Arid Landscapes And Hidden Treasures: Exploring Australia’s Deserts On The Map
Arid Landscapes and Hidden Treasures: Exploring Australia’s Deserts on the Map
Related Articles: Arid Landscapes and Hidden Treasures: Exploring Australia’s Deserts on the Map
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Arid Landscapes and Hidden Treasures: Exploring Australia’s Deserts on the Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Arid Landscapes and Hidden Treasures: Exploring Australia’s Deserts on the Map

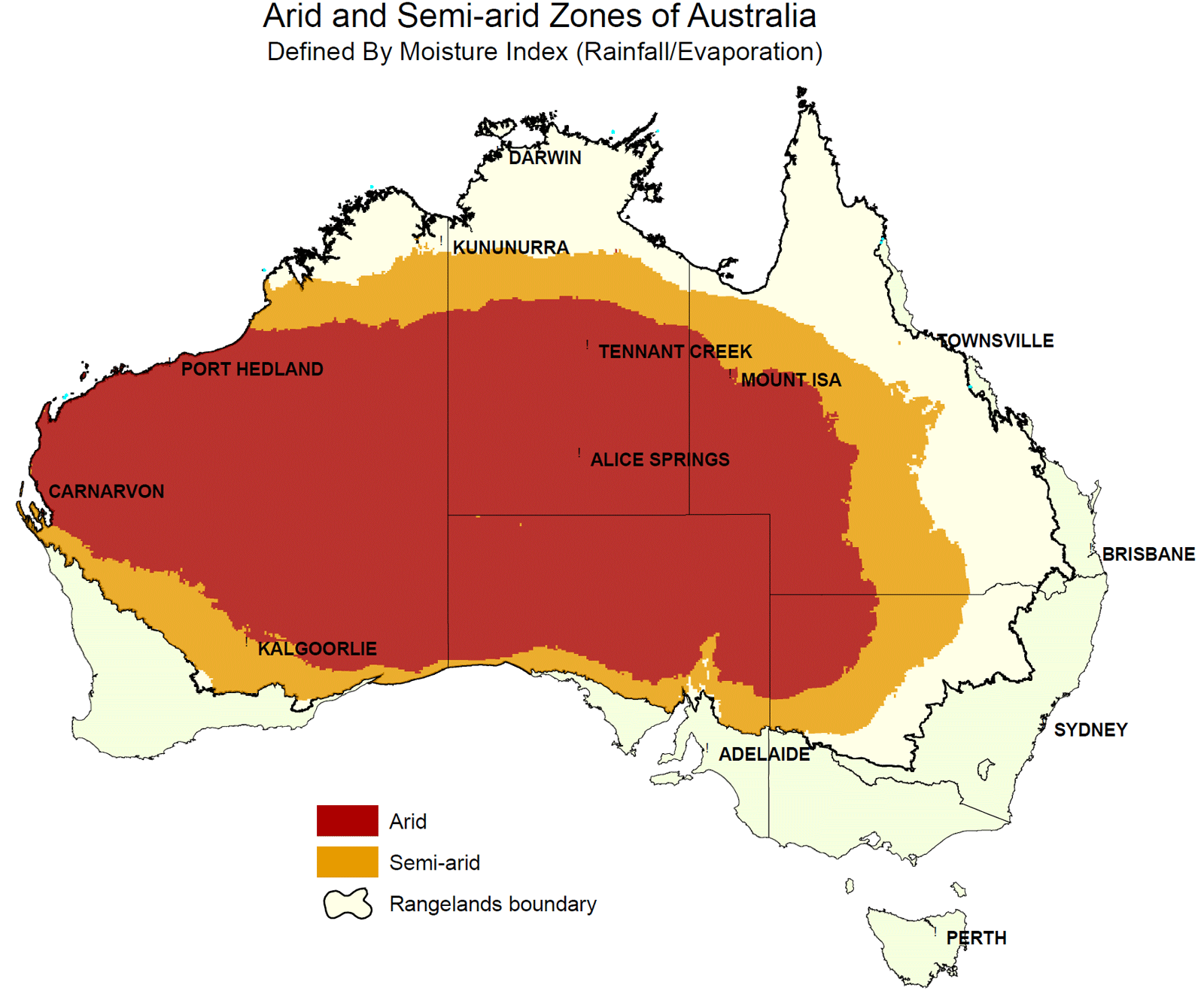
Australia, the world’s smallest continent, boasts a vast and diverse landscape, with deserts dominating a significant portion of its interior. Understanding the geographic distribution of these arid regions is crucial for appreciating the unique ecosystems, cultural heritage, and economic potential they represent. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of Australia’s deserts on the map, highlighting their ecological importance, cultural significance, and potential for sustainable development.
