Understanding Florida’s Climate Zones: A Guide To The Sunshine State
Understanding Florida’s Climate Zones: A Guide to the Sunshine State
Related Articles: Understanding Florida’s Climate Zones: A Guide to the Sunshine State
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding Florida’s Climate Zones: A Guide to the Sunshine State. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Understanding Florida’s Climate Zones: A Guide to the Sunshine State
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Understanding Florida’s Climate Zones: A Guide to the Sunshine State
- 3.1 The Importance of Climate Zones in Florida
- 3.2 Understanding Florida’s Climate Zones
- 3.3 The Impact of Climate Zones on Florida’s Landscape and Ecology
- 3.4 FAQs About Climate Zones in Florida
- 3.5 Tips for Utilizing the Florida Climate Zone Map
- 3.6 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Understanding Florida’s Climate Zones: A Guide to the Sunshine State
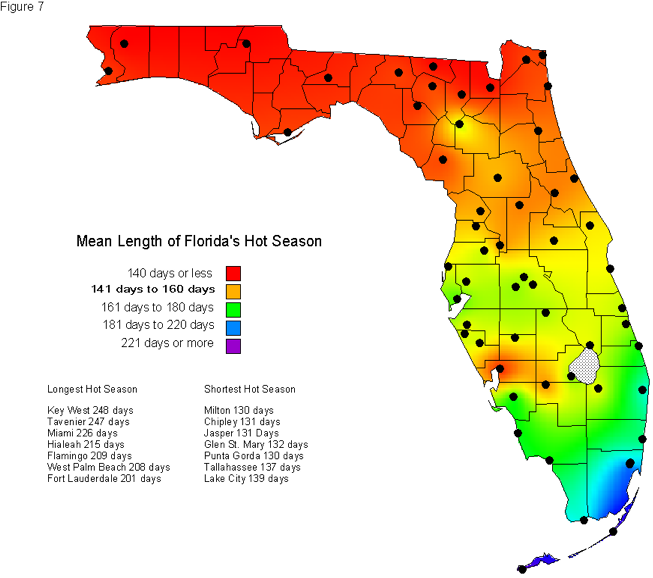
Florida, known for its year-round warmth and stunning beaches, is a state of diverse climates. To better understand the nuances of these climates and their impact on various aspects of life in Florida, the state utilizes a climate zone map. This map categorizes different regions of Florida based on their average annual minimum temperatures, providing valuable information for a range of applications, from landscaping and agriculture to construction and energy efficiency.
The Importance of Climate Zones in Florida
The climate zone map is a crucial tool for various sectors within Florida:
1. Agriculture: Farmers rely on this map to determine which crops are best suited for their specific region. Knowing the average minimum temperature helps them select plants that can thrive in the local climate, ensuring successful harvests and optimal yields.
2. Landscaping: Understanding climate zones is essential for selecting plants and trees that can tolerate the local conditions. This ensures that landscaping projects are successful, with plants thriving and contributing to the aesthetic appeal of the region.
3. Construction: Building codes and regulations often incorporate climate zone data to ensure that structures are built to withstand the specific weather conditions of the area. This includes factors like wind resistance, roof design, and insulation requirements.
4. Energy Efficiency: The climate zone map helps determine the appropriate level of insulation and heating/cooling systems for homes and buildings. This information helps homeowners and businesses optimize energy consumption and minimize energy costs.
5. Public Health: Climate zones play a role in understanding the spread of diseases and pests. By knowing the temperature ranges in different regions, health officials can better predict and address potential public health risks.
6. Tourism: Tourists often choose their travel destinations based on climate. The climate zone map provides valuable information about the expected temperature ranges and weather patterns in different parts of Florida, helping travelers make informed decisions about their vacation plans.
