Navigating The Complex World Of Data: A Deep Dive Into RDF Maps
Navigating the Complex World of Data: A Deep Dive into RDF Maps
Related Articles: Navigating the Complex World of Data: A Deep Dive into RDF Maps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Complex World of Data: A Deep Dive into RDF Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Complex World of Data: A Deep Dive into RDF Maps
The ever-expanding realm of data necessitates efficient and standardized methods for its organization, access, and interpretation. Enter RDF Maps, a powerful tool designed to bridge the gap between diverse data sources and facilitate seamless data integration. This article delves into the intricacies of RDF Maps, exploring their core functionalities, benefits, and applications within the broader landscape of data management.
Understanding RDF Maps: A Foundation for Data Interoperability
RDF Maps, formally known as Resource Description Framework (RDF) Mapping Language, serve as a crucial element in the data integration process. They act as a bridge, enabling the translation of data from one format or structure to another, ultimately facilitating data exchange and interoperability.
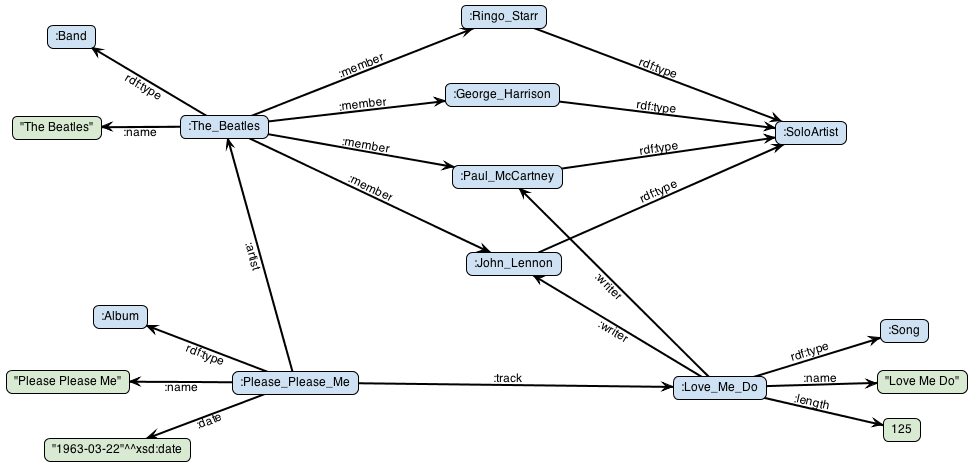
At its heart, RDF Maps leverage the expressive power of RDF, a widely accepted data model that represents information as a graph of interconnected resources. Each resource is described by a set of properties and their corresponding values, forming a web of relationships that can be easily understood and manipulated by machines.
The Mechanics of RDF Maps: Mapping Data to RDF
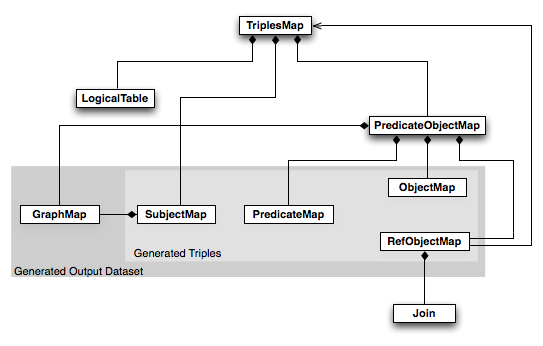
RDF Maps define a set of rules that map data from a source format, such as relational databases, XML documents, or spreadsheets, to an RDF representation. These rules specify how data elements in the source format correspond to RDF resources, properties, and values. This mapping process ensures that the original data is accurately translated into the RDF graph, preserving its semantic meaning.
Benefits of RDF Maps: A Powerful Tool for Data Integration
The use of RDF Maps offers several compelling advantages in the realm of data management and integration:
- Enhanced Data Interoperability: By standardizing data representations through RDF, RDF Maps enable seamless data exchange between different systems and applications, regardless of their underlying data formats. This interoperability fosters collaboration and data sharing across diverse platforms.
- Improved Data Accessibility: RDF Maps facilitate the retrieval and use of data from multiple sources in a unified manner. This accessibility empowers users to easily access and analyze data, regardless of its origin.
