Navigating The Landscape Of Labor: A Comprehensive Guide To The Union Map
Navigating the Landscape of Labor: A Comprehensive Guide to the Union Map
Related Articles: Navigating the Landscape of Labor: A Comprehensive Guide to the Union Map
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Landscape of Labor: A Comprehensive Guide to the Union Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Landscape of Labor: A Comprehensive Guide to the Union Map
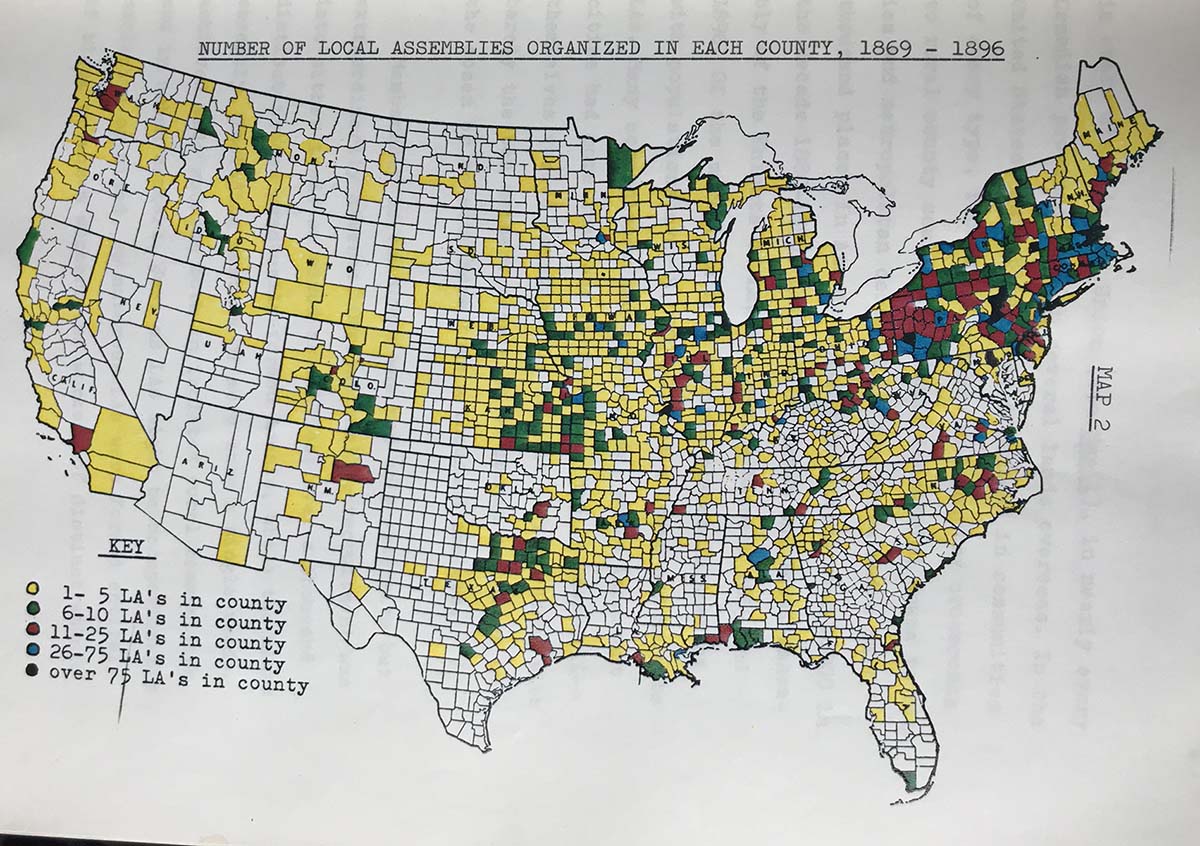
The union map, a visual representation of organized labor’s presence across industries and regions, is a powerful tool for understanding the current state of labor rights and collective bargaining. It provides a clear and concise picture of where unions are active, their strength in specific sectors, and the challenges they face. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of the union map, exploring its significance, benefits, and limitations.
Understanding the Union Map
The union map, also known as a labor map, is a visual representation of union density, which is the percentage of workers in a specific industry or region who are members of a labor union. It typically displays data in a geographical format, often using color-coding or shading to indicate varying levels of unionization.
Components of a Union Map:
- Industry-Specific Data: The map often presents information about union presence in different industries, such as healthcare, education, manufacturing, and transportation. This allows for a detailed analysis of union strength across various sectors.
- Regional Analysis: The map provides insights into unionization rates in different states, cities, and regions, highlighting areas with high union density and those with lower levels of organized labor.
