China’s Geographic Significance: A Comprehensive Overview
China’s Geographic Significance: A Comprehensive Overview
Related Articles: China’s Geographic Significance: A Comprehensive Overview
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to China’s Geographic Significance: A Comprehensive Overview. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
China’s Geographic Significance: A Comprehensive Overview
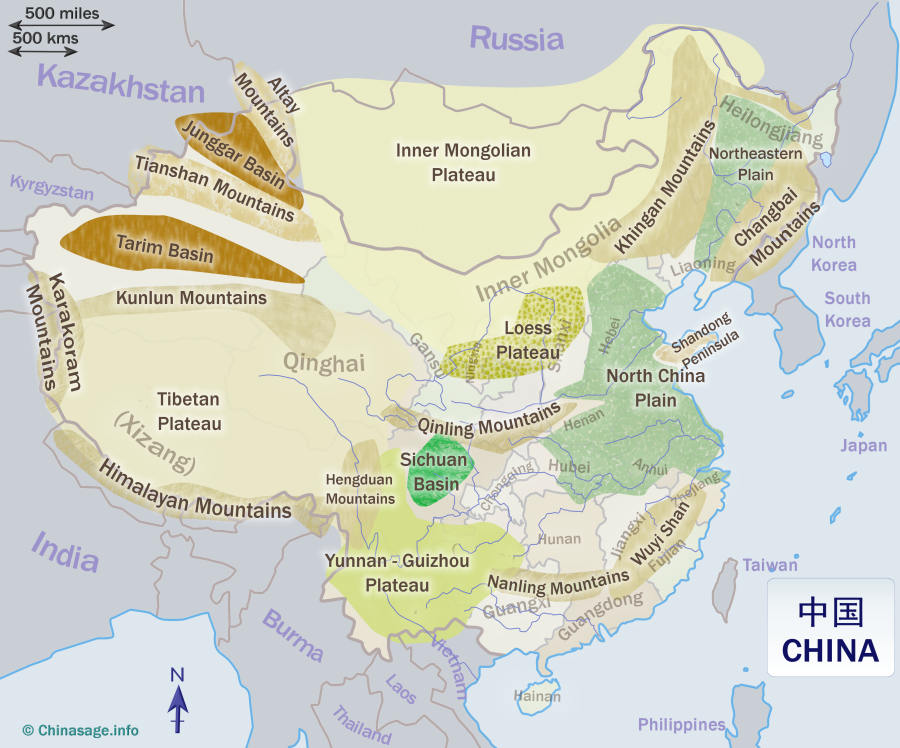
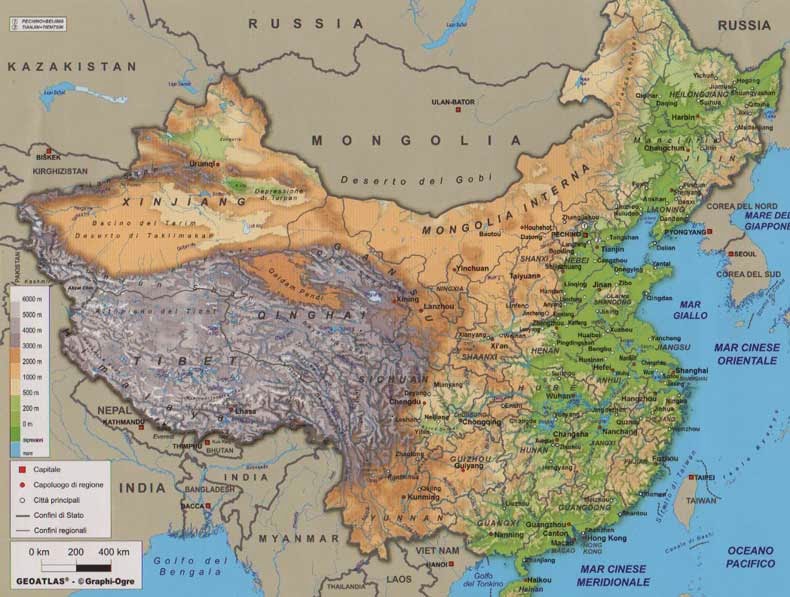
China, the world’s most populous nation, occupies a vast and strategically important position in Asia. Its geographical features and location have shaped its history, culture, and influence on the global stage. Understanding China’s map is crucial for comprehending its economic, political, and environmental dynamics.
