The Invisible Grid: Understanding The Equator And Prime Meridian
The Invisible Grid: Understanding the Equator and Prime Meridian
Related Articles: The Invisible Grid: Understanding the Equator and Prime Meridian
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Invisible Grid: Understanding the Equator and Prime Meridian. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Invisible Grid: Understanding the Equator and Prime Meridian

The Earth, a vast sphere suspended in space, appears chaotic at first glance. But beneath its swirling clouds and shifting continents lies a meticulously crafted grid, an invisible framework that helps us navigate and understand our planet. This grid is defined by two fundamental lines: the Equator and the Prime Meridian.
The Equator: A Circle of Equal Distance
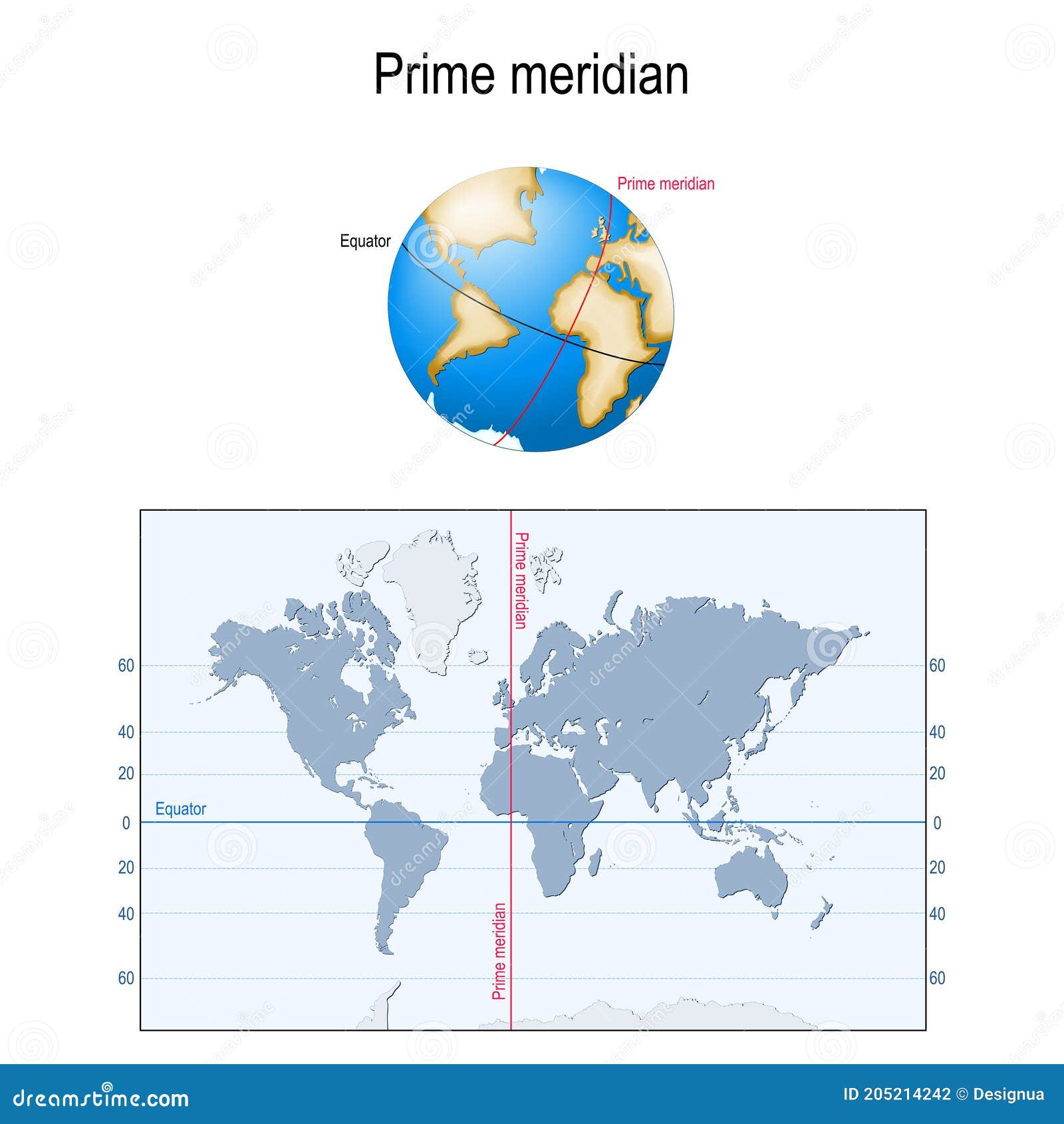
The Equator is an imaginary line that circles the Earth at 0 degrees latitude. It divides the planet into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres, each representing half of the Earth’s surface. This line is not just a geographical marker; it holds significant scientific and cultural importance.
