Tibet In China: A Complex Geographical And Political Landscape
Tibet in China: A Complex Geographical and Political Landscape
Related Articles: Tibet in China: A Complex Geographical and Political Landscape
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Tibet in China: A Complex Geographical and Political Landscape. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Tibet in China: A Complex Geographical and Political Landscape

Tibet, a region known for its towering mountains, vast plateaus, and rich cultural heritage, occupies a significant position in the geographic and political landscape of China. Understanding the relationship between Tibet and China requires delving into its historical context, geographical features, and the current political realities. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the region, exploring its significance and the complexities surrounding its integration into China.
The Historical Context:
Tibet’s history is marked by a complex tapestry of interactions with neighboring empires, including China. While Tibet’s relationship with China dates back centuries, the current political reality is rooted in the mid-20th century.
- Pre-1950s: Tibet maintained a degree of autonomy under its own system of governance, led by the Dalai Lama. This period saw a flourishing of Tibetan culture and religious institutions.
- 1950s-1959: The Chinese People’s Liberation Army entered Tibet, marking the beginning of a period of significant political and social change. The Dalai Lama fled to India in 1959, leading to a period of unrest and resistance in Tibet.
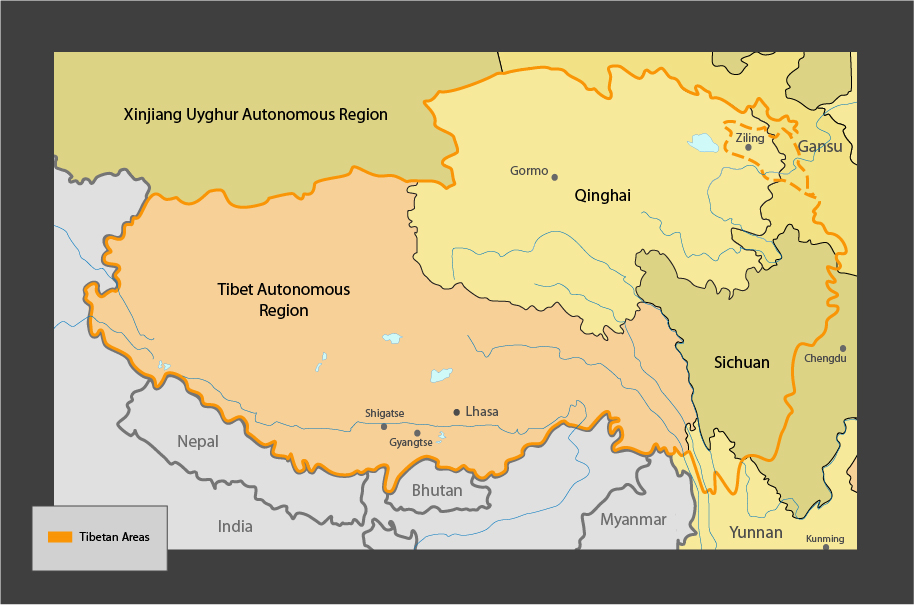
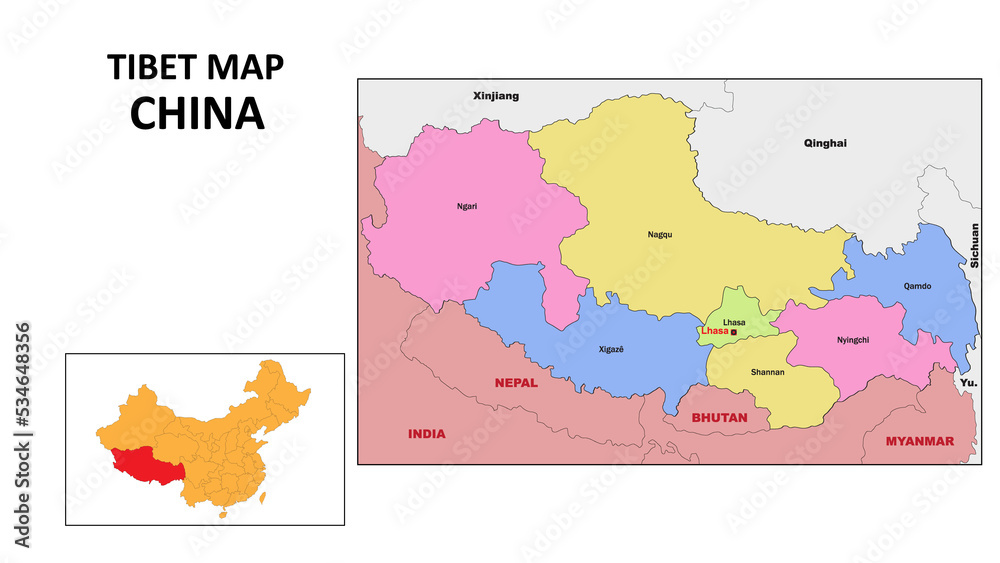
- Post-1959: The Chinese government established the Tibet Autonomous Region (TAR) within its administrative structure, integrating Tibet into the People’s Republic of China. This integration has been accompanied by significant economic development and modernization, alongside ongoing concerns about cultural preservation and human rights.
