A Geographical Perspective: Understanding The Map Of Israel And Surrounding Areas
A Geographical Perspective: Understanding the Map of Israel and Surrounding Areas
Related Articles: A Geographical Perspective: Understanding the Map of Israel and Surrounding Areas
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Geographical Perspective: Understanding the Map of Israel and Surrounding Areas. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Geographical Perspective: Understanding the Map of Israel and Surrounding Areas

The map of Israel and its surrounding areas is a complex tapestry of history, culture, and geopolitics. Understanding its intricate web of borders, territories, and landscapes is crucial for grasping the region’s multifaceted dynamics. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the map, delving into its physical features, historical context, and contemporary significance.
Physical Geography: A Land of Contrasts
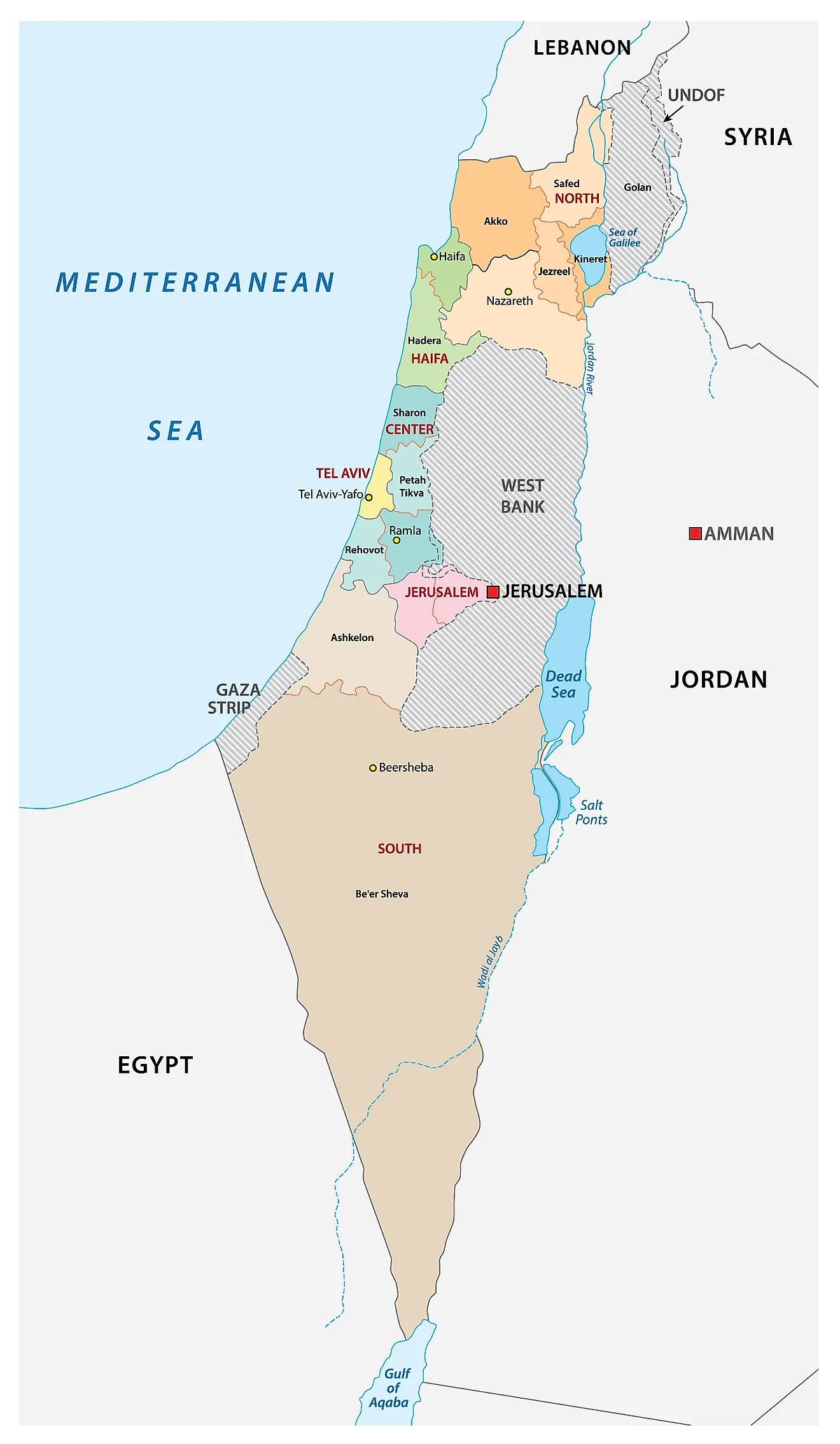
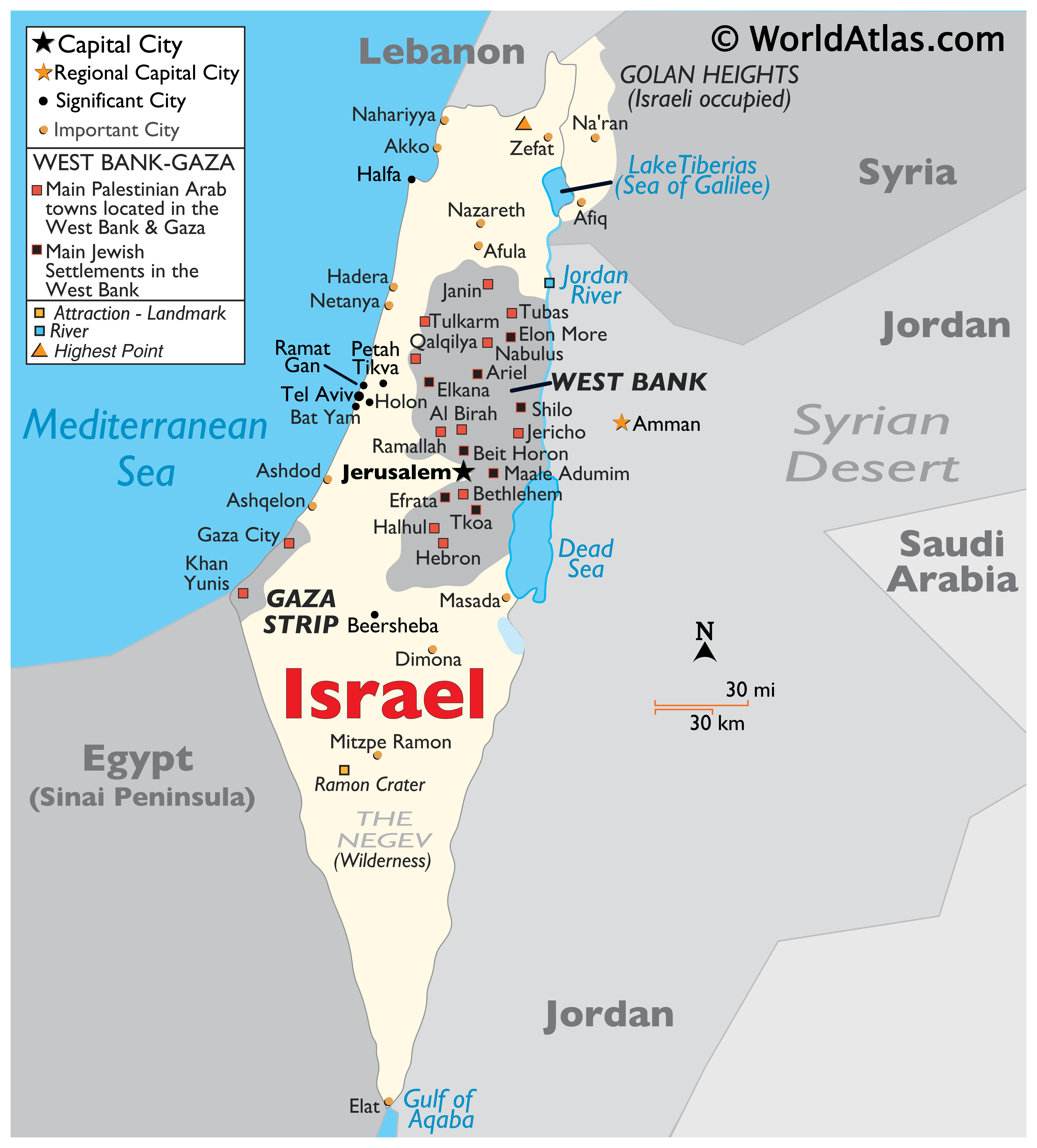
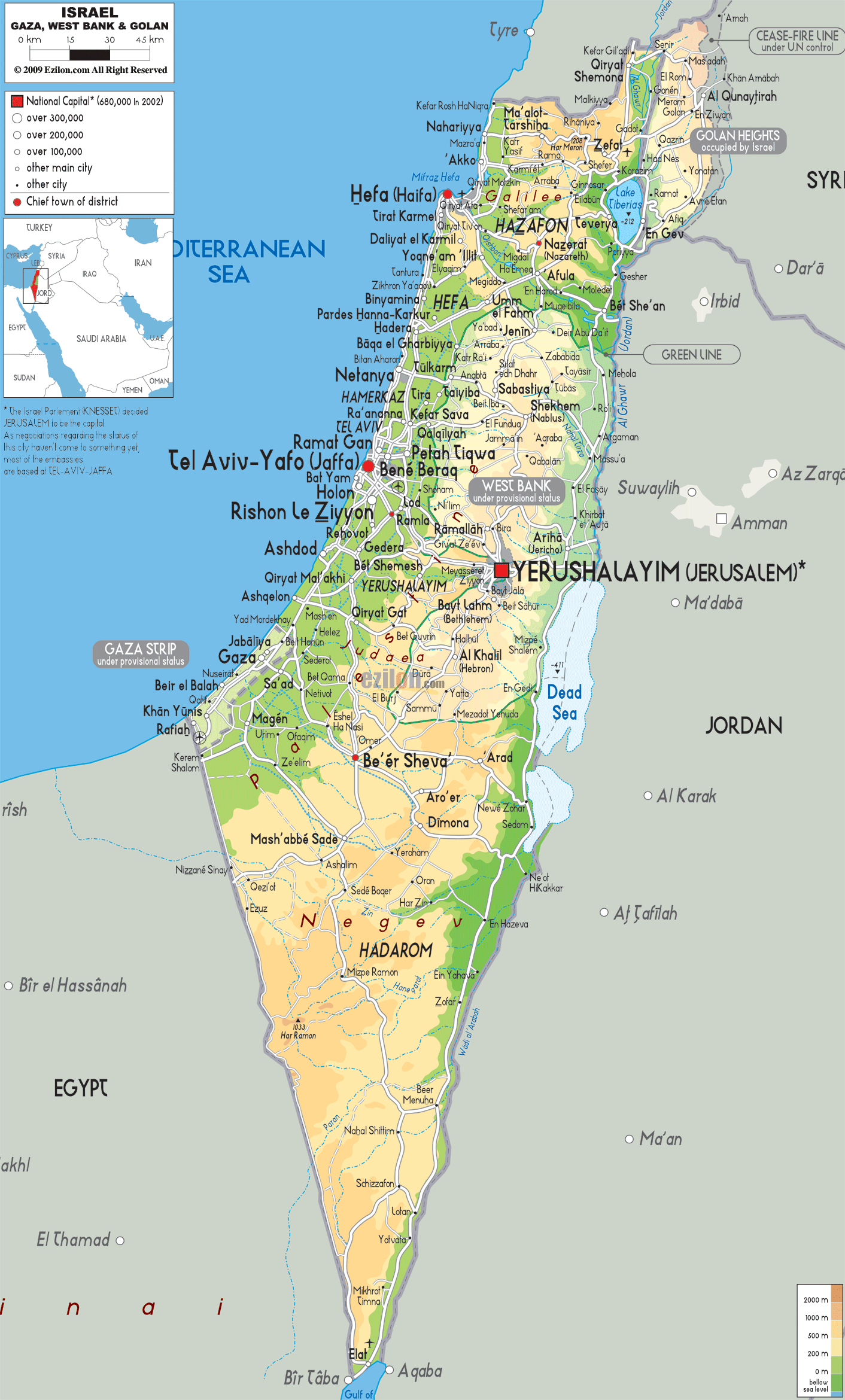
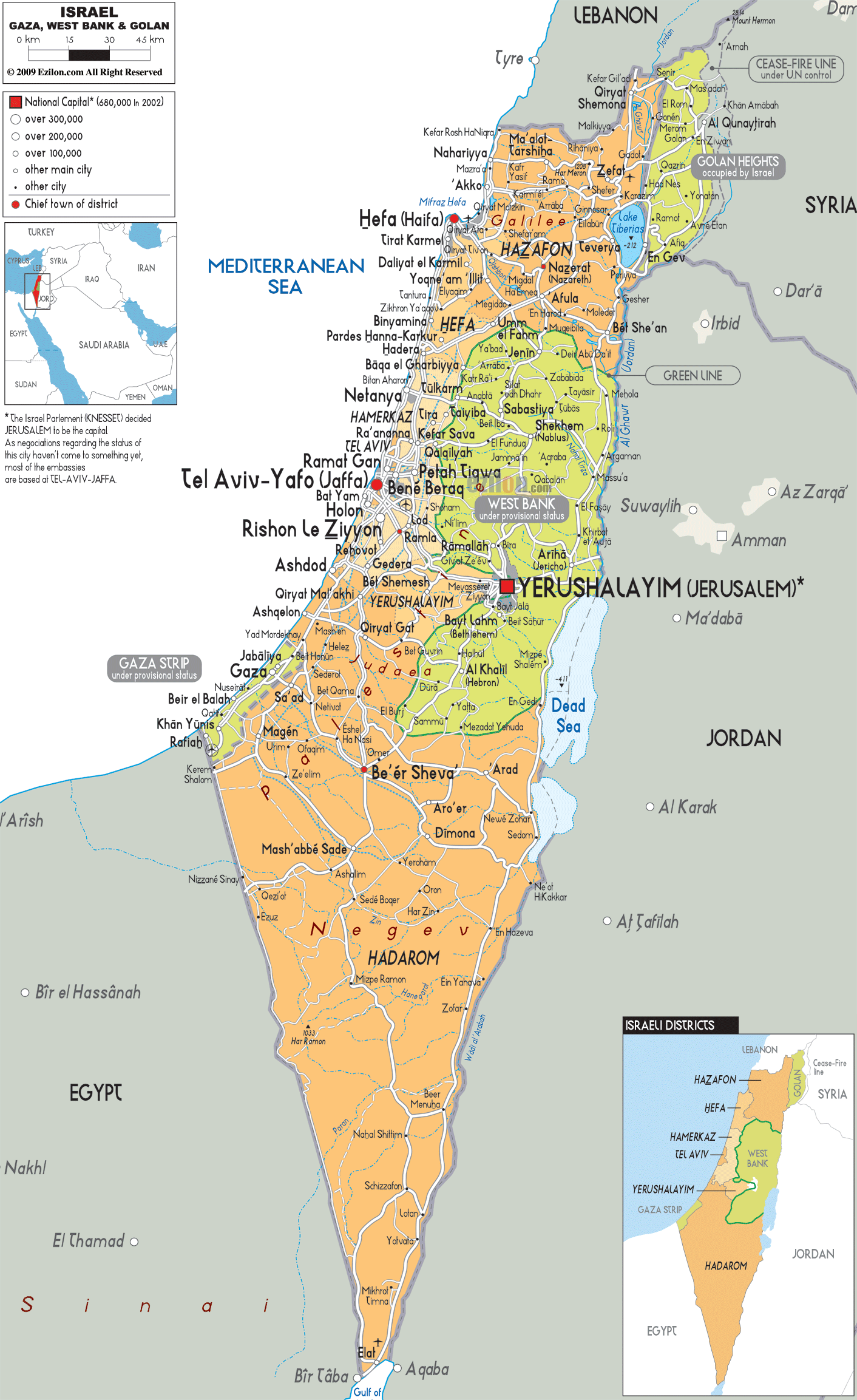
Israel, situated at the crossroads of three continents – Asia, Africa, and Europe – occupies a relatively small area of approximately 22,072 square kilometers. Its landscape is characterized by stark contrasts, ranging from the fertile coastal plains and rolling hills of the Mediterranean Sea to the arid Negev Desert in the south. The country is also home to the Dead Sea, the lowest point on Earth, and the mountainous terrain of the Golan Heights, overlooking the Syrian border.
Surrounding Territories: A Mosaic of Nations
Israel shares borders with five countries: Lebanon to the north, Syria to the northeast, Jordan to the east, Egypt to the southwest, and the Gaza Strip to the southwest. The Gaza Strip, a Palestinian territory, is separated from Israel by a heavily fortified border. The West Bank, another Palestinian territory, is located on the western side of the Jordan River, with its eastern boundary forming part of Jordan’s border.
Historical Context: A Land of Antiquity and Conflict
The region’s history spans millennia, with evidence of human settlements dating back to the Neolithic period. It has been a focal point for empires, religions, and civilizations, leaving an indelible mark on its cultural landscape. The land has witnessed the rise and fall of numerous empires, including the Roman, Byzantine, Ottoman, and British.
The establishment of the State of Israel in 1948 marked a turning point in the region’s history, leading to the Arab-Israeli conflict. The conflict, rooted in competing claims to the land, has resulted in numerous wars and unresolved territorial disputes, shaping the political landscape of the region.