Mapping the Arid Expanse:
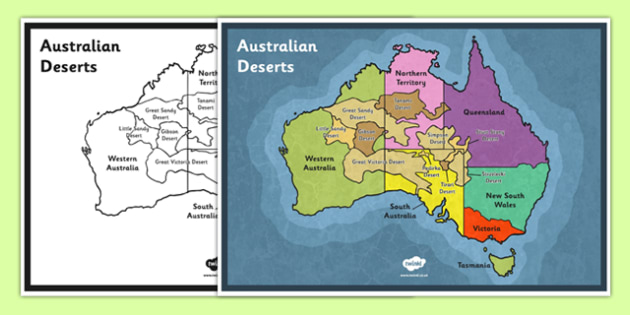
Australia’s deserts, encompassing approximately 70% of the continent, are classified into four major regions:
-
The Great Victoria Desert: Spanning across Western Australia and South Australia, this desert is the largest in Australia, known for its red sand dunes, spinifex grasslands, and unique flora and fauna.
-
The Gibson Desert: Located in Western Australia, this desert is characterized by its vast plains of sand and gravel, with sparse vegetation and harsh climatic conditions.
-
The Simpson Desert: Situated in South Australia, the Simpson Desert is renowned for its striking parallel sand dunes, stretching for hundreds of kilometers, and home to diverse Aboriginal cultures.
-
The Tanami Desert: This desert, situated in the Northern Territory, is known for its rugged terrain, vast sand plains, and unique geological formations, including the iconic Uluru (Ayers Rock).
Beyond the Aridity: Ecological Importance and Biodiversity:
Despite their harsh conditions, Australia’s deserts are home to a remarkable array of life, showcasing remarkable adaptations to survive extreme temperatures, limited water availability, and harsh sunlight.
-
Unique Flora: The deserts support a variety of resilient plant species, including spinifex grasses, acacia trees, and drought-tolerant wildflowers. These plants have evolved specialized mechanisms for water conservation and nutrient absorption.
-
Resilient Fauna: Desert animals, such as kangaroos, dingoes, lizards, and birds, have adapted to the arid environment through behavioral changes, physiological adjustments, and specialized diets.
-
Endemic Species: The deserts are home to numerous endemic species, found nowhere else in the world, highlighting the importance of conservation efforts to protect this unique biodiversity.
Cultural Significance and Indigenous Heritage:
Australia’s deserts have been home to Indigenous Australians for thousands of years. Their deep connection to the land is evident in their traditional knowledge, cultural practices, and sustainable living strategies adapted to the harsh environment.
-
Aboriginal Land Ownership: Many desert regions are recognized as Aboriginal land, with traditional owners playing a vital role in managing and protecting these areas.
-
Cultural Heritage Sites: The deserts are dotted with significant cultural sites, including rock art galleries, ceremonial grounds, and ancient burial sites, reflecting the rich history and spiritual connection of Indigenous communities.
-
Traditional Knowledge: Indigenous knowledge systems provide valuable insights into desert ecology, resource management, and sustainable living practices, offering lessons for modern-day conservation and development.
