A Journey Through Sub-Saharan Africa: Exploring A Continent Of Diversity And Resilience
A Journey Through Sub-Saharan Africa: Exploring a Continent of Diversity and Resilience
Related Articles: A Journey Through Sub-Saharan Africa: Exploring a Continent of Diversity and Resilience
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Journey Through Sub-Saharan Africa: Exploring a Continent of Diversity and Resilience. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Journey Through Sub-Saharan Africa: Exploring a Continent of Diversity and Resilience

Africa, the second-largest continent, is a tapestry of diverse landscapes, cultures, and histories. The region south of the Sahara Desert, known as Sub-Saharan Africa, holds a unique place in the world’s geography and human experience. This vast expanse, encompassing over 40 countries and numerous distinct ethnicities, boasts a rich tapestry of ecosystems, from sprawling savannas and lush rainforests to towering mountains and arid deserts. Understanding Sub-Saharan Africa’s geography is crucial for comprehending its intricate cultural, economic, and political dynamics.
A Geographic Overview:
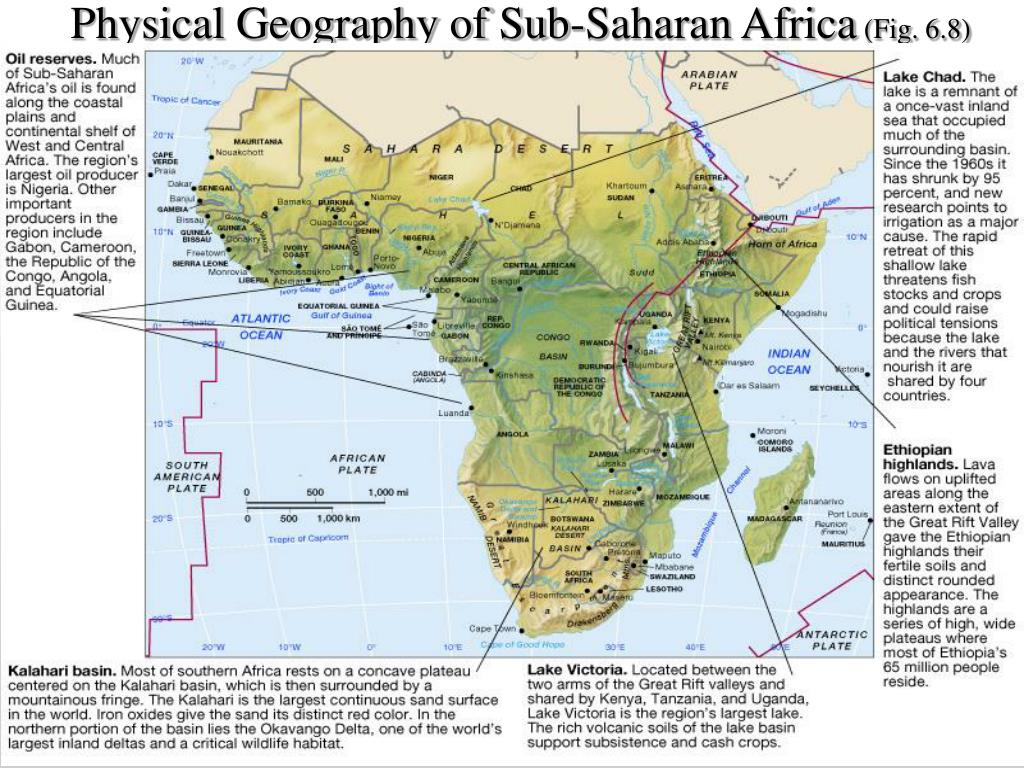
Sub-Saharan Africa, stretching from the Sahara Desert in the north to the southern tip of the continent, encompasses an area of approximately 10.7 million square kilometers. Its geography is defined by a diverse range of physical features:
-
The Great Rift Valley: This geological wonder, stretching over 6,000 kilometers, is a defining feature of East Africa. It is characterized by volcanic activity, deep valleys, and towering mountains, including Mount Kilimanjaro, Africa’s highest peak.
-
The Congo Basin: This vast basin, home to the Congo River, is the world’s second-largest rainforest, playing a vital role in global biodiversity and climate regulation.
-
The Sahel: This semi-arid region, bordering the Sahara Desert, is a transition zone between the desert and the more humid savannas to the south. It faces significant environmental challenges, including desertification and drought.
-
The Savannas: These vast grasslands, characterized by scattered trees and shrubs, dominate much of Sub-Saharan Africa. They are home to a wide range of wildlife, including elephants, lions, giraffes, and zebras.
-
The Drakensberg Mountains: This mountain range, located in South Africa, is a breathtaking landscape of rugged peaks and dramatic cliffs, offering stunning views and diverse ecosystems.
