Charting The West: Exploring The Geography And Significance Of The United States West Coast
Charting the West: Exploring the Geography and Significance of the United States West Coast
Related Articles: Charting the West: Exploring the Geography and Significance of the United States West Coast
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Charting the West: Exploring the Geography and Significance of the United States West Coast. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Charting the West: Exploring the Geography and Significance of the United States West Coast

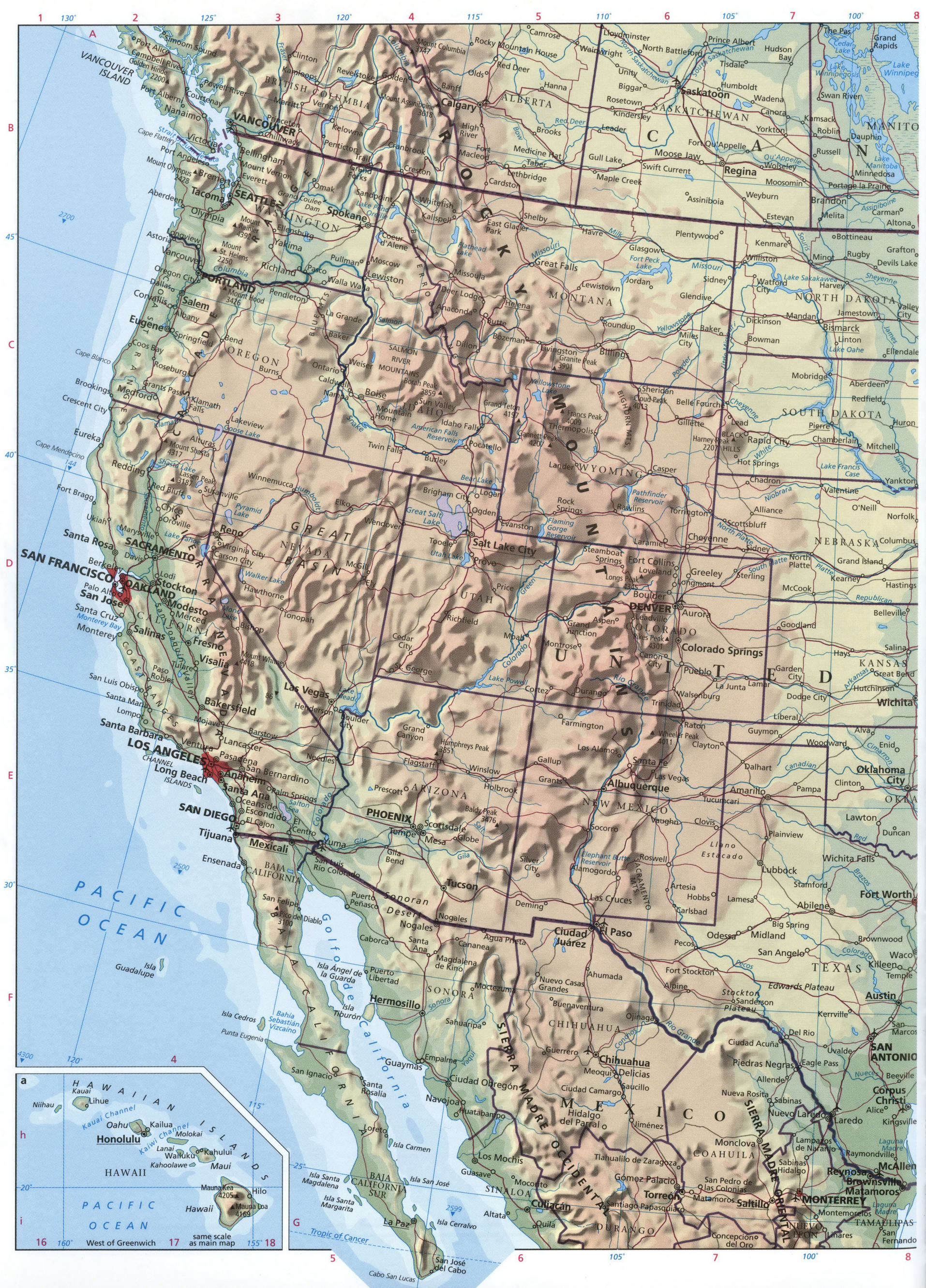
The United States West Coast, a vibrant tapestry of landscapes, cultures, and economic forces, stretches along the Pacific Ocean from the northern reaches of Washington state to the southern tip of California. Its geographic diversity, encompassing towering mountains, vast deserts, lush forests, and fertile valleys, has shaped a region rich in natural resources, cultural heritage, and economic potential. Understanding the intricacies of this region requires a comprehensive understanding of its diverse geography, its historical development, and its present-day significance.
