Navigating California’s Diverse Climates: Understanding The USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map
Navigating California’s Diverse Climates: Understanding the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map
Related Articles: Navigating California’s Diverse Climates: Understanding the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating California’s Diverse Climates: Understanding the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating California’s Diverse Climates: Understanding the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/CaliforniaNorthZones-57bbc5873df78c8763665b74.jpg)
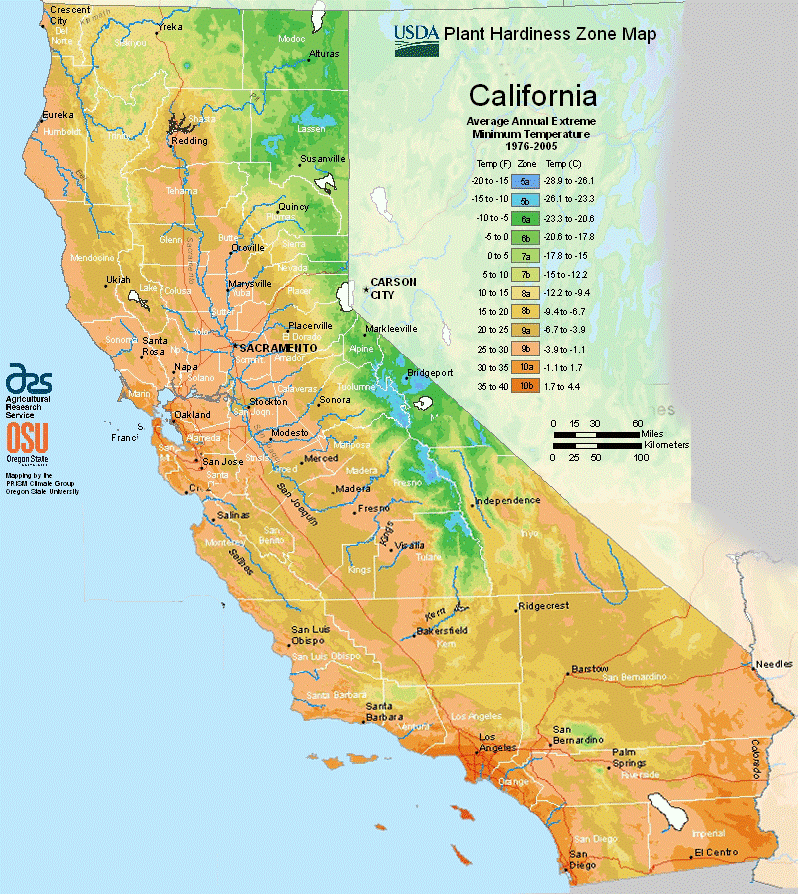