A Land of Extremes: China’s Diverse Geography
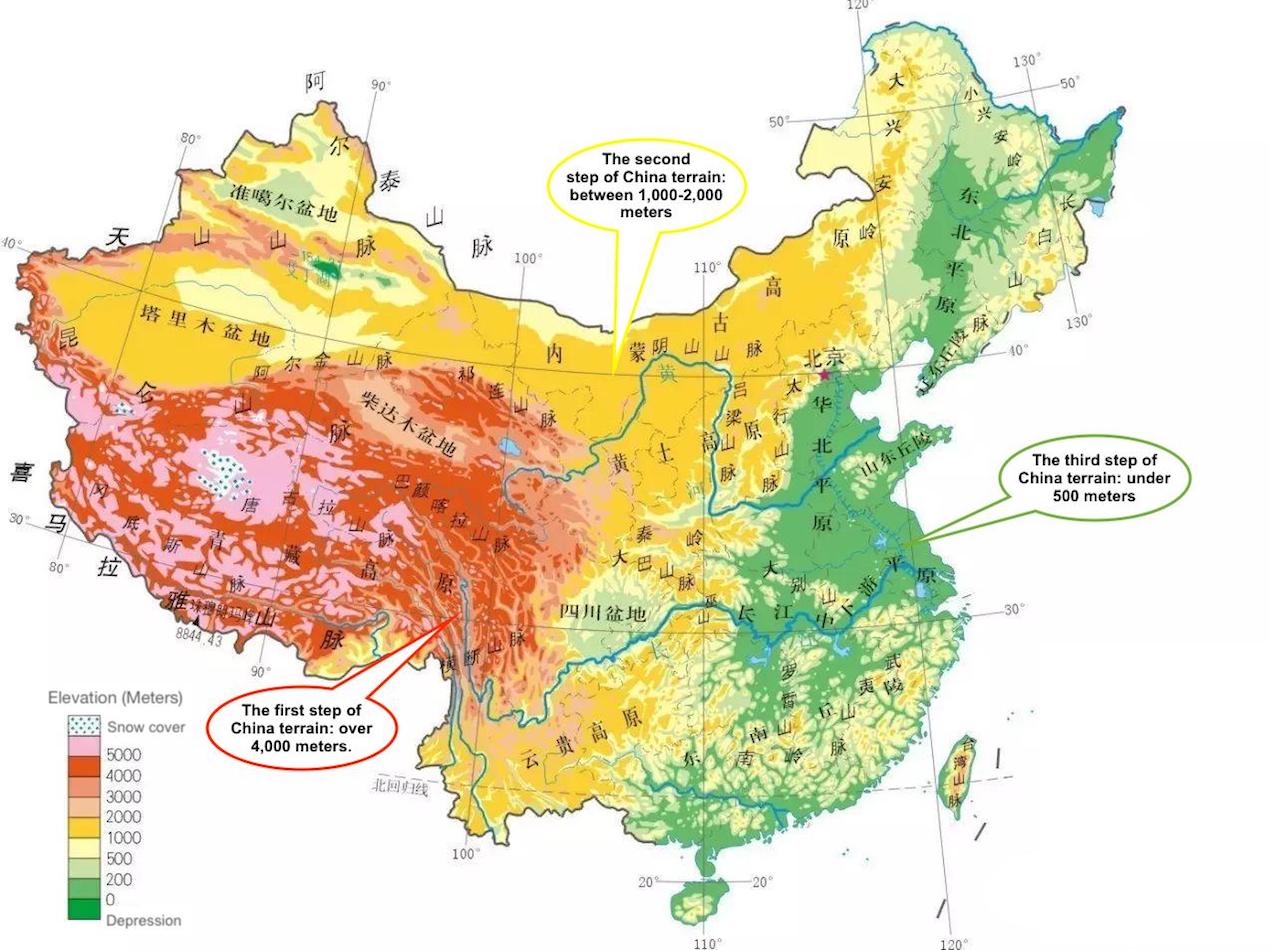
China’s diverse topography encompasses a remarkable range of landscapes, from towering mountains and expansive deserts to fertile plains and sprawling coastlines.
