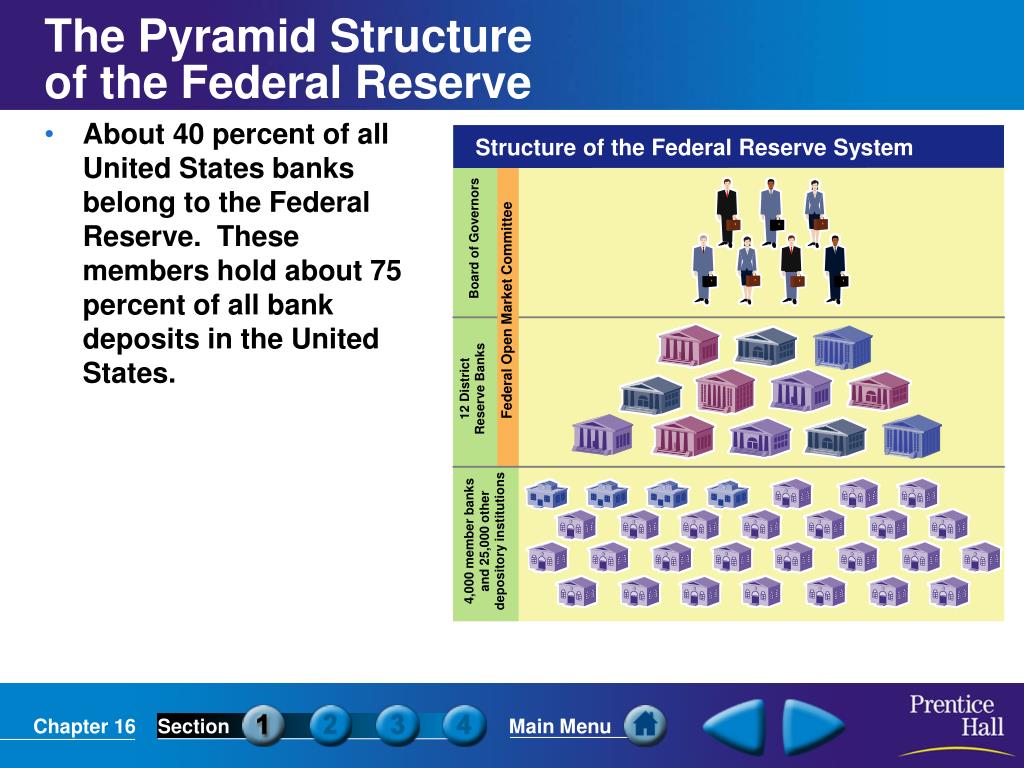
Each Federal Reserve Bank is governed by a Board of Directors, composed of nine members: three elected by member banks, three appointed by the Board of Governors, and three appointed by the Board of Governors from the public. The Board of Governors, based in Washington D.C., oversees the entire Federal Reserve System.
The Importance of Geographical Distribution
The decentralized structure of the Federal Reserve System offers several benefits:
- Regional Economic Expertise: Each Federal Reserve Bank possesses in-depth knowledge of the economic conditions and challenges specific to its district. This local expertise allows the Fed to tailor its policies to address the unique needs of different regions.
- Improved Communication: The regional Federal Reserve Banks act as intermediaries between the Board of Governors and local businesses, financial institutions, and communities. They gather information about economic activity and provide insights to the Board, facilitating a more informed decision-making process.
- Enhanced Responsiveness: The decentralized structure allows the Fed to respond quickly to regional economic shocks or crises. By working closely with local banks and businesses, the Federal Reserve Banks can provide immediate support and mitigate potential economic damage.
- Increased Accountability: The regional Federal Reserve Banks are accountable to the businesses and communities they serve. This local accountability ensures that the Fed’s policies are aligned with the needs of the people and businesses they are designed to benefit.
Functions of the Federal Reserve Banks
Each Federal Reserve Bank performs a range of critical functions, including:
- Providing financial services to banks and other financial institutions: This includes clearing checks, providing loans, and facilitating electronic payments.