Geographical Features:
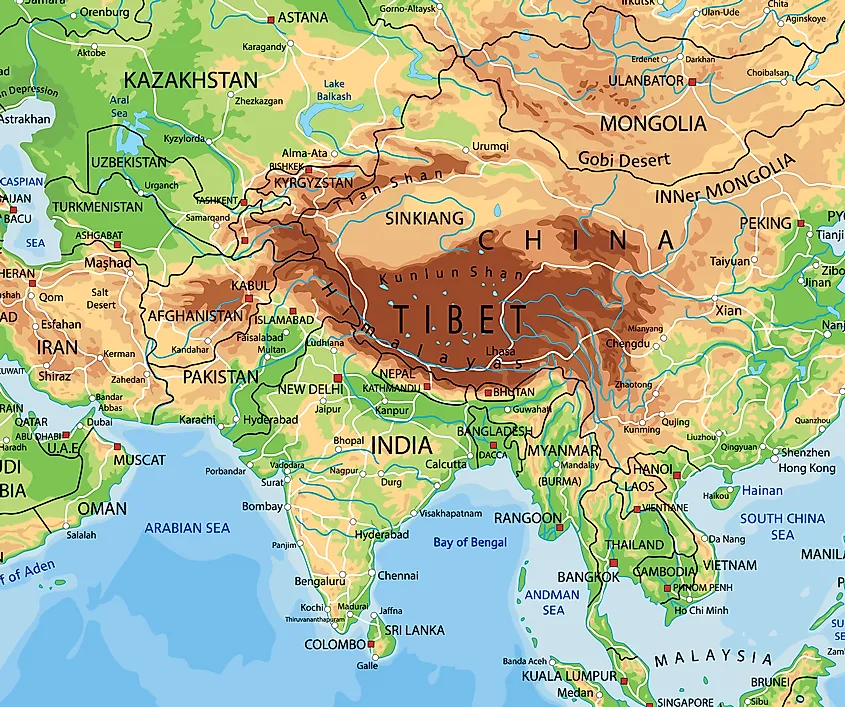
Tibet, known as the "Roof of the World," is characterized by its unique geographical features:
- The Tibetan Plateau: The vast plateau, spanning over 2,500,000 square kilometers, is the highest and largest plateau in the world. Its elevation, averaging over 4,000 meters, creates a unique ecosystem and climate.
- The Himalayas: The majestic Himalayas, home to the world’s highest peaks including Mount Everest, form the southern boundary of Tibet. These mountains play a crucial role in the region’s water resources and biodiversity.
- The Tibetan Rivers: The Yangtze, Yellow, Mekong, Brahmaputra, and Indus rivers all originate in Tibet, highlighting its importance as a water tower for Asia.
Political and Economic Landscape:
Tibet’s integration into China has brought about significant changes in its political and economic landscape:
- Tibet Autonomous Region (TAR): The TAR is the primary administrative unit for Tibet, governed by the Chinese government. While the region enjoys a degree of autonomy, it is ultimately subject to the central government in Beijing.
- Economic Development: China has invested heavily in infrastructure development, including roads, railways, and hydropower projects, in Tibet. This has led to economic growth, albeit with concerns about environmental impact and the potential for displacement of local communities.