Key Features of the Equator:
- Equal Distance from the Poles: The Equator is equidistant from both the North and South Poles, making it the largest circle of latitude on Earth.
- Longest Circle of Latitude: The Equator is the longest line of latitude, with a circumference of approximately 40,075 kilometers (24,901 miles).
- Climate Influence: The Equator experiences a tropical climate characterized by high temperatures and heavy rainfall throughout the year. This is due to the direct sunlight received at the Equator, leading to consistent solar energy input.
- Global Time Zones: The Equator plays a crucial role in defining time zones. The Earth is divided into 24 time zones, each spanning 15 degrees of longitude, with the prime meridian (0 degrees longitude) serving as the starting point.
- Cultural Significance: The Equator has held cultural significance for centuries. Many ancient civilizations recognized its importance in understanding the Earth’s movements and the changing seasons.
The Prime Meridian: A Line of Zero Longitude
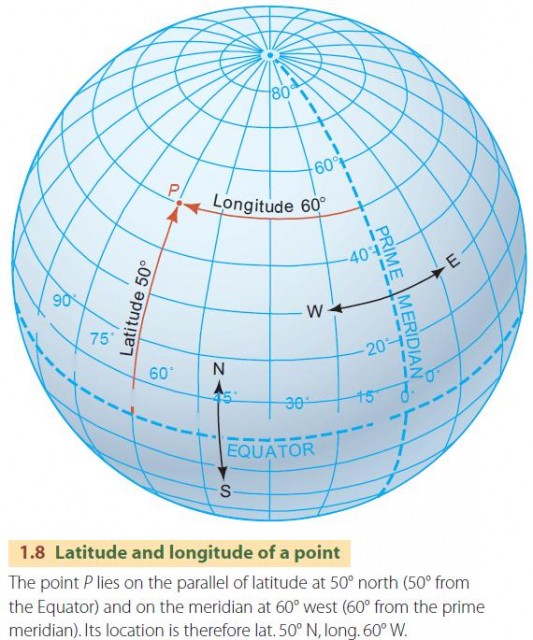
The Prime Meridian is another imaginary line that runs from the North Pole to the South Pole, passing through Greenwich, England. It is designated as 0 degrees longitude and serves as the starting point for measuring longitudes east and west.
Key Features of the Prime Meridian:
- Dividing the Earth: The Prime Meridian divides the Earth into the Eastern and Western Hemispheres, each representing half of the Earth’s surface.
- Global Time Reference: The Prime Meridian is the basis for the Coordinated Universal Time (UTC), the international standard time used worldwide.
- Historical Significance: The choice of Greenwich as the location for the Prime Meridian was influenced by the prominence of the Royal Observatory at Greenwich, which played a pivotal role in the development of navigation and timekeeping.
- International Agreement: The location of the Prime Meridian was formally established in 1884 at the International Meridian Conference in Washington D.C., with the participation of representatives from 25 countries.
The Importance of the Equator and Prime Meridian
The Equator and Prime Meridian, together, form the foundation of the Earth’s grid system, providing a framework for:
- Navigation: The grid system allows us to pinpoint specific locations on Earth using latitude and longitude coordinates. This is essential for navigation, mapping, and various other applications.