- Supervising and regulating banks within their district: This ensures the safety and soundness of the banking system and protects consumers from unfair or abusive practices.
- Conducting research and analysis of economic conditions: This provides insights into the local and national economy, informing the Fed’s monetary policy decisions.
- Promoting economic growth and stability: The Federal Reserve Banks work with local businesses and communities to foster economic development and ensure financial stability.
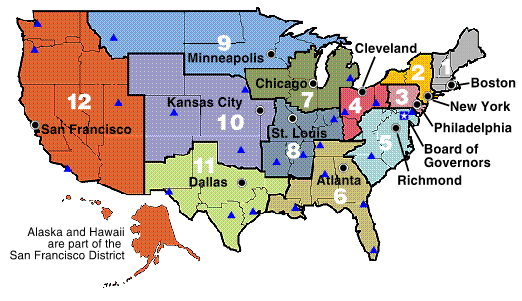
The Federal Reserve Map: A Visual Representation of the System
The Federal Reserve map is a visual representation of the twelve Federal Reserve Districts. It provides a clear and concise overview of the geographical structure of the Federal Reserve System. This map is a valuable tool for understanding the Fed’s reach and its role in supporting the economic well-being of the nation.
FAQs:
Q: What is the purpose of the Federal Reserve System?
A: The Federal Reserve System serves as the central bank of the United States, responsible for maintaining the stability of the financial system and promoting economic growth.
Q: Why is the Federal Reserve System decentralized?
A: The decentralized structure allows the Fed to leverage regional economic expertise, improve communication, enhance responsiveness, and increase accountability.
Q: How many Federal Reserve Banks are there?
A: There are twelve Federal Reserve Banks, each serving a specific geographical district.
Q: What are the main functions of the Federal Reserve Banks?
A: The Federal Reserve Banks provide financial services to banks, supervise and regulate banks, conduct economic research, and promote economic growth and stability.
Q: How does the Federal Reserve map help in understanding the Fed’s structure?
A: The Federal Reserve map provides a visual representation of the twelve Federal Reserve Districts, highlighting the geographical reach and organization of the Fed.
Tips:
- Consult the Federal Reserve website: The Federal Reserve website provides detailed information about each Federal Reserve Bank, including its history, functions, and contact information.
- Utilize the Federal Reserve map as a reference tool: The map can help you identify the Federal Reserve Bank responsible for your region and gain a better understanding of the Fed’s geographical reach.
- Stay informed about economic developments: The Federal Reserve publishes economic reports and releases statements on monetary policy decisions. Keeping informed about these developments can help you understand the Fed’s role in shaping the economy.
Conclusion:
The Federal Reserve System’s decentralized structure, with its twelve regional Federal Reserve Banks, is crucial for effectively managing the nation’s financial system and fostering economic growth. The geographical distribution allows the Fed to leverage local expertise, improve communication, enhance responsiveness, and increase accountability. The Federal Reserve map serves as a visual representation of this structure, providing a valuable tool for understanding the Fed’s reach and its role in supporting the economic well-being of the United States. By understanding the structure and functions of the Federal Reserve System, individuals and businesses can gain a deeper appreciation for its importance in shaping the economic landscape of the nation.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Structure of the Federal Reserve System: A Geographical Perspective. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- A Comprehensive Guide To The Map Of Lakewood, California
- Thailand: A Jewel In The Heart Of Southeast Asia
- Navigating The Nation: A Guide To Free United States Map Vectors
- Navigating The Tapestry Of Arkansas: A Comprehensive Guide To Its Towns And Cities
- Mapping The Shifting Sands: A Look At 9th Century England
- A Journey Through Greene County, New York: Exploring The Land Of Catskill Mountains And Scenic Beauty
- The United States Of America In 1783: A Nation Forged In Boundaries
- Unraveling The Magic: A Comprehensive Guide To The Wizard Of Oz Map In User Experience Design
Leave a Reply