Navigating The Tennessee District Map: Understanding The Boundaries Of Representation
Navigating the Tennessee District Map: Understanding the Boundaries of Representation
Related Articles: Navigating the Tennessee District Map: Understanding the Boundaries of Representation
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Tennessee District Map: Understanding the Boundaries of Representation. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Tennessee District Map: Understanding the Boundaries of Representation
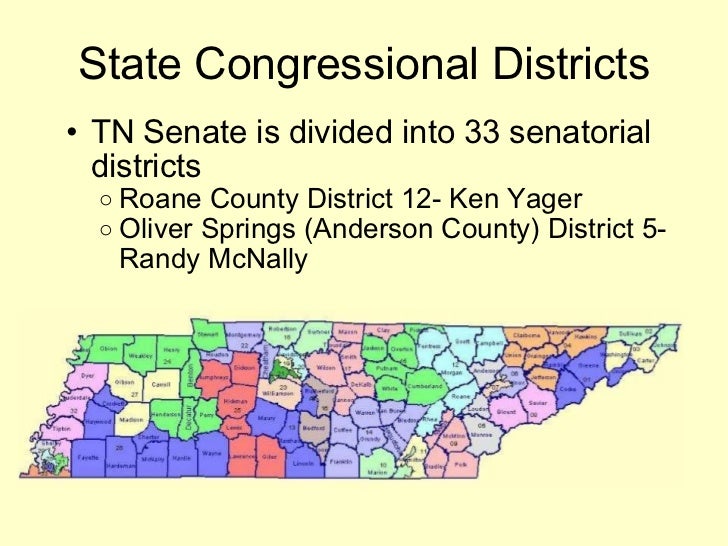
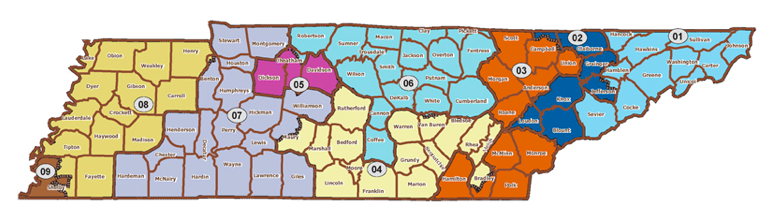
The Tennessee district map, a complex tapestry of lines and boundaries, is more than just a visual representation of the state’s geography. It serves as a crucial framework for political representation, defining the constituencies that elect representatives to various levels of government. Understanding the intricacies of this map is essential for navigating the political landscape of Tennessee, as it directly impacts the voice and representation of its citizens.
The Evolution of Tennessee’s District Map:
The Tennessee district map has undergone numerous revisions throughout history, reflecting shifts in population, political ideologies, and legal challenges. The map is subject to redistricting every ten years following the decennial census, a process mandated by the U.S. Constitution to ensure equal representation based on population. Each redistricting cycle involves a complex interplay of political considerations, legal constraints, and demographic shifts, leading to potential changes in the boundaries of congressional, state legislative, and local districts.
Key Components of the Tennessee District Map:
The Tennessee district map is comprised of distinct geographical areas, each representing a specific electoral unit. These units include:
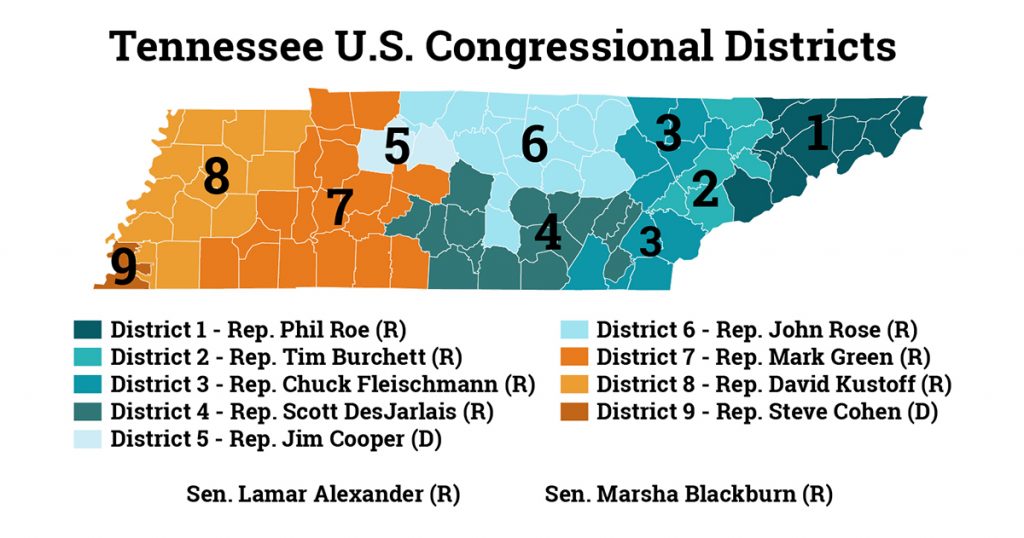
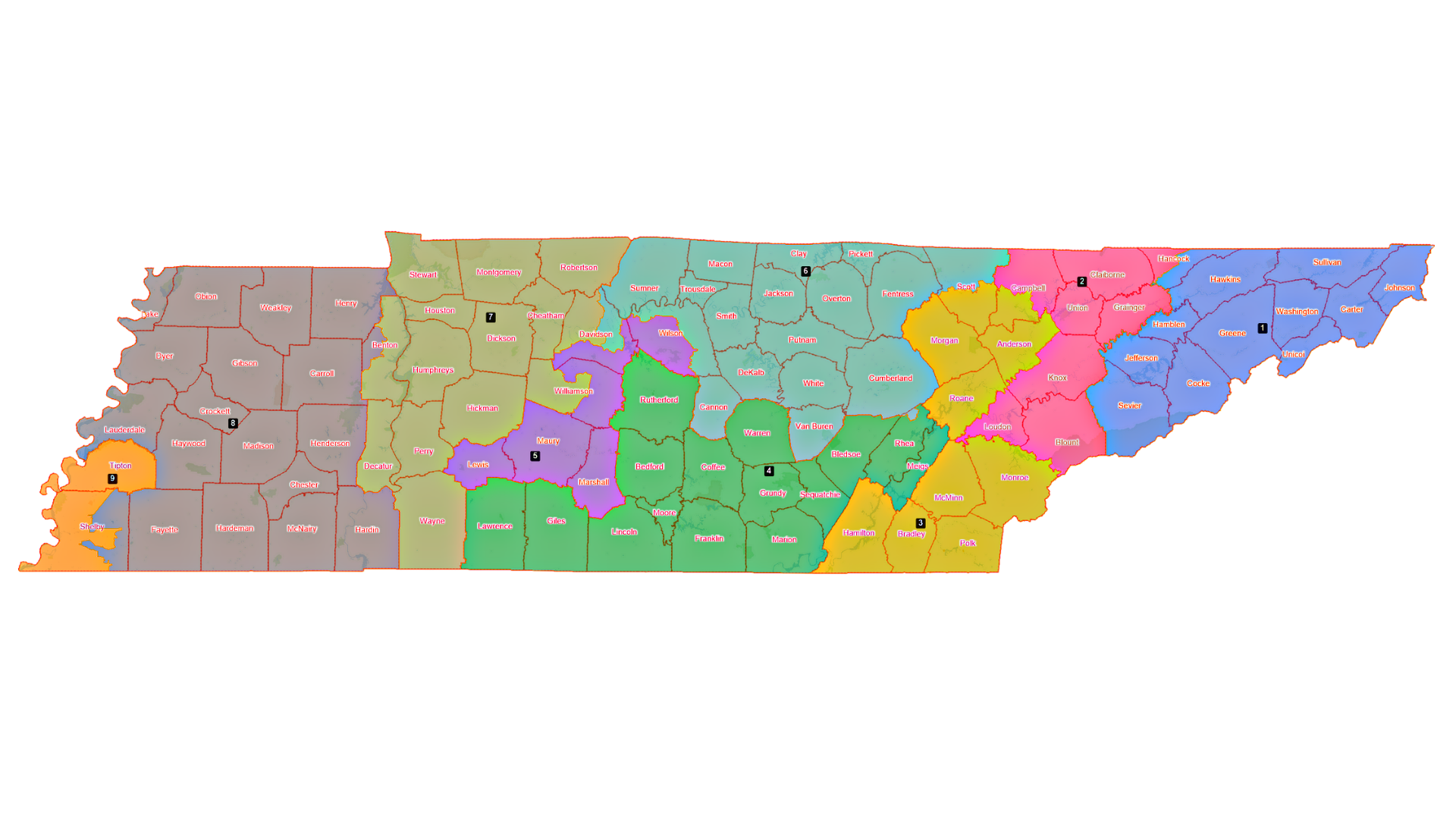
- Congressional Districts: Tennessee is divided into nine congressional districts, each electing one representative to the U.S. House of Representatives. These districts are drawn to ensure equal representation based on population, with each district containing roughly the same number of residents.