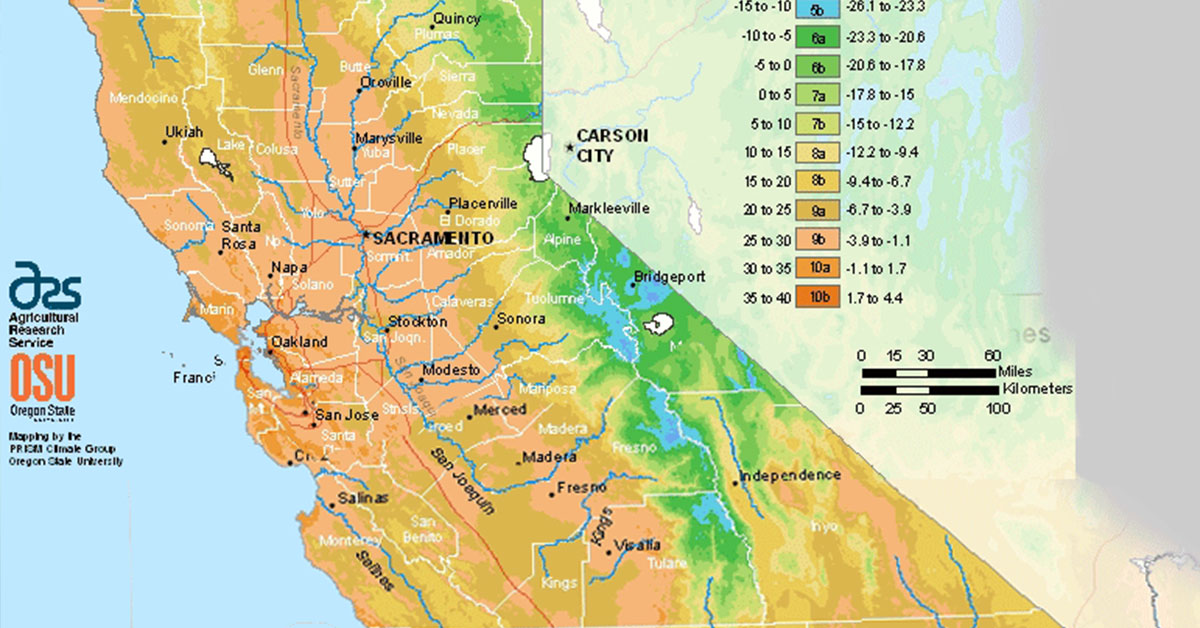
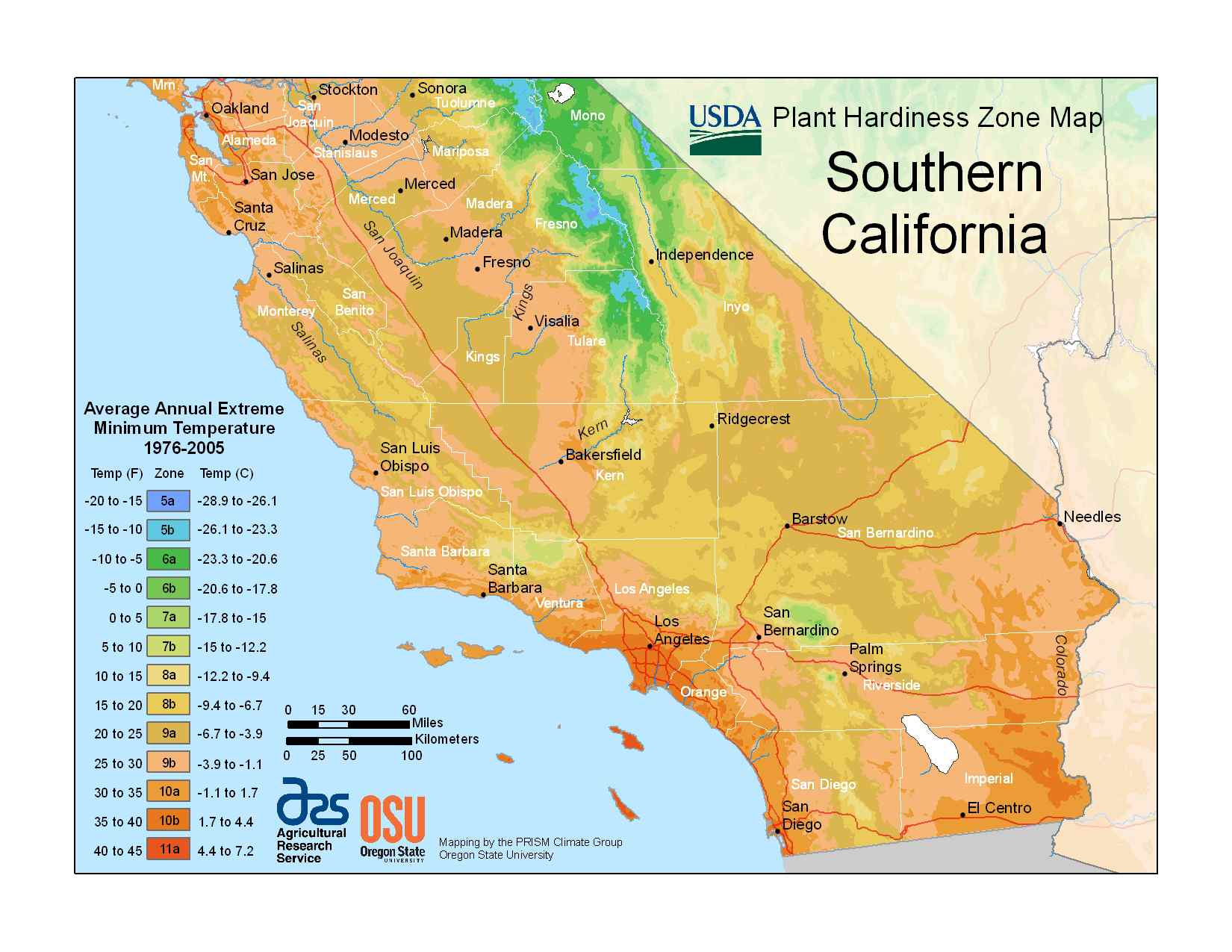
California, renowned for its varied landscapes and diverse ecosystems, presents a unique challenge for gardeners and plant enthusiasts. The state’s vast geographical expanse, ranging from the scorching deserts of the southeast to the towering redwoods of the north, encompasses a remarkable spectrum of microclimates. To navigate this climatic complexity, the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) has developed a Plant Hardiness Zone Map, providing a valuable tool for understanding and predicting plant survival in different regions.