A Land of Contrasts: The West Coast’s Diverse Geography
The West Coast’s geography is a defining characteristic, shaping its climate, ecosystems, and human settlements. The region is characterized by a dramatic interplay of mountain ranges, coastal plains, and oceanic influences.
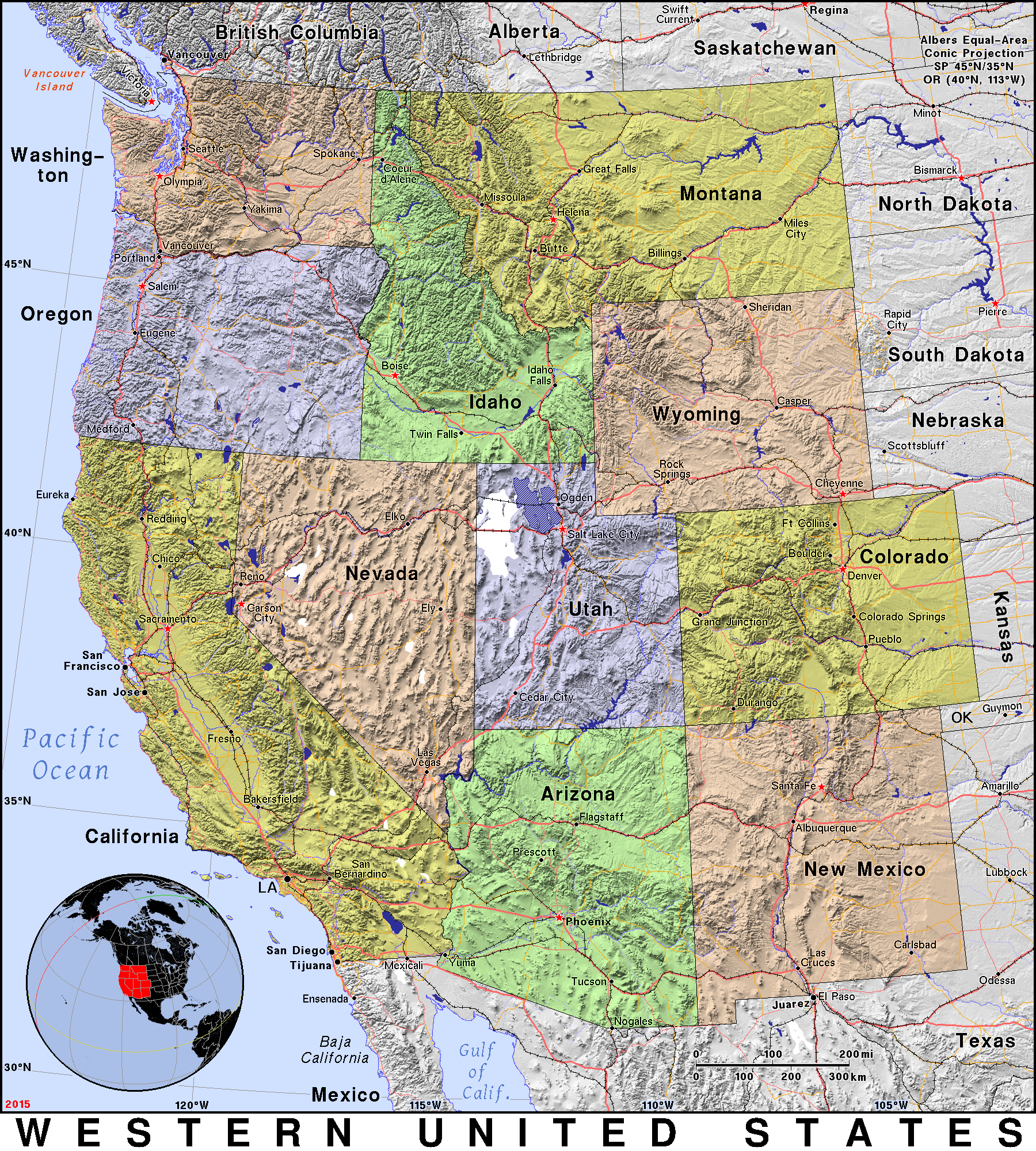
- The Coastal Ranges: The Pacific Coast Ranges, a series of mountain ranges running parallel to the coast, form a significant geographical feature. These ranges, including the Coast Mountains of British Columbia, the Cascade Range, the Sierra Nevada, and the Transverse Ranges, create a distinct barrier between the coast and the interior, influencing rainfall patterns and creating distinct microclimates.
- The Interior Basins and Plateaus: East of the coastal ranges lie vast interior basins and plateaus, characterized by arid conditions and sparse vegetation. These include the Columbia Plateau, the Great Basin, and the Mojave Desert. These areas are often characterized by dramatic temperature fluctuations and limited water resources.