Beyond the Landscape: A Cultural Mosaic:
Sub-Saharan Africa is not just a geographical entity; it is a vibrant cultural mosaic. The continent’s diverse ethnicities, languages, and traditions have shaped a rich heritage that continues to evolve and thrive.
-
Language Diversity: Sub-Saharan Africa is home to over 2,000 languages, representing a remarkable linguistic diversity. The region’s linguistic landscape reflects its long history of cultural exchange and interaction.
-
Traditional Arts and Crafts: From intricate wood carvings and vibrant textiles to elaborate masks and musical instruments, Sub-Saharan Africa’s artistic traditions are a testament to the creativity and ingenuity of its people.
-
Religious Diversity: The region is home to a diverse range of religious beliefs, including Christianity, Islam, traditional African religions, and other faiths. This religious diversity reflects the complex history of cultural exchange and interaction in the region.
Economic Challenges and Opportunities:
Sub-Saharan Africa faces significant economic challenges, including poverty, inequality, and lack of access to essential resources. However, the region also holds immense potential for economic growth and development.
-
Natural Resources: The region is rich in natural resources, including minerals, oil, gas, and agricultural products. These resources offer opportunities for economic development and diversification.
-
Growing Population: Sub-Saharan Africa has a rapidly growing population, presenting both challenges and opportunities. The region’s young population represents a potential workforce for future economic growth.
-
Technological Advancements: The increasing adoption of technology, particularly in areas like mobile banking and e-commerce, is creating new opportunities for economic development and innovation.
The Importance of Understanding Sub-Saharan Africa:
Understanding the geography, culture, and economic dynamics of Sub-Saharan Africa is crucial for several reasons:
-
Global Interconnectedness: The region’s economic, political, and social issues have significant global implications. Understanding Sub-Saharan Africa is essential for addressing global challenges like climate change, poverty, and inequality.
-
Cultural Exchange: The region’s rich cultural heritage offers opportunities for cultural exchange and understanding. By engaging with Sub-Saharan Africa’s arts, music, and traditions, we can broaden our perspectives and appreciate the diversity of human experience.
-
Economic Opportunities: The region’s economic potential offers opportunities for investment and collaboration. Understanding Sub-Saharan Africa’s economic landscape can facilitate sustainable development and improve the lives of its people.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Q: What is the largest country in Sub-Saharan Africa?
A: The largest country in Sub-Saharan Africa is the Democratic Republic of the Congo, with a land area of 2,344,858 square kilometers.
Q: What is the most populous country in Sub-Saharan Africa?
A: The most populous country in Sub-Saharan Africa is Nigeria, with a population of over 200 million.
Q: What are some of the major rivers in Sub-Saharan Africa?
A: Some of the major rivers in Sub-Saharan Africa include the Congo River, the Nile River, the Niger River, and the Zambezi River.
Q: What are some of the major languages spoken in Sub-Saharan Africa?
A: Some of the major languages spoken in Sub-Saharan Africa include Swahili, Yoruba, Hausa, Amharic, and Zulu.
Q: What are some of the major challenges facing Sub-Saharan Africa?
A: Some of the major challenges facing Sub-Saharan Africa include poverty, inequality, conflict, climate change, and disease.
Tips for Understanding Sub-Saharan Africa:
-
Engage with diverse perspectives: Seek out information from a variety of sources, including academic research, news reports, and personal accounts.
-
Explore the region’s rich cultural heritage: Learn about the region’s music, art, literature, and traditions.
-
Support sustainable development initiatives: Consider supporting organizations working to promote economic development and social justice in Sub-Saharan Africa.
-
Travel to the region: Experiencing Sub-Saharan Africa firsthand can provide valuable insights into its culture, landscape, and people.
Conclusion:
Sub-Saharan Africa is a continent of immense diversity, resilience, and potential. Understanding its geography, culture, and economic dynamics is crucial for navigating the complexities of the 21st century. By engaging with the region’s rich heritage, embracing its potential, and supporting sustainable development, we can contribute to a brighter future for Sub-Saharan Africa and the world.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Journey Through Sub-Saharan Africa: Exploring a Continent of Diversity and Resilience. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- A Comprehensive Guide To The Map Of Lakewood, California
- Thailand: A Jewel In The Heart Of Southeast Asia
- Navigating The Nation: A Guide To Free United States Map Vectors
- Navigating The Tapestry Of Arkansas: A Comprehensive Guide To Its Towns And Cities
- Mapping The Shifting Sands: A Look At 9th Century England
- A Journey Through Greene County, New York: Exploring The Land Of Catskill Mountains And Scenic Beauty
- The United States Of America In 1783: A Nation Forged In Boundaries
- Unraveling The Magic: A Comprehensive Guide To The Wizard Of Oz Map In User Experience Design
Leave a Reply