- The Himalayas: The mighty Himalayas, forming the world’s highest mountain range, mark China’s southwestern border. The Tibetan Plateau, located within this region, is a high-altitude plateau with vast stretches of grasslands and glaciers, playing a crucial role in regulating regional climate and water resources.
- The North China Plain: This fertile plain, located in eastern China, is the heartland of Chinese agriculture and population density. It is fed by the Yellow River, known as the "cradle of Chinese civilization."
- The Yangtze River: The Yangtze River, the longest in Asia, flows through central and eastern China, providing vital transportation routes and irrigation for agriculture. The Yangtze River Delta, where it meets the East China Sea, is one of the most densely populated and economically vibrant regions in the world.
- The Gobi Desert: Located in northern China, the Gobi Desert is a vast expanse of arid land, posing challenges to human settlement and agricultural development.
- The Coastal Regions: China’s eastern coastline is characterized by numerous bays, inlets, and islands, providing access to major shipping routes and maritime resources.
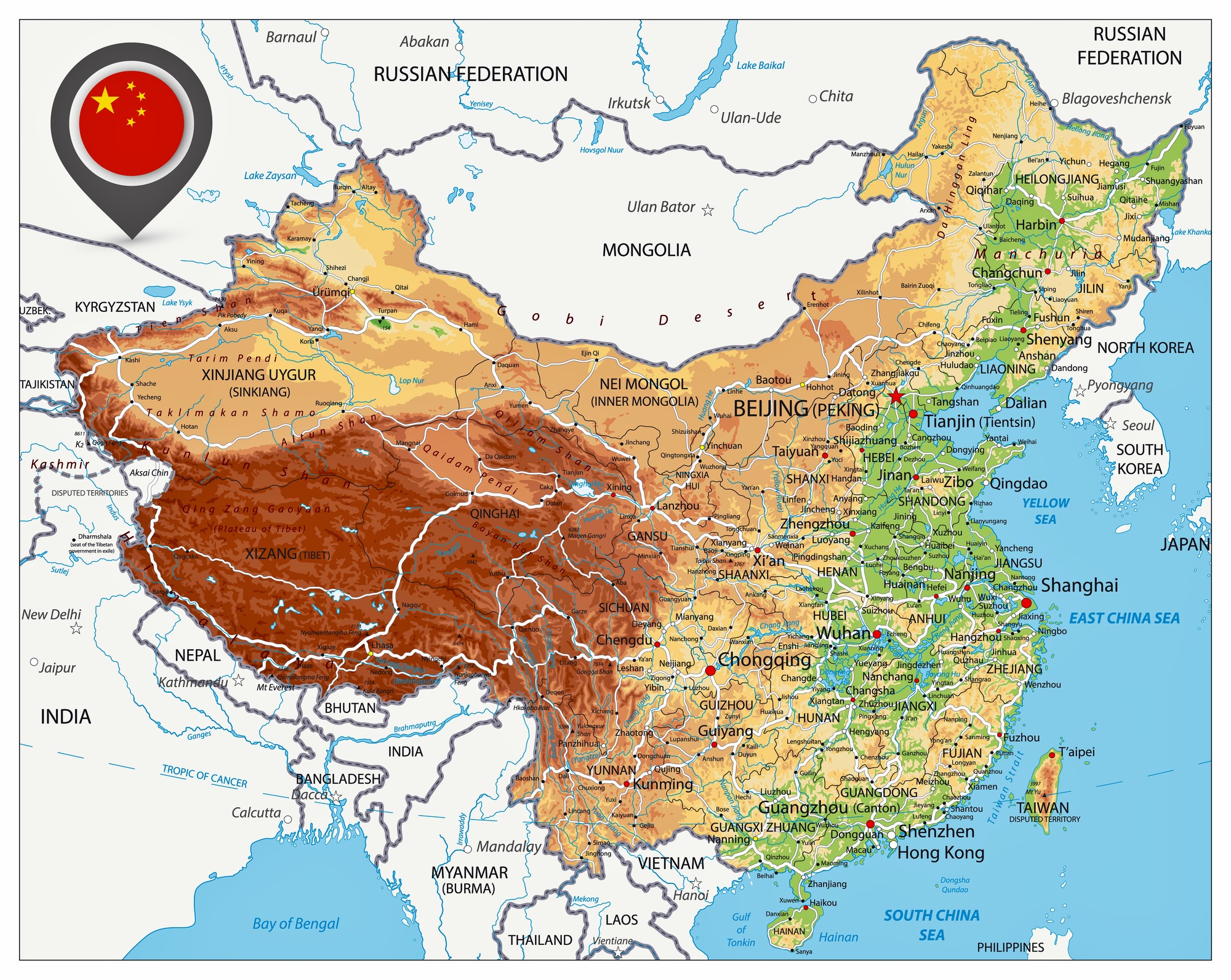
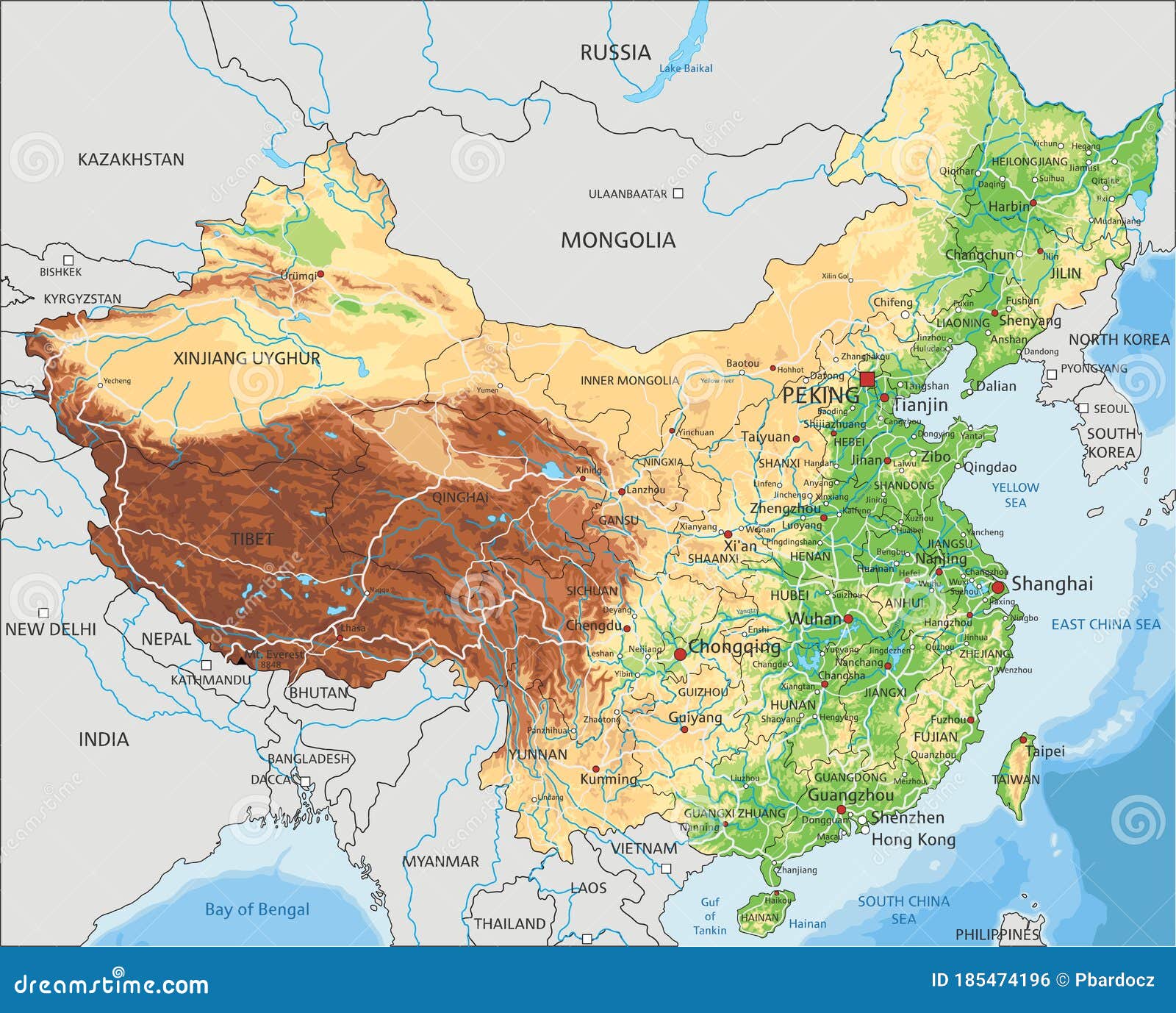
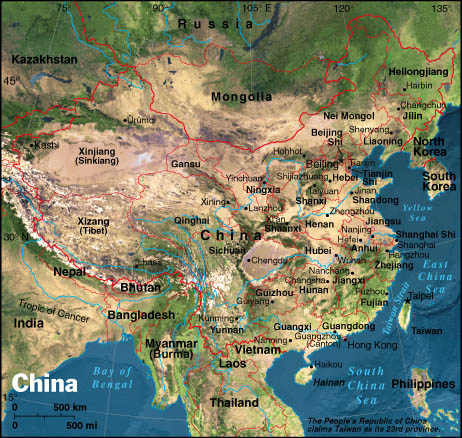
China’s Position in Asia: A Strategic Crossroads
China’s location in East Asia places it at the heart of a dynamic region, connecting it to major economies and cultural centers.