- Mapping: The grid system is used to create maps, charts, and other spatial representations of the Earth’s surface.
- Timekeeping: The Prime Meridian serves as the reference point for global time zones, ensuring consistency in timekeeping across different parts of the world.
- Scientific Research: The grid system is crucial for conducting scientific research related to geography, geology, climate, and other fields.
FAQs about the Equator and Prime Meridian:
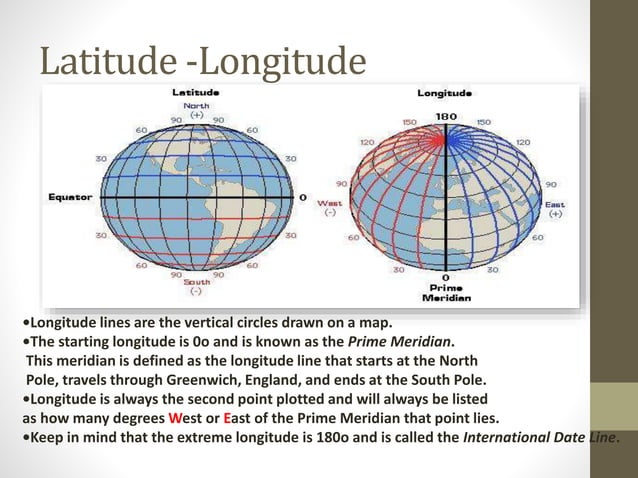
1. What is the difference between latitude and longitude?
Latitude measures the distance north or south of the Equator, expressed in degrees. Longitude measures the distance east or west of the Prime Meridian, also expressed in degrees.
2. Can you cross the Equator multiple times?
Yes, you can cross the Equator multiple times. For example, if you travel from the Northern Hemisphere to the Southern Hemisphere and back again, you would cross the Equator twice.
3. Is the Prime Meridian the only reference point for longitude?
The Prime Meridian is the internationally recognized reference point for longitude. However, other countries have historically used different reference points for their own purposes.
4. What are the implications of climate change on the Equator?
Climate change is expected to have significant impacts on the Equator, including changes in precipitation patterns, rising sea levels, and increased frequency of extreme weather events.
5. How is the Equator used in astronomy?
The Equator is an important reference point in astronomy. The celestial equator, which is the projection of the Earth’s Equator onto the celestial sphere, is used to define celestial coordinates and track the movement of celestial objects.
Tips for Understanding the Equator and Prime Meridian:
- Use a globe: A globe is a physical representation of the Earth and provides a clear visual understanding of the Equator and Prime Meridian.
- Explore maps: Maps are essential tools for visualizing the Earth’s grid system and understanding the location of different places.
- Consult online resources: There are numerous websites and online resources that provide detailed information about the Equator and Prime Meridian.
- Engage in discussions: Discuss the concepts of latitude, longitude, and the grid system with others to deepen your understanding.
Conclusion:
The Equator and Prime Meridian, though invisible lines, play a vital role in our understanding of the Earth. They provide a framework for navigation, mapping, timekeeping, and scientific research. As we continue to explore and learn more about our planet, these fundamental lines will remain essential tools for understanding the complexities of our world.

/Latitude-and-Longitude-58b9d1f35f9b58af5ca889f1.jpg)


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Invisible Grid: Understanding the Equator and Prime Meridian. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- A Comprehensive Guide To The Map Of Lakewood, California
- Thailand: A Jewel In The Heart Of Southeast Asia
- Navigating The Nation: A Guide To Free United States Map Vectors
- Navigating The Tapestry Of Arkansas: A Comprehensive Guide To Its Towns And Cities
- Mapping The Shifting Sands: A Look At 9th Century England
- A Journey Through Greene County, New York: Exploring The Land Of Catskill Mountains And Scenic Beauty
- The United States Of America In 1783: A Nation Forged In Boundaries
- Unraveling The Magic: A Comprehensive Guide To The Wizard Of Oz Map In User Experience Design
Leave a Reply