Pennsylvania House District Map: A Guide To Representation And Redistricting
Pennsylvania House District Map: A Guide to Representation and Redistricting
Related Articles: Pennsylvania House District Map: A Guide to Representation and Redistricting
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Pennsylvania House District Map: A Guide to Representation and Redistricting. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Pennsylvania House District Map: A Guide to Representation and Redistricting

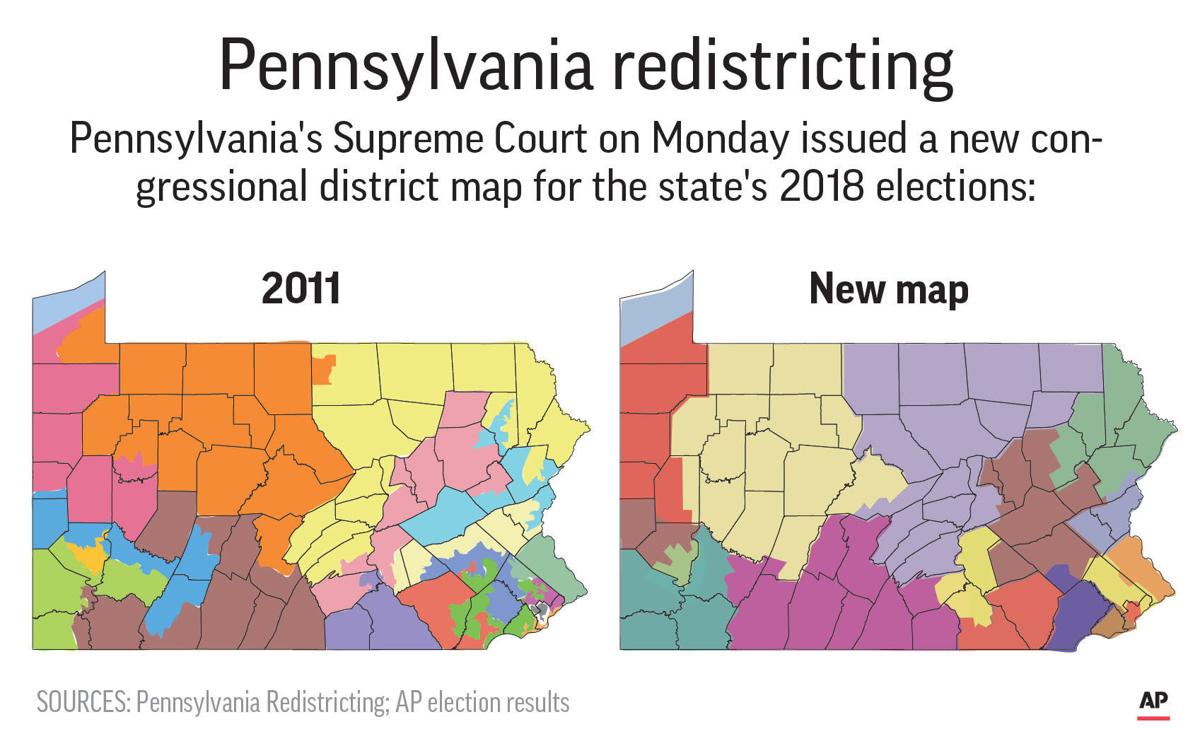
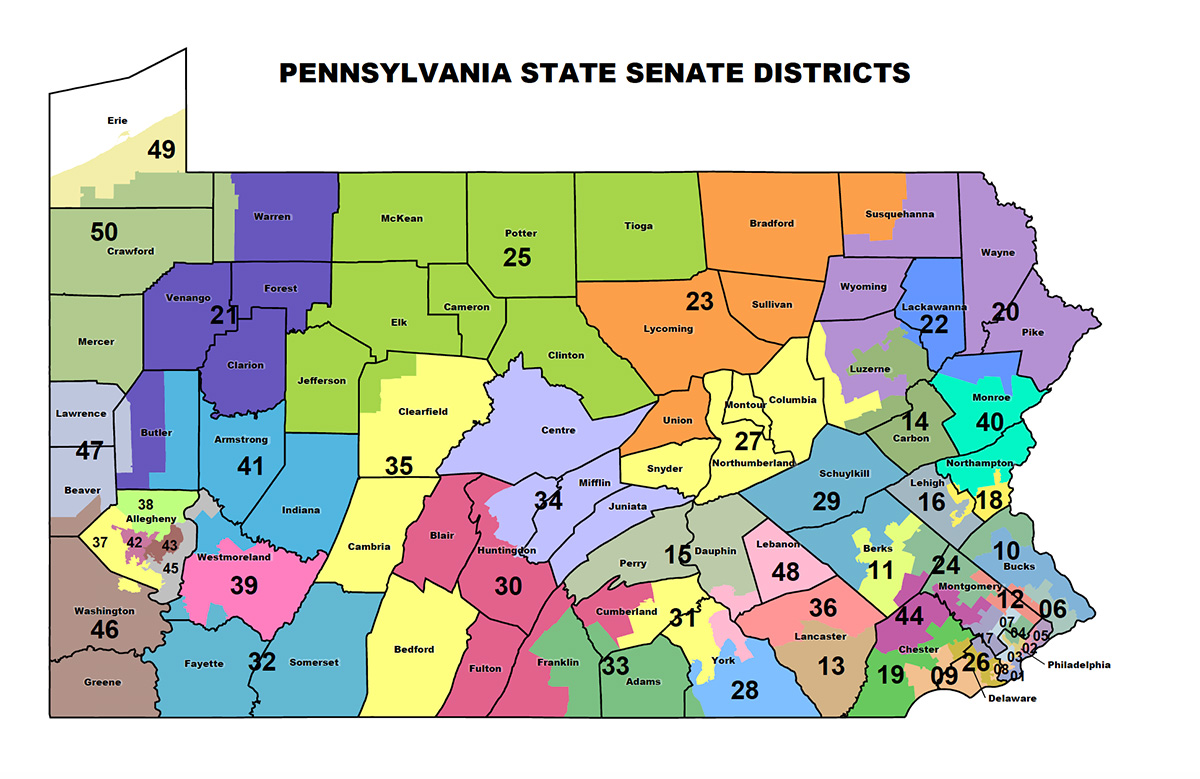
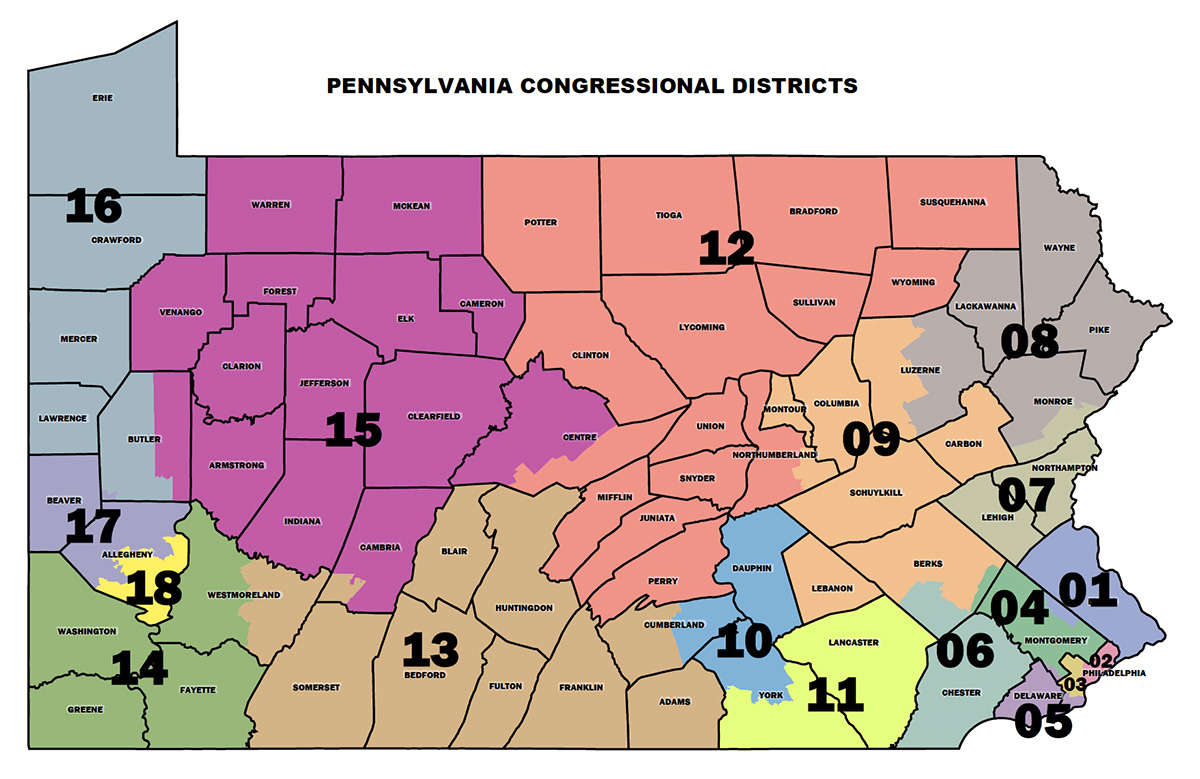
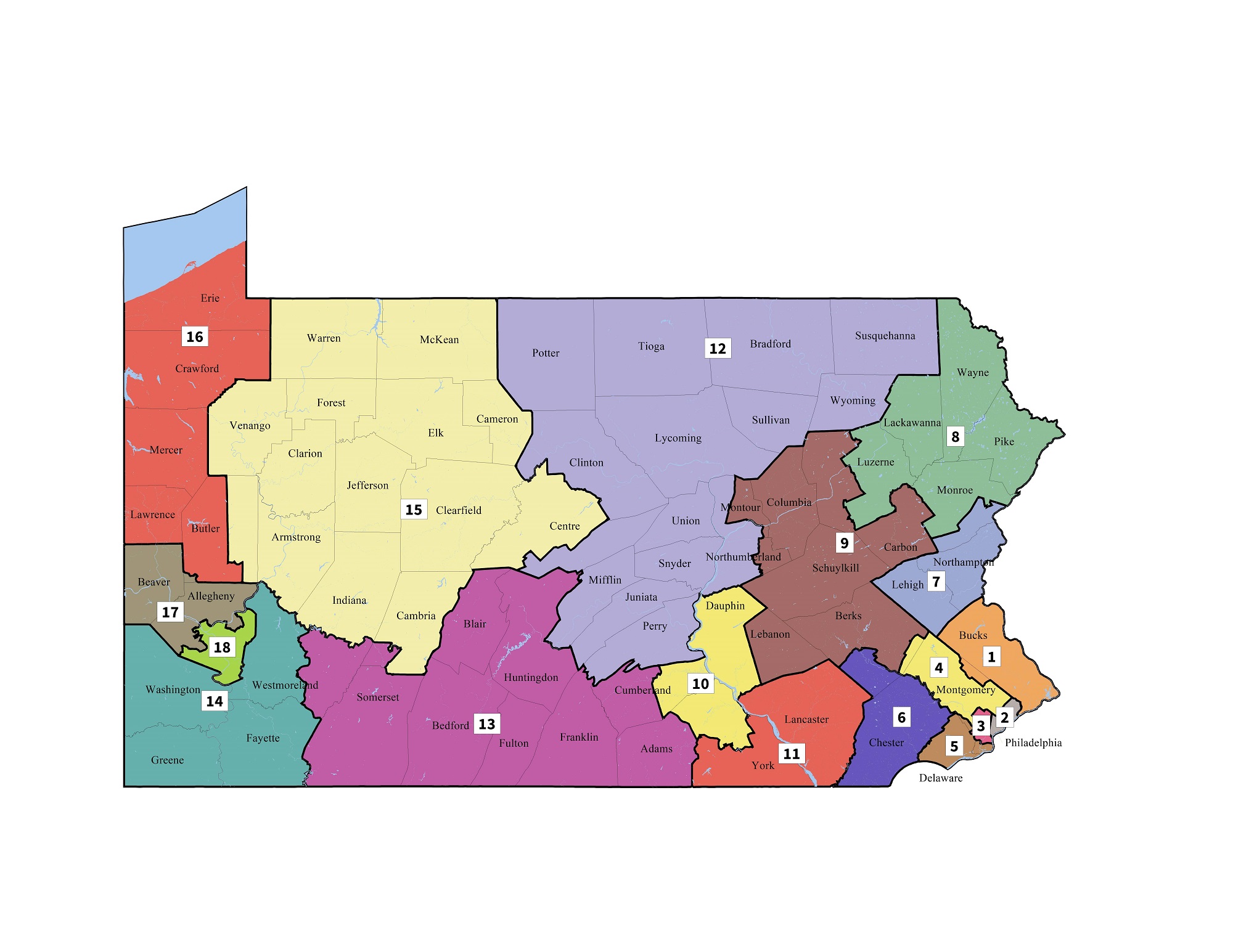
The Pennsylvania House District map is a fundamental element of the state’s political landscape. It divides the Commonwealth into 203 distinct districts, each represented by a single member in the Pennsylvania House of Representatives. This map, along with the Senate map, determines the boundaries of electoral districts and thus influences the composition and power dynamics of the legislature. Understanding the intricacies of the map is crucial for both voters and political observers, as it directly impacts representation, policy-making, and the political climate within the state.
The Importance of District Boundaries
District boundaries are not arbitrary lines on a map. They are the product of a complex process known as redistricting, which occurs every ten years following the decennial census. Redistricting aims to ensure equal representation by adjusting district boundaries to reflect population shifts and changes in demographics. This process is vital to maintain the principle of "one person, one vote," guaranteeing that all citizens have equal weight in the electoral process.
However, redistricting is often a contentious issue, as it can be used to manipulate electoral outcomes by creating districts that favor one party or group over another. This practice, known as gerrymandering, can lead to uncompetitive elections, reduced voter participation, and a lack of diverse representation in the legislature.