- Neighboring Countries: China shares land borders with 14 countries, including Russia, Mongolia, India, Vietnam, and North Korea. This proximity fosters economic and cultural exchange, but also presents challenges in managing border disputes and maintaining regional stability.
- Maritime Influence: China’s extensive coastline offers significant access to the Pacific Ocean, enabling it to play a major role in global trade and maritime security. Its maritime claims in the South China Sea have become a point of contention with neighboring countries.
- Connectivity and Infrastructure: China’s strategic location has fueled the development of extensive infrastructure projects, including high-speed rail lines, highways, and pipelines, connecting it to neighboring countries and facilitating trade and investment.
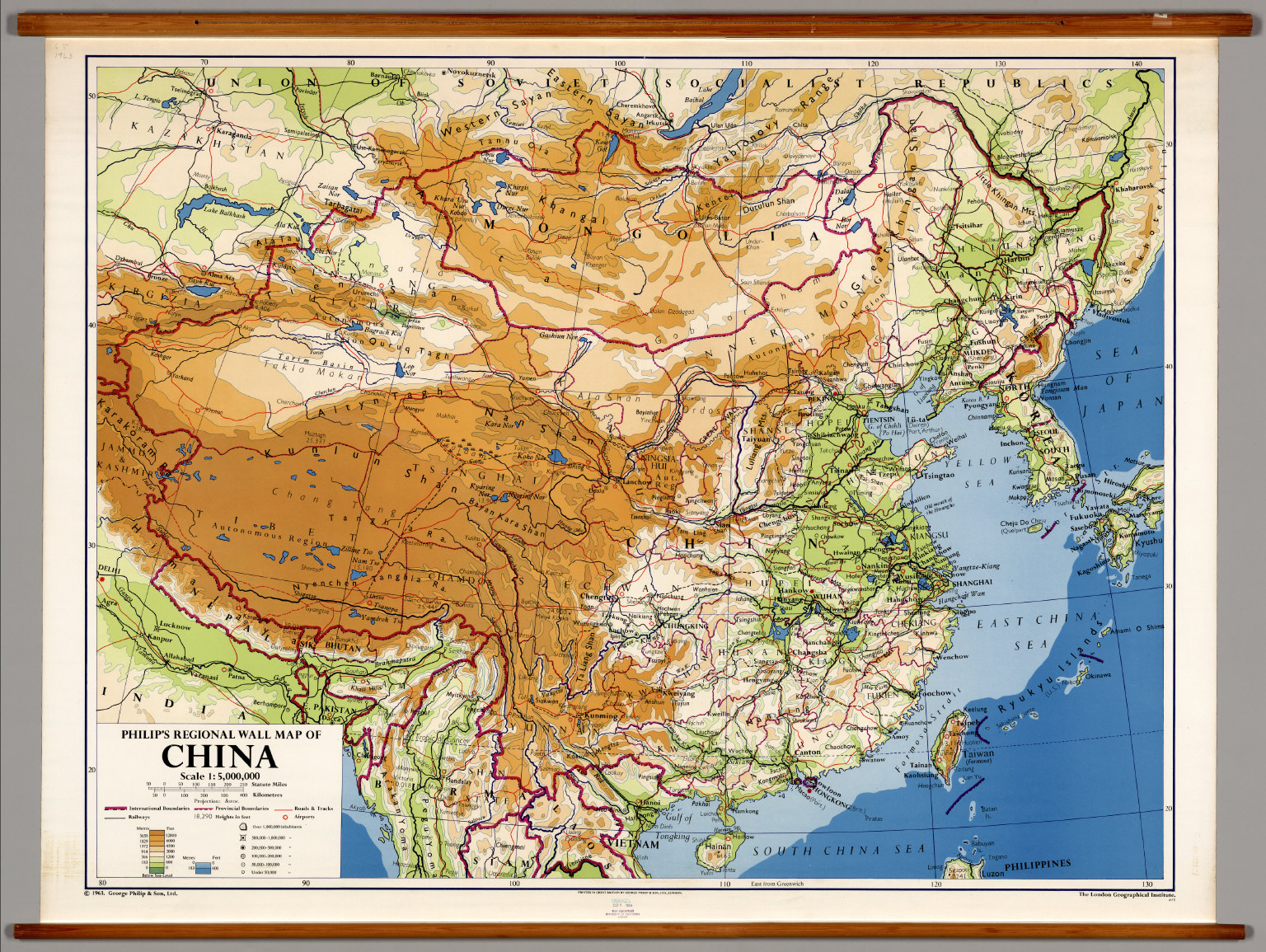
The Importance of Understanding China’s Map
Comprehending China’s geography is essential for understanding its history, culture, and contemporary challenges.
- Historical Development: China’s diverse geography has shaped its historical development, influencing its cultural traditions, agricultural practices, and political structures.
- Economic Growth: China’s location has contributed to its economic growth by facilitating access to global markets and resources. Its vast landmass and diverse resources provide opportunities for industrial development and agricultural production.
- Environmental Challenges: China faces significant environmental challenges, including air and water pollution, deforestation, and desertification, which are exacerbated by its rapid economic growth and population density.