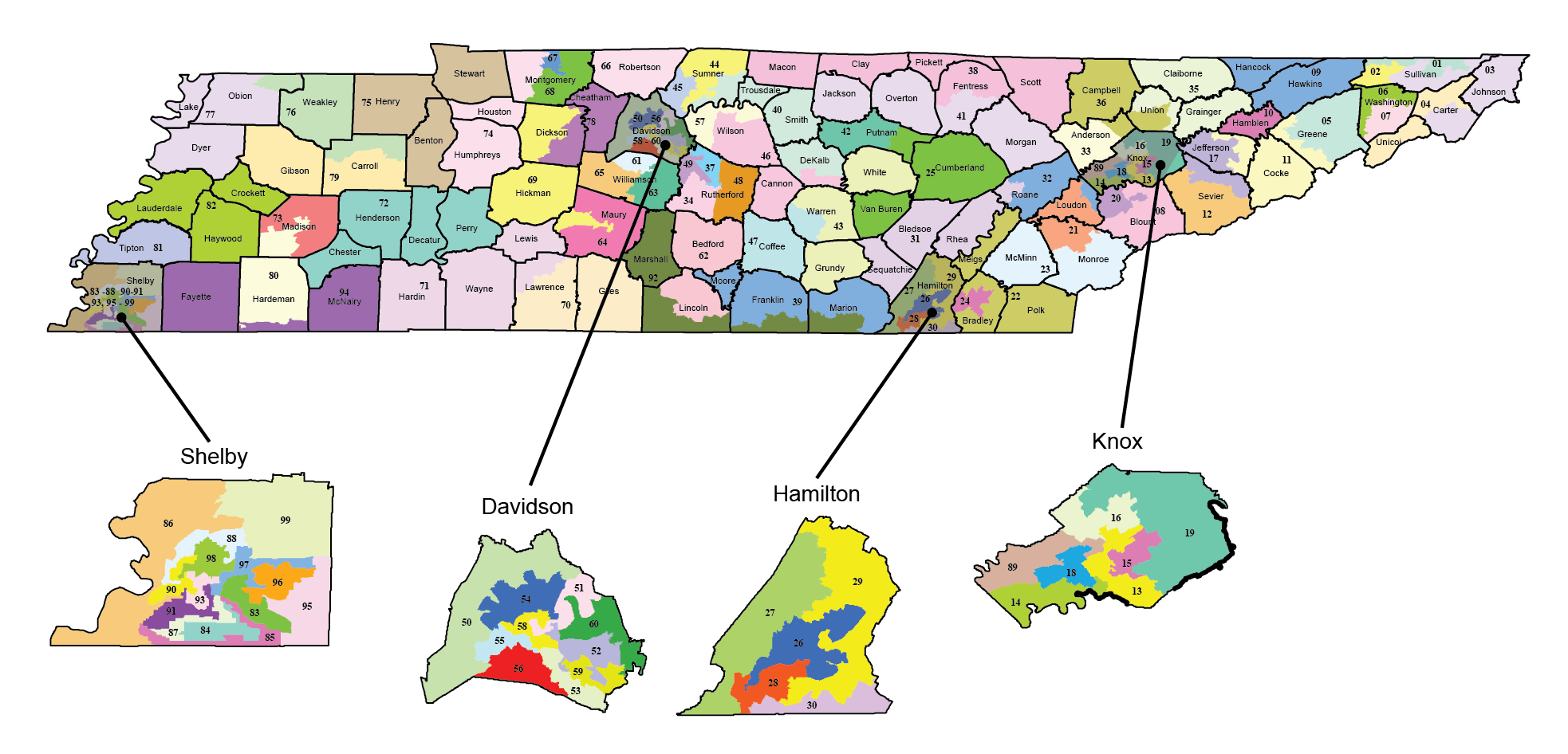
- State Legislative Districts: The state legislature is composed of two chambers: the Senate and the House of Representatives. Tennessee has 33 Senate districts and 99 House districts, each representing a specific geographic area within the state.