The Foundation of the Map: Temperature and Plant Hardiness
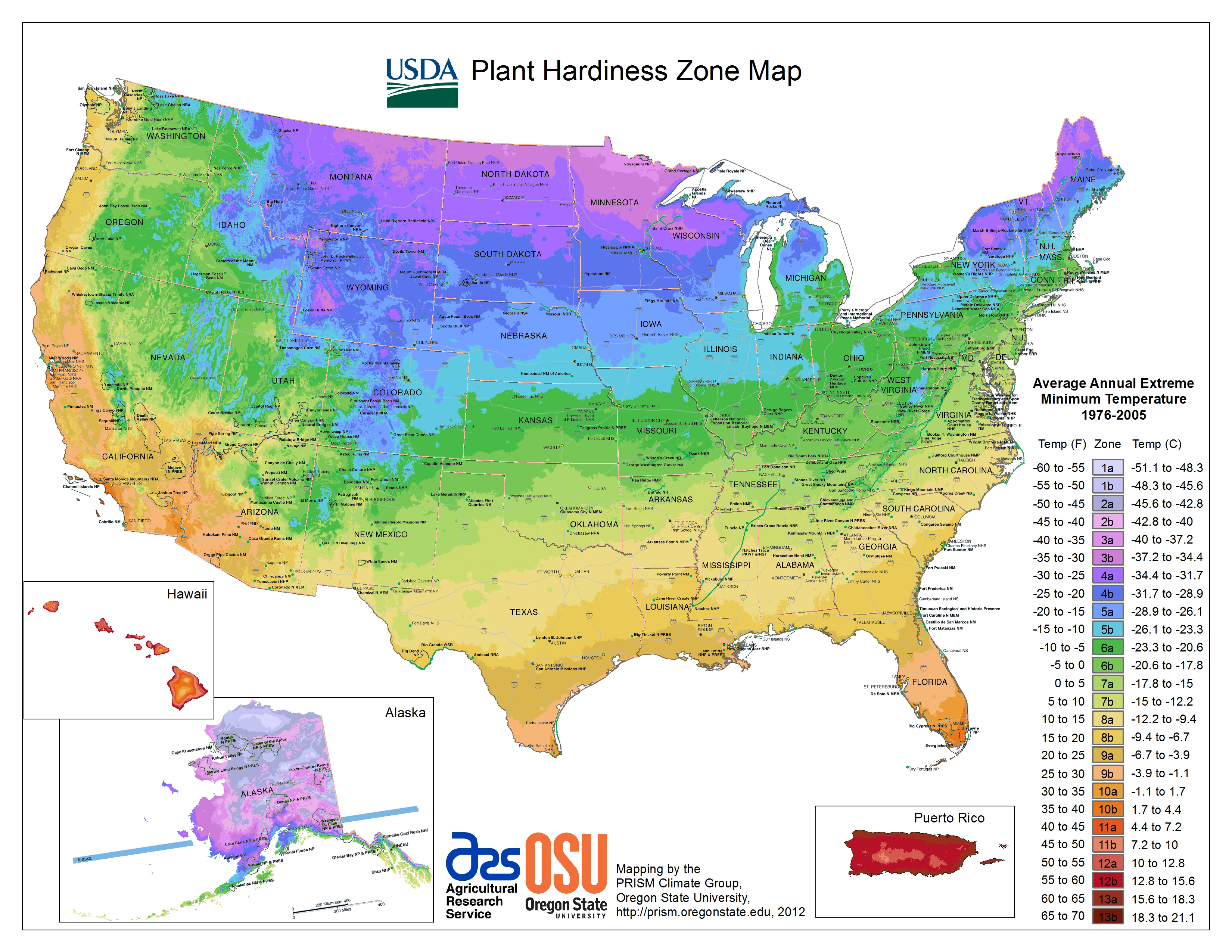
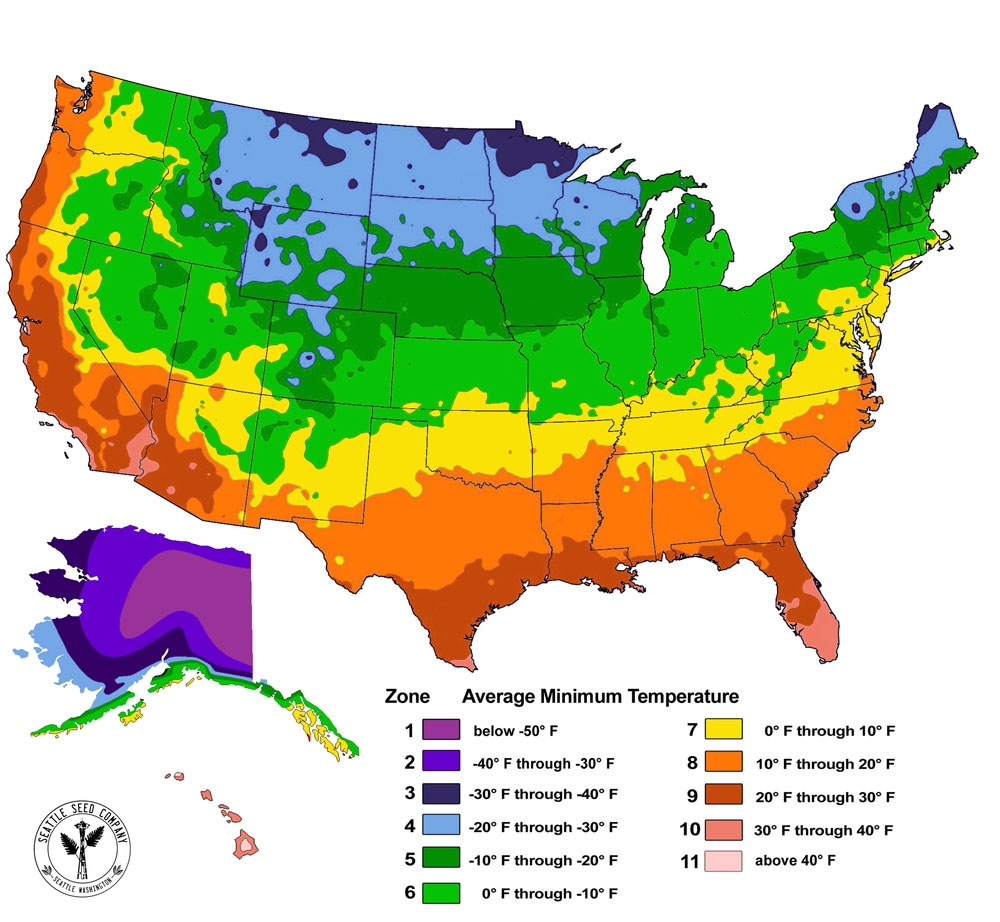
The USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map is a valuable resource for gardeners, landscapers, and plant enthusiasts alike. It provides a standardized system for classifying regions based on their average annual minimum winter temperature. These zones, designated by Roman numerals from 1 to 13, represent a range of cold hardiness, with lower numbers indicating colder climates and higher numbers representing warmer regions.
California, with its diverse climate, spans a significant range on the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map. The state’s coastal regions, influenced by the Pacific Ocean, enjoy mild winters and are classified as Zones 8-10. Inland valleys, shielded from the moderating influence of the ocean, experience colder winters, falling into Zones 7-9. The mountainous regions of California, with their higher elevations and colder temperatures, are categorized as Zones 4-7.