- Regional Stability: China’s strategic location and growing influence in Asia have significant implications for regional stability and security. Its relationships with neighboring countries and its role in international organizations are crucial for maintaining peace and cooperation.
FAQs about China’s Map
Q: What are the major mountain ranges in China?
A: The major mountain ranges in China include the Himalayas, the Kunlun Mountains, the Tian Shan Mountains, and the Qinling Mountains.
Q: What are the major rivers in China?
A: The major rivers in China include the Yangtze River, the Yellow River, the Pearl River, and the Mekong River.
Q: What are the major deserts in China?
A: The major deserts in China include the Gobi Desert, the Taklamakan Desert, and the Badain Jaran Desert.
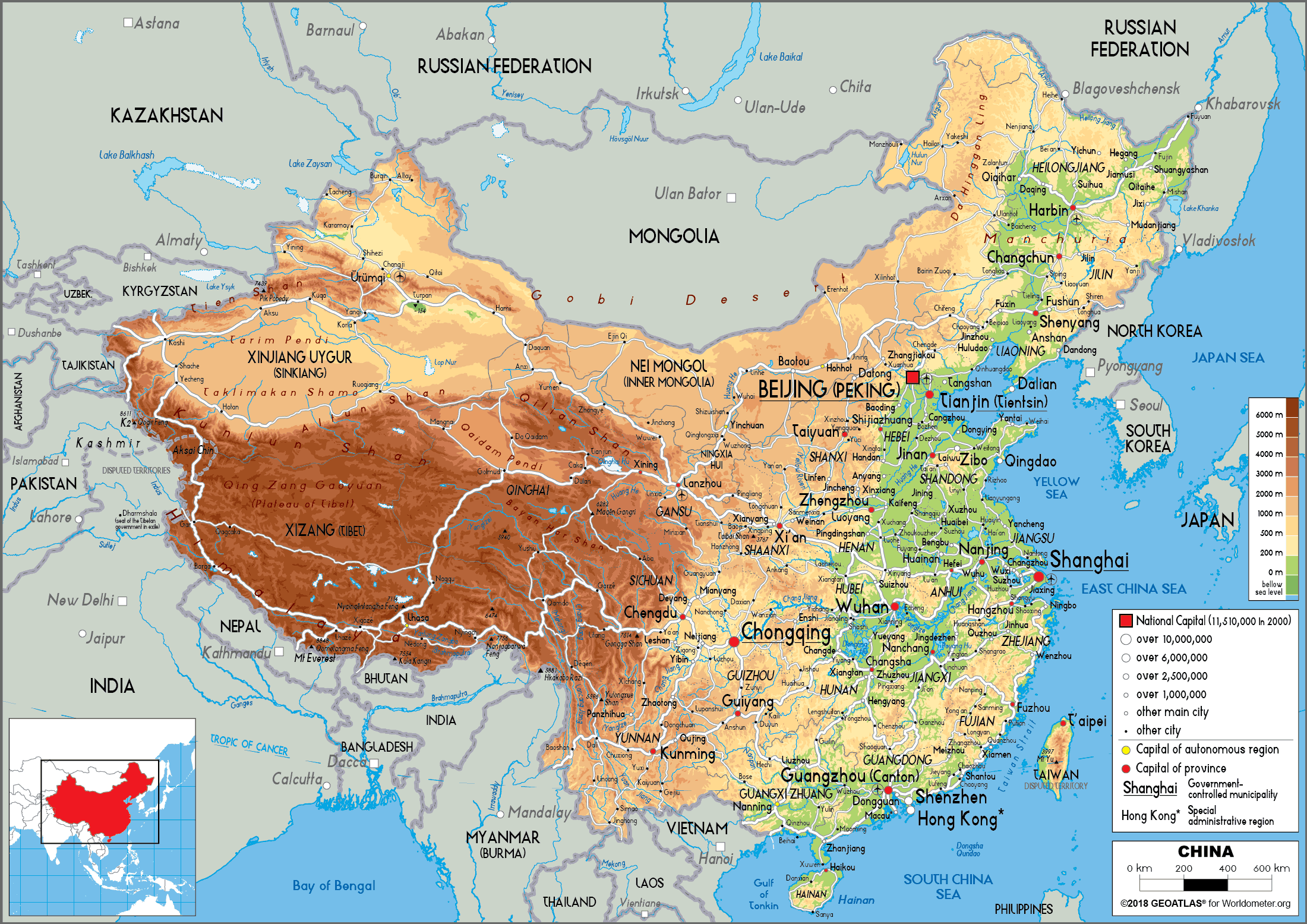
Q: What are the major cities in China?
A: The major cities in China include Beijing, Shanghai, Guangzhou, Shenzhen, Chongqing, and Chengdu.
Q: What are the major economic zones in China?
A: The major economic zones in China include the Yangtze River Delta, the Pearl River Delta, and the Bohai Economic Rim.
Tips for Understanding China’s Map
- Use online maps and atlases: Explore interactive maps and atlases that provide detailed information about China’s geography, including its provinces, cities, and major geographical features.
- Study historical maps: Examining historical maps can provide insights into China’s territorial evolution and the changing dynamics of its borders over time.