- Cultural Preservation: The Chinese government has implemented policies aimed at preserving Tibetan culture, including the promotion of Tibetan language and traditional arts. However, concerns remain about the impact of cultural assimilation and the restrictions on religious freedom.
The Importance of Tibet in China:
Tibet holds significant strategic importance for China:
- Water Resources: Tibet’s rivers provide vital water resources for a large portion of China, making the region crucial for the country’s water security.
- Strategic Location: Tibet’s location on the border of China, India, Nepal, and Bhutan makes it strategically important for China’s national defense and regional influence.
- Tourism and Economic Growth: Tibet’s unique landscapes and cultural heritage have attracted tourists from around the world, contributing to the region’s economic development.
Challenges and Controversies:
The relationship between Tibet and China remains complex and contentious:
- Human Rights Concerns: The Chinese government’s policies in Tibet have been criticized by international human rights organizations for restrictions on freedom of speech, assembly, and religion.
- Cultural Assimilation: The promotion of Mandarin Chinese and the suppression of Tibetan language and culture have raised concerns about the erosion of Tibetan identity.
- Environmental Concerns: The rapid development in Tibet has raised concerns about environmental degradation, including deforestation, pollution, and the impact on the region’s fragile ecosystem.
FAQs about Tibet in China:
- Q: Is Tibet independent or part of China?
- A: Tibet is currently an autonomous region within the People’s Republic of China. The Chinese government maintains that Tibet has been part of China for centuries, while Tibetan activists argue for independence or greater autonomy.
- Q: What is the Dalai Lama’s role in Tibet?
- A: The Dalai Lama is the spiritual leader of Tibetan Buddhism and is revered as the embodiment of Avalokiteshvara, the Bodhisattva of Compassion. He played a significant role in Tibet’s pre-1959 governance. After fleeing to India, he continues to advocate for Tibetan rights and autonomy.
- Q: What is the situation of human rights in Tibet?
- A: The human rights situation in Tibet remains a subject of ongoing debate and concern. International human rights organizations have documented instances of repression, restrictions on freedom of speech, and limitations on religious freedom. The Chinese government maintains that it protects human rights and promotes development in Tibet.
- Q: What is the impact of China’s development policies on Tibet?
- A: China’s development policies in Tibet have led to significant economic growth, but also raised concerns about environmental degradation, cultural assimilation, and displacement of local communities.
Tips for Understanding Tibet in China:
- Read diverse perspectives: Explore sources from both Chinese and Tibetan perspectives to gain a balanced understanding of the complex relationship between the two.
- Consider historical context: Understand the historical background of the relationship between Tibet and China, including the pre-1950s period, the 1950s-1959 events, and the post-1959 integration.
- Recognize the diversity of voices: Acknowledge that there are various perspectives within Tibet, including those who support the current political arrangement and those who advocate for greater autonomy or independence.
- Engage with current events: Stay informed about current events in Tibet, including political developments, cultural initiatives, and environmental concerns.
Conclusion:
The relationship between Tibet and China is a complex and multifaceted issue with historical, geographical, political, and cultural dimensions. Understanding the historical context, geographical features, political realities, and the challenges and controversies surrounding the region is crucial for a nuanced perspective. While the integration of Tibet into China has brought about significant changes and economic development, it has also raised concerns about cultural preservation, human rights, and environmental sustainability. The future of Tibet in China remains a subject of ongoing debate and requires careful consideration of the diverse perspectives and complexities involved.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Tibet in China: A Complex Geographical and Political Landscape. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- A Comprehensive Guide To The Map Of Lakewood, California
- Thailand: A Jewel In The Heart Of Southeast Asia
- Navigating The Nation: A Guide To Free United States Map Vectors
- Navigating The Tapestry Of Arkansas: A Comprehensive Guide To Its Towns And Cities
- Mapping The Shifting Sands: A Look At 9th Century England
- A Journey Through Greene County, New York: Exploring The Land Of Catskill Mountains And Scenic Beauty
- The United States Of America In 1783: A Nation Forged In Boundaries
- Unraveling The Magic: A Comprehensive Guide To The Wizard Of Oz Map In User Experience Design
Leave a Reply