- The Pacific Ocean: The Pacific Ocean, a powerful force shaping the West Coast, exerts a profound influence on the region’s climate, ecosystems, and economy. The ocean currents, particularly the California Current, bring cool, nutrient-rich waters to the coast, supporting a diverse marine ecosystem and influencing the region’s climate patterns.
The West Coast’s Historical Tapestry: From Indigenous Cultures to Modernity
The history of the West Coast is a complex and fascinating narrative, intertwined with the stories of indigenous peoples, European colonization, and the rise of modern American society.
- Indigenous Cultures: For millennia, the West Coast was home to diverse indigenous cultures, each adapted to the specific environment and resources of their territory. The Coast Salish, Chinook, and Nuu-chah-nulth peoples of the Pacific Northwest, the Chumash, Tongva, and Cahuilla of California, and the numerous tribes of the Great Basin, each developed unique traditions, languages, and cultural practices.
- European Colonization: European exploration and colonization began in the late 18th and early 19th centuries, with the arrival of Spanish explorers, British fur traders, and American settlers. The arrival of Europeans brought significant changes, including the displacement of indigenous populations, the introduction of new diseases, and the establishment of new economic and social structures.
- The Gold Rush and Beyond: The discovery of gold in California in 1848 triggered a massive influx of people, transforming the region’s demographics and economy. This period saw the rapid growth of cities, the expansion of agriculture, and the development of infrastructure. The West Coast’s role in the American expansion continued with the development of railroads, the establishment of mining towns, and the rise of major urban centers.
Economic Powerhouses: The West Coast’s Economic Landscape
The West Coast today is a vibrant economic powerhouse, driven by a diverse mix of industries, technological innovation, and a dynamic entrepreneurial spirit.
- Technology and Innovation: The West Coast, particularly Silicon Valley in California, has emerged as a global hub for technology and innovation. Companies like Google, Apple, Microsoft, and Amazon have revolutionized industries and driven economic growth. The region’s concentration of research universities, venture capital firms, and skilled labor has fostered a culture of innovation and entrepreneurship.
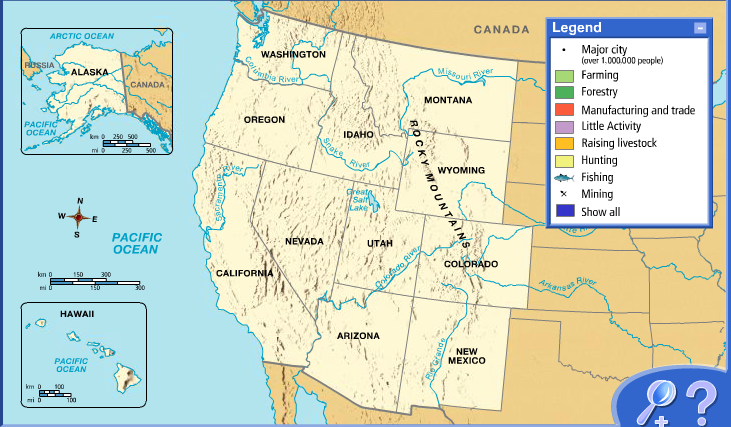
- Agriculture and Natural Resources: The West Coast remains a significant agricultural producer, with California being a major contributor to the nation’s food supply. The region’s diverse climate and fertile soils allow for the production of a wide variety of crops, including fruits, vegetables, nuts, and wine grapes. The region also possesses vast natural resources, including timber, minerals, and energy sources, contributing to its economic strength.
- Tourism and Recreation: The West Coast’s stunning natural beauty attracts millions of tourists annually. From the beaches of California to the mountains of Oregon and Washington, the region offers a diverse range of recreational opportunities, including hiking, skiing, surfing, and whale watching. Tourism plays a significant role in the West Coast’s economy, supporting hotels, restaurants, and other businesses.
Challenges and Opportunities: The West Coast’s Future
While the West Coast enjoys significant economic and cultural advantages, it also faces challenges that require careful consideration and proactive solutions.
- Climate Change: The West Coast is particularly vulnerable to the impacts of climate change, including rising sea levels, more frequent and intense wildfires, and changes in water availability. These challenges require innovative solutions to mitigate the effects of climate change and ensure the region’s long-term sustainability.
- Housing Affordability: The West Coast, particularly California, faces a severe housing affordability crisis, driven by high demand and limited supply. This issue has significant consequences for residents, businesses, and the overall economic health of the region.
- Social Equity: The West Coast, despite its progressive image, faces challenges related to social equity, including income inequality, racial disparities, and access to education and healthcare. Addressing these issues is crucial to ensuring a more equitable and just society.
Understanding the West Coast: FAQs
Q: What are the major cities on the West Coast?