- Read about China’s geography: Consult books, articles, and research papers that offer comprehensive analyses of China’s geographical features and their impact on the country’s development.
- Travel to China: Visiting China allows for firsthand experience of its diverse landscapes and provides a deeper understanding of its geographical context.
Conclusion
China’s map is a complex and dynamic entity, reflecting the country’s immense size, diverse geography, and strategic location. Understanding China’s map is crucial for comprehending its history, culture, and contemporary challenges. Its geographic features have shaped its economic growth, environmental concerns, and regional influence, making it a vital factor in understanding the dynamics of Asia and the world. By exploring China’s map, we gain a deeper appreciation for the country’s unique characteristics and its role in shaping the global landscape.

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into China’s Geographic Significance: A Comprehensive Overview. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- A Comprehensive Guide To The Map Of Lakewood, California
- Thailand: A Jewel In The Heart Of Southeast Asia
- Navigating The Nation: A Guide To Free United States Map Vectors
- Navigating The Tapestry Of Arkansas: A Comprehensive Guide To Its Towns And Cities
- Mapping The Shifting Sands: A Look At 9th Century England
- A Journey Through Greene County, New York: Exploring The Land Of Catskill Mountains And Scenic Beauty
- The United States Of America In 1783: A Nation Forged In Boundaries
- Unraveling The Magic: A Comprehensive Guide To The Wizard Of Oz Map In User Experience Design
Leave a Reply