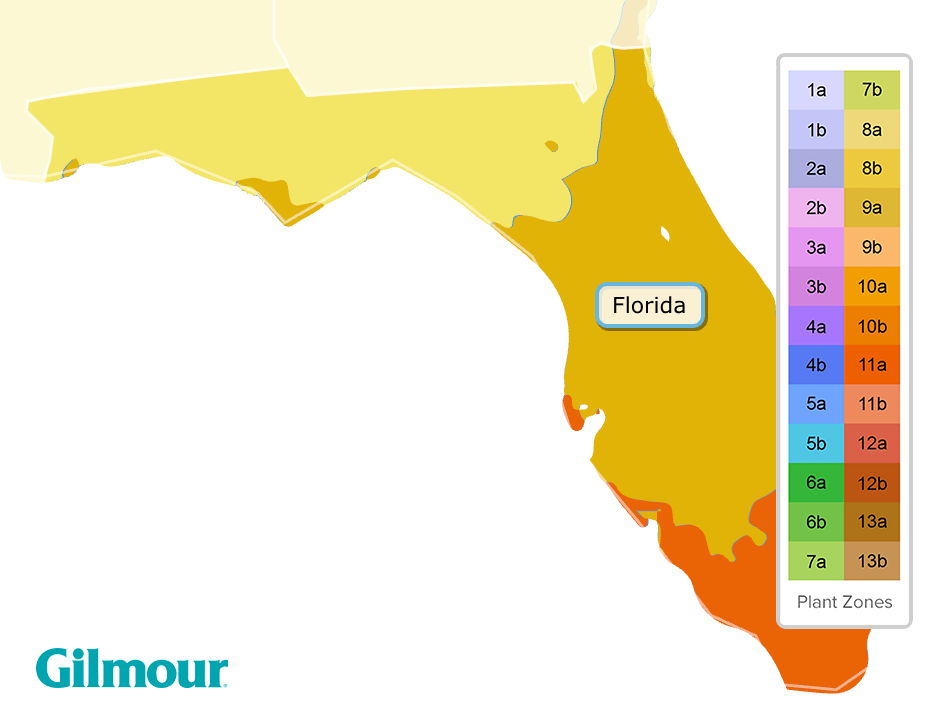
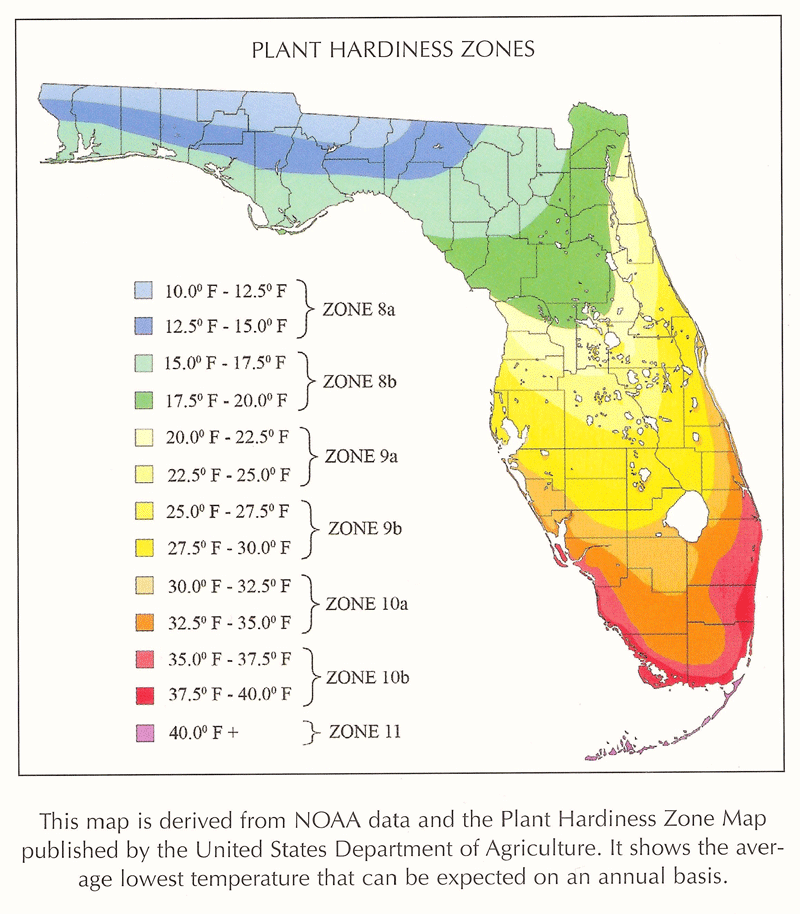
Understanding Florida’s Climate Zones
Florida is divided into three distinct climate zones, each with its own unique characteristics:
Zone 9a: This zone encompasses the southernmost portion of Florida, including the Florida Keys and the southern tip of the peninsula. It experiences the warmest temperatures, with average annual minimum temperatures ranging from 30°F to 35°F. This zone is characterized by a tropical climate with warm winters and hot, humid summers.