- County and Municipal Districts: Local governments, such as counties and municipalities, also have their own district maps. These maps define the boundaries of electoral wards or precincts, determining the areas represented by local officials like county commissioners, mayors, and city council members.
The Importance of District Boundaries:
The boundaries of these districts have significant implications for the political landscape of Tennessee. They influence:
- Electoral Outcomes: District boundaries can impact the outcome of elections by concentrating or diluting the voting power of specific groups, such as racial minorities or particular political affiliations.
- Representation: The composition of districts determines who represents the constituents in government, impacting the policies and priorities addressed by elected officials.
- Political Power: The drawing of district lines can be used to consolidate or fragment political power, potentially favoring one party or group over another.
Navigating the District Map: Tools and Resources:
Several tools and resources are available to help individuals navigate the Tennessee district map and understand its implications:
- Online Mapping Platforms: Websites like the Tennessee Secretary of State’s website and the U.S. Census Bureau offer interactive maps that allow users to visualize district boundaries and access relevant data.
- Electoral Data Resources: Websites like the Tennessee Election Commission and the National Conference of State Legislatures provide information on past election results, voter registration statistics, and other data related to district boundaries.
- Political Advocacy Organizations: Organizations like the League of Women Voters and Common Cause advocate for fair redistricting practices and provide resources for understanding the impact of district boundaries on political representation.
FAQs Regarding the Tennessee District Map:
Q: How often are district boundaries redrawn in Tennessee?
A: District boundaries in Tennessee are redrawn every ten years following the decennial census, as mandated by the U.S. Constitution.
Q: Who is responsible for redrawing district boundaries?
A: In Tennessee, the General Assembly is responsible for redrawing district boundaries. This process involves a complex interplay between legislative committees, political parties, and public input.
Q: What are the legal criteria for drawing district boundaries?
A: The legal criteria for drawing district boundaries are governed by the U.S. Constitution and the Voting Rights Act. These criteria include:
- Equal Population: Each district must contain roughly the same number of residents to ensure equal representation.
- Contiguity: Districts must be geographically contiguous, meaning that all parts of a district must be connected.
- Racial Fairness: Districts cannot be drawn to dilute the voting power of racial minorities.
Q: What are the potential consequences of gerrymandering?
A: Gerrymandering, the manipulation of district boundaries for partisan advantage, can have several negative consequences:
- Reduced Competition: Gerrymandered districts can create safe seats for one party, reducing competition and voter choice.
- Increased Polarization: Gerrymandering can exacerbate political polarization by creating districts that are overwhelmingly dominated by one party.
- Underrepresentation: Gerrymandering can lead to the underrepresentation of certain groups, particularly minorities, by diluting their voting power.
Tips for Understanding the Tennessee District Map:
- Explore Online Resources: Utilize online mapping platforms and electoral data resources to visualize district boundaries and access relevant information.
- Engage with Local Officials: Reach out to your local representatives and ask questions about the district map and its impact on your community.
- Participate in Public Hearings: Attend public hearings and provide input on redistricting proposals.
- Support Fair Redistricting Advocacy: Support organizations advocating for fair redistricting practices and transparency in the process.
Conclusion:
The Tennessee district map is a crucial tool for understanding the political landscape of the state, defining the boundaries of representation and influencing electoral outcomes. It is essential for citizens to understand the map’s intricacies, the implications of district boundaries, and the ongoing efforts to ensure fair and equitable representation. By engaging with the redistricting process, utilizing available resources, and advocating for fair practices, individuals can contribute to shaping a political system that reflects the diverse voices and interests of the Tennessee community.

![]()


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Tennessee District Map: Understanding the Boundaries of Representation. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- A Comprehensive Guide To The Map Of Lakewood, California
- Thailand: A Jewel In The Heart Of Southeast Asia
- Navigating The Nation: A Guide To Free United States Map Vectors
- Navigating The Tapestry Of Arkansas: A Comprehensive Guide To Its Towns And Cities
- Mapping The Shifting Sands: A Look At 9th Century England
- A Journey Through Greene County, New York: Exploring The Land Of Catskill Mountains And Scenic Beauty
- The United States Of America In 1783: A Nation Forged In Boundaries
- Unraveling The Magic: A Comprehensive Guide To The Wizard Of Oz Map In User Experience Design
Leave a Reply