Contemporary Significance: A Hub of Innovation and Conflict
Despite its historical and political complexities, Israel has emerged as a global hub for innovation and technology. Its vibrant economy, particularly in the fields of high-tech, agriculture, and pharmaceuticals, has earned it international recognition. However, the ongoing Israeli-Palestinian conflict continues to cast a shadow over the region, posing challenges to peace and stability.
Understanding the Map: Key Features
1. The Green Line: This line, established in 1949 after the 1948 Arab-Israeli War, marked the armistice line between Israel and its neighboring Arab states. It is often considered the pre-1967 border of Israel, though its status remains contested.
2. The West Bank and Gaza Strip: These Palestinian territories are located within the pre-1967 borders of Israel and are subject to ongoing negotiations between Israel and the Palestinians.
3. The Golan Heights: Captured by Israel from Syria in the 1967 Six-Day War, the Golan Heights remains a disputed territory, with Syria claiming its return.
4. Jerusalem: This holy city, revered by Jews, Christians, and Muslims, is a major source of contention between Israel and the Palestinians. East Jerusalem, captured by Israel in 1967, is claimed by Palestinians as the capital of their future state.
5. The Dead Sea: The lowest point on Earth, the Dead Sea is a natural wonder shared by Israel and Jordan. Its mineral-rich waters attract tourists from around the world.
Benefits of Understanding the Map
A comprehensive understanding of the map of Israel and its surrounding areas offers numerous benefits:
- Informed Decision-Making: It provides crucial context for understanding geopolitical events, enabling informed decision-making on issues related to the region.
- Historical Perspective: It offers insight into the region’s rich history, highlighting the complexities of its present-day dynamics.
- Cultural Appreciation: It fosters appreciation for the diverse cultures and civilizations that have flourished in the region.
- Peacebuilding Efforts: It promotes understanding and dialogue, fostering peacebuilding efforts by highlighting the commonalities and challenges shared by the region’s inhabitants.
FAQs on the Map of Israel and Surrounding Areas
1. What is the status of the West Bank and Gaza Strip?
The West Bank and Gaza Strip are considered Palestinian territories under Israeli occupation. Their status remains contested, with ongoing negotiations between Israel and the Palestinians aiming to resolve their final status.
2. What is the significance of the Green Line?
The Green Line is often considered the pre-1967 border of Israel, though its status is contested. It serves as a reference point in discussions about land swaps and territorial adjustments.
3. What is the current status of Jerusalem?
Jerusalem is a city claimed by both Israel and the Palestinians. Israel considers it its undivided capital, while Palestinians claim East Jerusalem as the capital of their future state. The city’s status remains a major obstacle to peace negotiations.
4. What are the main challenges to peace in the region?
The main challenges to peace in the region include unresolved territorial disputes, the status of Jerusalem, the issue of Palestinian refugees, and the ongoing conflict between Israel and Hamas in the Gaza Strip.
5. What are some key initiatives aimed at resolving the conflict?
Key initiatives aimed at resolving the conflict include the Oslo Accords, the Road Map for Peace, and the two-state solution, which proposes the creation of an independent Palestinian state alongside Israel.
Tips for Understanding the Map
- Use reliable sources: Consult reputable maps, atlases, and online resources to ensure accuracy.
- Study the historical context: Understanding the region’s history is crucial for comprehending its present-day dynamics.
- Explore diverse perspectives: Engage with multiple viewpoints to gain a comprehensive understanding of the region’s complexities.
- Follow current events: Stay informed about ongoing developments and their implications for the region.
Conclusion
The map of Israel and its surrounding areas is a microcosm of the world’s complexities. Its physical features, historical context, and contemporary significance reflect the intertwined nature of geopolitics, culture, and religion. By understanding the map’s intricate details, we can gain valuable insights into the region’s challenges and opportunities, fostering dialogue, understanding, and ultimately, peace.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Geographical Perspective: Understanding the Map of Israel and Surrounding Areas. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- A Comprehensive Guide To The Map Of Lakewood, California
- Thailand: A Jewel In The Heart Of Southeast Asia
- Navigating The Nation: A Guide To Free United States Map Vectors
- Navigating The Tapestry Of Arkansas: A Comprehensive Guide To Its Towns And Cities
- Mapping The Shifting Sands: A Look At 9th Century England
- A Journey Through Greene County, New York: Exploring The Land Of Catskill Mountains And Scenic Beauty
- The United States Of America In 1783: A Nation Forged In Boundaries
- Unraveling The Magic: A Comprehensive Guide To The Wizard Of Oz Map In User Experience Design
Leave a Reply