Zone 9b: This zone covers a large portion of South Florida, extending from the southern tip of the peninsula north to the Orlando area. It experiences slightly cooler temperatures than Zone 9a, with average annual minimum temperatures ranging from 35°F to 40°F. While still classified as tropical, this zone experiences a slightly more pronounced winter season with cooler temperatures and occasional frost.
Zone 8b: This zone covers the northern portion of Florida, including the panhandle and much of the central part of the state. It experiences the coolest temperatures, with average annual minimum temperatures ranging from 40°F to 45°F. This zone is characterized by a subtropical climate with warm winters and hot, humid summers, but with a more defined winter season and the potential for occasional frost.
The Impact of Climate Zones on Florida’s Landscape and Ecology
The distinct climate zones in Florida have a significant impact on the state’s diverse landscape and unique ecosystems:
1. Vegetation: Florida’s climate zones influence the types of plants and trees that thrive in each region. In the warmer southern zones, tropical plants like palms, ferns, and orchids flourish. In the cooler northern zones, subtropical plants like citrus trees, live oaks, and magnolias dominate the landscape.
2. Wildlife: The different climate zones support a wide variety of animal species. The warmer southern zones are home to unique reptiles and amphibians, while the cooler northern zones attract a greater diversity of bird species.
3. Coastal Ecosystems: Florida’s coastline is heavily influenced by climate zones. The warmer southern zones experience more intense hurricanes, while the cooler northern zones are more susceptible to colder water temperatures and sea level rise.
4. Agriculture: The climate zones determine the suitability of different crops for various regions of Florida. Citrus fruits, for example, thrive in the warmer southern zones, while vegetables like tomatoes and peppers are well-suited for the cooler northern zones.
FAQs About Climate Zones in Florida
1. What is the purpose of the Florida climate zone map?
The climate zone map is a valuable tool that helps residents, businesses, and government agencies understand the specific climate conditions in different regions of Florida. This information is crucial for various applications, from landscaping and agriculture to construction and energy efficiency.
2. How are the climate zones determined?
Climate zones are determined by the average annual minimum temperature in a specific region. This data is collected over a long period, typically 30 years, to establish a reliable baseline for temperature ranges.
3. What is the difference between a tropical and subtropical climate?
Tropical climates experience warm temperatures year-round, with no distinct winter season. Subtropical climates have a more defined winter season, with cooler temperatures and the potential for occasional frost.
4. What are the benefits of understanding climate zones?
Understanding climate zones helps individuals and organizations make informed decisions about various aspects of life in Florida, including landscaping, agriculture, construction, energy efficiency, and public health.
5. Where can I find the Florida climate zone map?
The Florida climate zone map can be found on the website of the University of Florida’s Institute of Food and Agricultural Sciences (IFAS). It is also available through other sources, such as the Florida Department of Agriculture and Consumer Services.