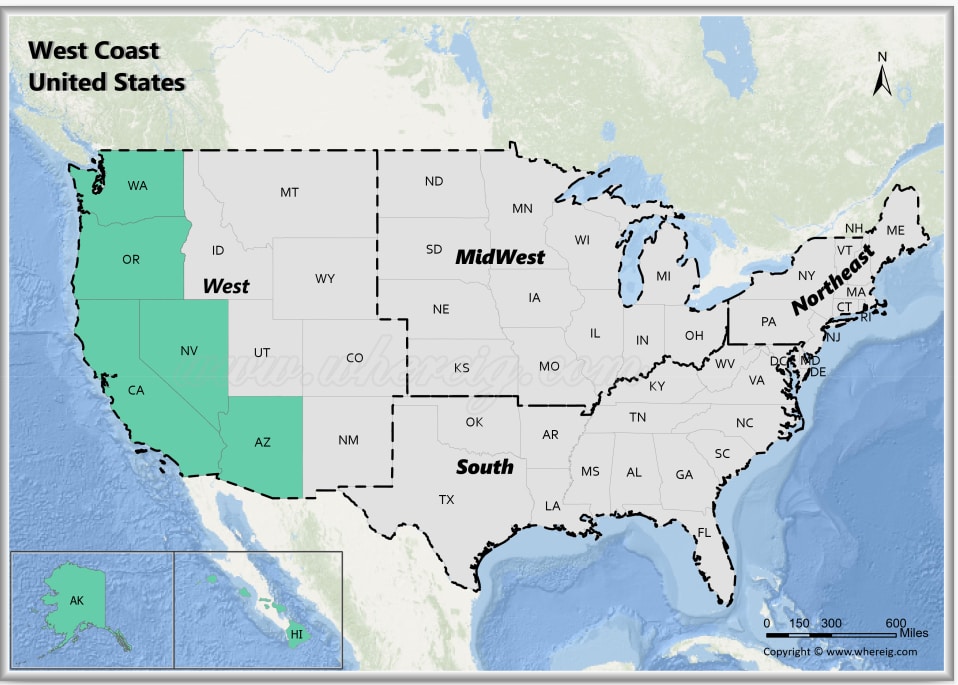
A: The major cities on the West Coast include Seattle, Portland, San Francisco, Los Angeles, San Diego, and Vancouver (Canada).
Q: What is the climate like on the West Coast?
A: The climate varies significantly along the West Coast, ranging from temperate rainforest in the Pacific Northwest to Mediterranean climates in California.
Q: What are the major industries on the West Coast?
A: The major industries on the West Coast include technology, agriculture, tourism, and entertainment.
Q: What are some of the challenges facing the West Coast?
A: The West Coast faces challenges related to climate change, housing affordability, and social equity.
Q: What are some of the opportunities for the West Coast?
A: The West Coast has significant opportunities in technology, renewable energy, and sustainable agriculture.
Tips for Exploring the West Coast:
- Plan your itinerary carefully: The West Coast offers a vast array of experiences, so planning ahead is crucial.
- Consider the time of year: The weather varies significantly along the coast, so choose the best time to visit based on your interests.
- Be prepared for diverse landscapes: From mountains to deserts to beaches, the West Coast offers a diverse range of environments.
- Embrace the local culture: The West Coast is home to a rich and diverse culture, so take the time to explore local restaurants, museums, and festivals.
- Be mindful of the environment: The West Coast is a fragile ecosystem, so be respectful of the natural environment and practice responsible tourism.
Conclusion:
The United States West Coast, a dynamic and multifaceted region, stands as a testament to the power of geography, history, and human ingenuity. Its diverse landscapes, vibrant cultures, and thriving economy have shaped a region of profound significance in the national and global landscape. As the West Coast navigates the challenges and opportunities of the 21st century, its ability to innovate, adapt, and embrace sustainability will determine its future trajectory. Understanding the intricacies of this remarkable region, its past, present, and potential future, is essential for appreciating its enduring influence on the world.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Charting the West: Exploring the Geography and Significance of the United States West Coast. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- A Comprehensive Guide To The Map Of Lakewood, California
- Thailand: A Jewel In The Heart Of Southeast Asia
- Navigating The Nation: A Guide To Free United States Map Vectors
- Navigating The Tapestry Of Arkansas: A Comprehensive Guide To Its Towns And Cities
- Mapping The Shifting Sands: A Look At 9th Century England
- A Journey Through Greene County, New York: Exploring The Land Of Catskill Mountains And Scenic Beauty
- The United States Of America In 1783: A Nation Forged In Boundaries
- Unraveling The Magic: A Comprehensive Guide To The Wizard Of Oz Map In User Experience Design
Leave a Reply