- Historical Trends: Some union maps incorporate historical data, allowing for the analysis of changes in unionization rates over time. This helps to identify long-term trends and understand the factors influencing union growth or decline.
Benefits of the Union Map:
The union map offers numerous benefits for various stakeholders:
- Workers: The map empowers workers by providing them with information about union presence in their industry and region. This knowledge can help them make informed decisions about joining a union and advocating for their rights.
- Unions: The map helps unions understand their strength and identify areas where they can focus their organizing efforts. It also allows unions to track their progress and measure the effectiveness of their campaigns.
- Employers: The map provides employers with insights into the level of unionization in their industry and region. This information can help them understand the potential for unionization in their workplace and develop strategies to address worker concerns.
- Researchers and Policymakers: The map serves as a valuable resource for researchers and policymakers studying labor relations and the impact of unionization on the economy and society. It provides data for analyzing trends and developing policies aimed at strengthening or reforming labor laws.
Limitations of the Union Map:
Despite its benefits, the union map has limitations that should be considered:
- Data Accuracy: The accuracy of the map depends on the quality and availability of data. Data collection methods and reporting standards can vary, leading to potential inaccuracies or inconsistencies.
- Oversimplification: The map often presents a simplified view of complex labor relations. It does not capture the nuances of unionization, such as the presence of different types of unions or the level of worker engagement in union activities.
- Limited Scope: The map typically focuses on union density, neglecting other important aspects of labor relations, such as collective bargaining agreements, worker satisfaction, and the impact of unionization on workplace conditions.
FAQs about the Union Map:
1. What is the purpose of the union map?
The purpose of the union map is to visually represent the presence and strength of labor unions across industries and regions. It provides a clear and concise picture of unionization rates, allowing stakeholders to understand the current landscape of organized labor.
2. How is the data for the union map collected?
Data for the union map is typically collected from various sources, including government agencies, union membership records, and surveys. Data collection methods and reporting standards can vary, which may affect the accuracy of the map.
3. What are the key indicators used on the union map?
The key indicators used on the union map are typically union density, which is the percentage of workers in a specific industry or region who are members of a labor union. Some maps may also include other indicators, such as the number of union members, the number of collective bargaining agreements, or the level of worker satisfaction.
4. How can I use the union map to my advantage?
Workers can use the union map to understand the presence of unions in their industry and region, helping them make informed decisions about joining a union. Unions can use the map to identify areas where they can focus their organizing efforts and track their progress. Employers can use the map to understand the potential for unionization in their workplace and develop strategies to address worker concerns.
5. Are there any limitations to the union map?
The union map has limitations, including the accuracy of the data, the oversimplification of complex labor relations, and the limited scope of information presented. It is important to consider these limitations when interpreting the map.
Tips for Using the Union Map:
- Understand the data sources: Before interpreting the map, it is essential to understand the data sources used and the potential limitations associated with the data.
- Consider the context: The map should be interpreted within the context of the specific industry, region, and historical period.
- Look beyond union density: While union density is an important indicator, it is crucial to consider other aspects of labor relations, such as collective bargaining agreements, worker satisfaction, and the impact of unionization on workplace conditions.
- Use the map as a starting point: The union map is a valuable tool, but it should not be considered the sole source of information. It is essential to conduct further research and analysis to gain a comprehensive understanding of labor relations in a specific industry or region.
Conclusion:
The union map is a powerful tool for understanding the current state of organized labor. It provides a visual representation of union density, allowing stakeholders to identify areas of strength, weakness, and potential for growth. While it has limitations, the map remains a valuable resource for workers, unions, employers, researchers, and policymakers seeking to navigate the complex landscape of labor relations. By using the map effectively and considering its limitations, stakeholders can gain valuable insights and contribute to a more equitable and just labor system.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Landscape of Labor: A Comprehensive Guide to the Union Map. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- A Comprehensive Guide To The Map Of Lakewood, California
- Thailand: A Jewel In The Heart Of Southeast Asia
- Navigating The Nation: A Guide To Free United States Map Vectors
- Navigating The Tapestry Of Arkansas: A Comprehensive Guide To Its Towns And Cities
- Mapping The Shifting Sands: A Look At 9th Century England
- A Journey Through Greene County, New York: Exploring The Land Of Catskill Mountains And Scenic Beauty
- The United States Of America In 1783: A Nation Forged In Boundaries
- Unraveling The Magic: A Comprehensive Guide To The Wizard Of Oz Map In User Experience Design
Leave a Reply