Understanding the Map’s Significance for California
The USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map is not merely a theoretical construct; it has practical implications for a range of activities in California:
1. Successful Gardening and Landscaping: By understanding the specific zone of their location, gardeners can select plant species that are well-suited to the local climate. Choosing plants that thrive within the designated zone ensures optimal growth, reduced maintenance, and a greater chance of success.
2. Informed Plant Selection: The map serves as a crucial tool for nurseries, garden centers, and plant suppliers, allowing them to stock and recommend plants that are appropriate for the specific climates of their customers.
3. Effective Agricultural Planning: Farmers and agriculturalists use the map to determine suitable crops and growing seasons for their regions. This information helps optimize yields, minimize risks, and ensure the success of agricultural endeavors.
4. Conservation and Ecosystem Management: The map contributes to conservation efforts by aiding in the selection of native plant species that are adapted to specific climates. This practice helps maintain biodiversity and promote healthy ecosystems.
5. Urban Planning and Development: The map provides valuable insights for urban planners and developers, guiding the selection of appropriate vegetation for public spaces, parks, and residential areas.
Beyond Zones: Other Factors Influencing Plant Growth
While the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map provides a valuable framework for understanding plant hardiness, it’s essential to recognize that other factors also play a significant role in plant survival and growth:
- Microclimates: Within a single zone, variations in elevation, proximity to water bodies, and urban heat islands can create microclimates with distinct temperature regimes.
- Soil Type: Soil composition, drainage, and nutrient content influence plant growth and can impact plant hardiness.
- Sunlight Exposure: The amount of sunlight a plant receives directly affects its growth and development.
- Wind Exposure: Wind can exacerbate cold temperatures and desiccate plants, impacting their survival.
- Precipitation: Rainfall patterns and irrigation practices significantly influence plant growth and hardiness.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions About California’s Plant Hardiness Zones
Q: What is the difference between a hardiness zone and a climate zone?
A: Hardiness zones focus specifically on average minimum winter temperatures, while climate zones encompass a broader range of climatic factors, including temperature, precipitation, humidity, and wind patterns.
Q: Can I grow plants outside my zone?
A: While it’s possible to grow plants outside their designated zone, it requires careful selection and extra care. Some plants may require winter protection or may not reach their full potential.
Q: How can I determine my specific zone?
A: The USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map is readily available online, and you can locate your specific zone using an interactive map or by entering your zip code.
Q: Does the map change over time?
A: The USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map is periodically updated to reflect changes in climate patterns. However, these updates are typically infrequent and often reflect long-term trends.
Tips: Optimizing Plant Growth in California’s Diverse Climates
- Choose plants adapted to your specific zone. Consult with local nurseries or gardening experts for recommendations.
- Consider microclimates. Observe your garden and identify areas with different sun exposure, wind protection, and soil conditions.
- Protect plants from frost and cold temperatures. Utilize techniques like mulching, frost blankets, or winterizing shrubs.
- Water deeply and infrequently. Encourage deep root development and improve drought tolerance.
- Amend your soil. Improve drainage, add organic matter, and ensure proper nutrient levels.
Conclusion: Embracing California’s Climate Diversity
The USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map provides a valuable framework for understanding and navigating the diverse climates of California. By utilizing this resource and considering the factors that influence plant growth, gardeners, landscapers, and agriculturalists can cultivate thriving landscapes and ensure the success of their horticultural endeavors. The map is not a rigid rule but rather a guide, offering valuable insights for making informed decisions about plant selection, cultivation, and conservation. By embracing California’s unique climate diversity and employing appropriate practices, we can create vibrant and resilient ecosystems that flourish in our state’s diverse landscapes.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating California’s Diverse Climates: Understanding the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- A Comprehensive Guide To The Map Of Lakewood, California
- Thailand: A Jewel In The Heart Of Southeast Asia
- Navigating The Nation: A Guide To Free United States Map Vectors
- Navigating The Tapestry Of Arkansas: A Comprehensive Guide To Its Towns And Cities
- Mapping The Shifting Sands: A Look At 9th Century England
- A Journey Through Greene County, New York: Exploring The Land Of Catskill Mountains And Scenic Beauty
- The United States Of America In 1783: A Nation Forged In Boundaries
- Unraveling The Magic: A Comprehensive Guide To The Wizard Of Oz Map In User Experience Design
Leave a Reply