Economic Potential and Sustainable Development:
While the deserts may seem desolate, they hold significant economic potential, with opportunities for sustainable development and economic diversification.
-
Ecotourism: The unique landscapes and wildlife attract tourists from around the world, creating economic opportunities in tourism, accommodation, and recreation.
-
Mineral Resources: The deserts are rich in mineral deposits, including gold, iron ore, and uranium, contributing to the Australian economy.
-
Renewable Energy: The vast and open spaces of the deserts offer potential for solar and wind energy generation, contributing to a sustainable energy future.
Challenges and Conservation:
The deserts face various challenges, including climate change, invasive species, and unsustainable land management practices.
-
Climate Change Impacts: Rising temperatures and increased aridity pose significant threats to desert ecosystems, impacting water availability, plant growth, and animal populations.
-
Invasive Species: Introduced species, such as feral camels, goats, and rabbits, compete with native species for resources and disrupt delicate ecological balances.
-
Sustainable Land Management: Balancing economic development with environmental protection is crucial to ensure the long-term health and resilience of desert ecosystems.
FAQs about Australia’s Deserts:
Q: What is the driest desert in Australia?
A: The Simpson Desert, located in South Australia, is considered the driest desert in Australia, receiving an average annual rainfall of less than 150 millimeters.
Q: Are there any permanent rivers in Australia’s deserts?
A: Most of Australia’s deserts lack permanent rivers, with water sources primarily relying on occasional rainfall and underground aquifers. The Finke River, in the Northern Territory, is one of the few permanent rivers in the desert region.
Q: What are the major threats to desert ecosystems?
A: Climate change, invasive species, and unsustainable land management practices are major threats to desert ecosystems, leading to habitat loss, biodiversity decline, and ecosystem degradation.
Q: What are some examples of adaptations by desert animals?
A: Desert animals have evolved various adaptations to survive the harsh conditions, including:
- Nocturnal Activity: Many animals are active at night to avoid the extreme daytime heat.
- Water Conservation: Some animals obtain water from their diet, while others have specialized kidneys for efficient water retention.
- Burrowing: Many animals burrow underground to escape the heat and find shelter.
Tips for Responsible Travel in Australia’s Deserts:
- Plan Ahead: Prepare for extreme temperatures, limited water availability, and potential hazards.
- Respect Cultural Sites: Be mindful of the cultural significance of desert areas and avoid disturbing archaeological sites.
- Leave No Trace: Pack out all trash and avoid disturbing the natural environment.
- Support Sustainable Tourism: Choose eco-friendly accommodations and tour operators committed to environmental conservation.
Conclusion:
Australia’s deserts, despite their harsh conditions, are a testament to the resilience of life and the power of adaptation. These arid landscapes are not just barren wastelands but vibrant ecosystems teeming with unique biodiversity, cultural heritage, and economic potential. Understanding the geographic distribution of these deserts on the map is crucial for appreciating their ecological importance, cultural significance, and potential for sustainable development. By embracing responsible tourism, promoting sustainable land management practices, and supporting conservation efforts, we can ensure the continued health and prosperity of these remarkable landscapes for generations to come.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Arid Landscapes and Hidden Treasures: Exploring Australia’s Deserts on the Map. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- A Comprehensive Guide To The Map Of Lakewood, California
- Thailand: A Jewel In The Heart Of Southeast Asia
- Navigating The Nation: A Guide To Free United States Map Vectors
- Navigating The Tapestry Of Arkansas: A Comprehensive Guide To Its Towns And Cities
- Mapping The Shifting Sands: A Look At 9th Century England
- A Journey Through Greene County, New York: Exploring The Land Of Catskill Mountains And Scenic Beauty
- The United States Of America In 1783: A Nation Forged In Boundaries
- Unraveling The Magic: A Comprehensive Guide To The Wizard Of Oz Map In User Experience Design
Leave a Reply