Tips for Utilizing the Florida Climate Zone Map
1. Consult the map before starting any landscaping projects. Choose plants and trees that are well-suited to the specific climate zone of your region.
2. Consider the climate zone when designing or building a home or business. Incorporate appropriate insulation, heating/cooling systems, and building materials to ensure energy efficiency and comfort.
3. Use the map to guide your agricultural practices. Select crops that are best suited for the specific climate zone of your farm or garden.
4. Stay informed about weather patterns and potential risks associated with your climate zone. This includes hurricanes, droughts, and other extreme weather events.
5. Share the information about climate zones with others. Help raise awareness about the importance of understanding and adapting to Florida’s diverse climates.
Conclusion
The climate zone map of Florida is a valuable resource that provides essential information about the state’s diverse climates. By understanding the specific climate conditions in different regions, individuals, businesses, and government agencies can make informed decisions that promote sustainability, efficiency, and resilience in the face of climate change. The map is a testament to the importance of data-driven approaches to understanding and adapting to the unique characteristics of Florida’s environment.
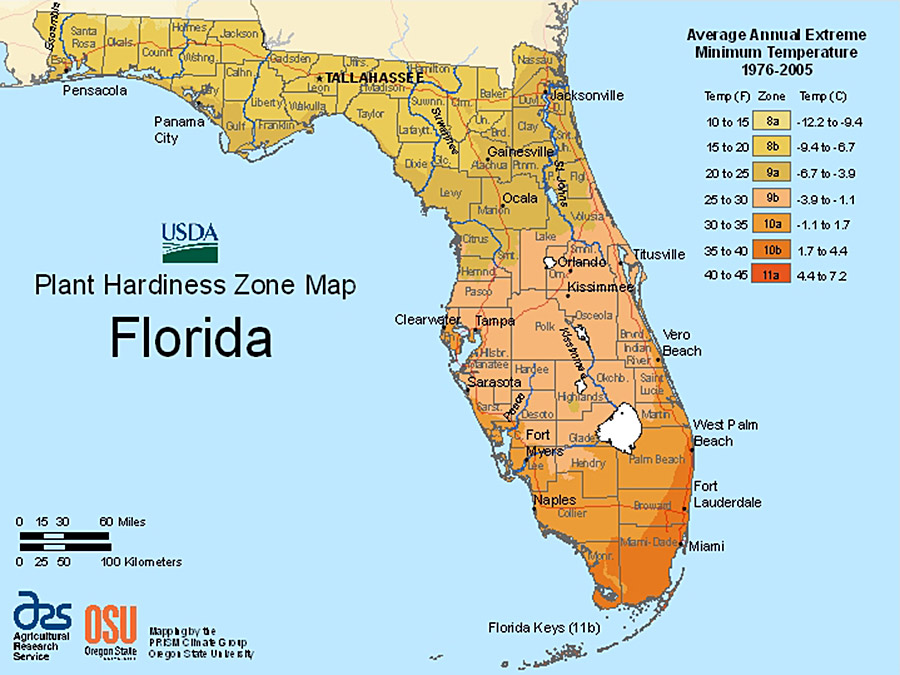
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/florida-climate-and-weather-1513648-Final-5c0ac19946e0fb0001129d95.png)
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Florida’s Climate Zones: A Guide to the Sunshine State. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- A Comprehensive Guide To The Map Of Lakewood, California
- Thailand: A Jewel In The Heart Of Southeast Asia
- Navigating The Nation: A Guide To Free United States Map Vectors
- Navigating The Tapestry Of Arkansas: A Comprehensive Guide To Its Towns And Cities
- Mapping The Shifting Sands: A Look At 9th Century England
- A Journey Through Greene County, New York: Exploring The Land Of Catskill Mountains And Scenic Beauty
- The United States Of America In 1783: A Nation Forged In Boundaries
- Unraveling The Magic: A Comprehensive Guide To The Wizard Of Oz Map In User Experience Design
Leave a Reply