The Pennsylvania House District Map: A Historical Perspective
The current Pennsylvania House District map is the result of a series of redistricting efforts throughout the state’s history. In the early 20th century, the state legislature was responsible for drawing district lines, which often resulted in gerrymandered districts designed to benefit the ruling party. This led to calls for reform, culminating in the creation of the Pennsylvania Legislative Reapportionment Commission (LRRC) in 1971.
The LRRC, a bipartisan commission composed of five members, was tasked with drawing district boundaries based on population data and other relevant factors. However, the commission’s work has been criticized for its susceptibility to partisan influence, leading to legal challenges and concerns about fairness.
The 2020 Redistricting Process
Following the 2020 census, the LRRC embarked on the most recent redistricting process. The commission faced significant challenges, including a rapidly changing population landscape, increasing political polarization, and the potential for gerrymandering.
After months of public hearings, legal battles, and political maneuvering, the commission finally released a new map in February 2022. The map was met with mixed reactions, with some praising its adherence to population equality while others criticized its potential for partisan bias.
Key Features of the Pennsylvania House District Map
The current Pennsylvania House District map exhibits several key features:
- Population Equality: Each district is designed to contain roughly the same number of residents, ensuring that each voter has equal representation.
- Compactness: Districts are generally compact and contiguous, minimizing the need for voters to be spread across large geographical areas.
- Respect for Communities of Interest: The map aims to avoid dividing communities with shared interests or identities, preserving local representation.
- Minority Representation: The map incorporates provisions to ensure adequate representation for minority groups, promoting inclusivity and diversity in the legislature.
Understanding the Map: Resources and Tools
Navigating the complexities of the Pennsylvania House District map can be challenging. Fortunately, several resources are available to help voters and political observers understand the map and its implications:
- Pennsylvania Legislative Reapportionment Commission (LRRC): The LRRC website provides access to the official district maps, redistricting data, and other relevant documents.
- Pennsylvania Department of State: The Department of State website offers information on voter registration, election results, and other electoral processes.
- Third-Party Organizations: Several non-partisan organizations, such as the League of Women Voters, provide resources and analysis related to redistricting and district maps.
FAQs about the Pennsylvania House District Map
Q: How can I find my House District?
A: You can find your House District by entering your address into the Pennsylvania Department of State’s voter registration website.
Q: What is the role of the Pennsylvania Legislative Reapportionment Commission (LRRC)?
A: The LRRC is a bipartisan commission responsible for drawing district boundaries every ten years following the census.
Q: How does the redistricting process work?
A: Redistricting involves adjusting district boundaries to reflect population shifts and ensure equal representation. The process typically involves public hearings, data analysis, and legal challenges.
Q: What is gerrymandering?
A: Gerrymandering is the manipulation of district boundaries to favor one party or group over another, potentially resulting in unfair elections and reduced voter participation.
Q: What are the potential consequences of a poorly drawn district map?
A: A poorly drawn district map can lead to uncompetitive elections, reduced voter participation, and a lack of diverse representation in the legislature.
Tips for Understanding the Pennsylvania House District Map
- Familiarize yourself with the redistricting process: Understanding the process behind district boundary changes can help you interpret the map and its implications.
- Explore the resources available: Utilize websites like the LRRC and the Department of State to access data, maps, and other information.
- Engage with local organizations: Participate in public hearings and discussions organized by non-partisan groups like the League of Women Voters.
- Pay attention to election coverage: Follow news reports and analyses related to redistricting and district maps to stay informed about the latest developments.
Conclusion
The Pennsylvania House District map is a vital tool for understanding the state’s political landscape. It determines the boundaries of electoral districts, shaping the composition of the legislature and influencing policy-making. While the map aims to ensure fair representation, it remains a subject of debate and scrutiny, particularly due to the potential for gerrymandering. By understanding the map’s history, key features, and ongoing challenges, voters and political observers can better navigate the complex world of Pennsylvania politics and advocate for a fair and equitable system of representation.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Pennsylvania House District Map: A Guide to Representation and Redistricting. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- A Comprehensive Guide To The Map Of Lakewood, California
- Thailand: A Jewel In The Heart Of Southeast Asia
- Navigating The Nation: A Guide To Free United States Map Vectors
- Navigating The Tapestry Of Arkansas: A Comprehensive Guide To Its Towns And Cities
- Mapping The Shifting Sands: A Look At 9th Century England
- A Journey Through Greene County, New York: Exploring The Land Of Catskill Mountains And Scenic Beauty
- The United States Of America In 1783: A Nation Forged In Boundaries
- Unraveling The Magic: A Comprehensive Guide To The Wizard Of Oz Map In User Experience Design
Leave a Reply