- Increased Data Quality: RDF Maps promote data consistency by enforcing a standardized structure and semantic interpretation. This ensures that data is represented accurately and coherently, leading to improved data quality.
- Enhanced Data Discovery: RDF Maps provide a clear and structured representation of data, enabling users to easily discover and understand the relationships between different data elements. This enhanced discoverability facilitates knowledge extraction and data analysis.
- Simplified Data Integration: RDF Maps streamline the process of integrating data from multiple sources. By providing a common framework for data representation, they simplify the integration process and reduce the complexity of managing diverse data formats.
Applications of RDF Maps: Bridging Data Silos
The versatility of RDF Maps makes them suitable for a wide range of applications across various domains:
- Semantic Web: RDF Maps play a crucial role in the development of the Semantic Web, enabling the seamless exchange of information between different web applications and services.
- Data Integration and Interoperability: RDF Maps are essential for integrating data from diverse sources, such as databases, spreadsheets, and web APIs, into a unified and interoperable data repository.
- Knowledge Management: RDF Maps facilitate the organization and management of knowledge within enterprise systems, enabling efficient information retrieval and knowledge discovery.
- Data Governance and Compliance: RDF Maps help enforce data standards and ensure data quality, contributing to effective data governance and compliance with regulations.
- Data Analytics and Visualization: RDF Maps provide a standardized data model for data analysis and visualization, enabling the extraction of insights and the creation of meaningful visualizations.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions about RDF Maps
1. What is the difference between RDF and RDF Maps?
RDF is a data model that represents information as a graph of interconnected resources. RDF Maps, on the other hand, are a language for mapping data from other formats into RDF. In essence, RDF defines the structure of data, while RDF Maps provide the mechanism for translating data into that structure.
2. How do I create an RDF Map?
Creating an RDF Map involves defining a set of rules that specify how data elements in the source format correspond to RDF resources, properties, and values. Several tools and languages are available for creating RDF Maps, such as RML (RDF Mapping Language) and ShEx (Schema-based Exchange).
3. What are the limitations of RDF Maps?
While RDF Maps offer significant benefits, they also have certain limitations. The mapping process can be complex, especially for large and complex datasets. Additionally, the development of RDF Maps requires specialized skills and knowledge.
4. Are there any alternative approaches to data integration?
Yes, several alternative approaches exist for data integration, such as data warehousing, ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) processes, and API integrations. However, RDF Maps offer a unique advantage in terms of semantic interoperability and standardized data representation.
5. How can I learn more about RDF Maps?
Several resources are available to learn more about RDF Maps, including online tutorials, documentation, and communities dedicated to RDF and data integration. The World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) provides comprehensive information on RDF and RDF Maps.
Tips for Utilizing RDF Maps Effectively
- Start with a clear understanding of your data sources and their structures.
- Define clear mapping rules that accurately translate data elements into RDF resources, properties, and values.
- Use a suitable tool or language for creating RDF Maps, such as RML or ShEx.
- Test your RDF Maps thoroughly to ensure accurate data translation and integration.
- Document your mapping process to facilitate future maintenance and updates.
Conclusion: A Powerful Tool for Data Interoperability and Beyond
RDF Maps have emerged as a crucial component in the landscape of data management, offering a powerful solution for bridging data silos and enabling seamless data integration. Their ability to translate data into a standardized RDF representation facilitates interoperability, improves data accessibility, and enhances data quality. As data continues to proliferate, RDF Maps will play an increasingly vital role in harnessing the power of information and unlocking its full potential. By embracing the capabilities of RDF Maps, organizations can unlock new possibilities for data collaboration, knowledge sharing, and informed decision-making in a rapidly evolving data-driven world.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Complex World of Data: A Deep Dive into RDF Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- A Comprehensive Guide To The Map Of Lakewood, California
- Thailand: A Jewel In The Heart Of Southeast Asia
- Navigating The Nation: A Guide To Free United States Map Vectors
- Navigating The Tapestry Of Arkansas: A Comprehensive Guide To Its Towns And Cities
- Mapping The Shifting Sands: A Look At 9th Century England
- A Journey Through Greene County, New York: Exploring The Land Of Catskill Mountains And Scenic Beauty
- The United States Of America In 1783: A Nation Forged In Boundaries
- Unraveling The Magic: A Comprehensive Guide To The Wizard Of Oz Map In User Experience Design
Leave a Reply