A Geographical Exploration Of Brazil: A Nation Bridging Continents
A Geographical Exploration of Brazil: A Nation Bridging Continents
Related Articles: A Geographical Exploration of Brazil: A Nation Bridging Continents
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Geographical Exploration of Brazil: A Nation Bridging Continents. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Geographical Exploration of Brazil: A Nation Bridging Continents

Brazil, the largest country in South America, is a vibrant tapestry of landscapes, cultures, and ecosystems. Its unique geographical position, straddling the equator and encompassing a vast swathe of the continent, profoundly shapes its identity and influence on the global stage.
Brazil’s Position on the World Map:
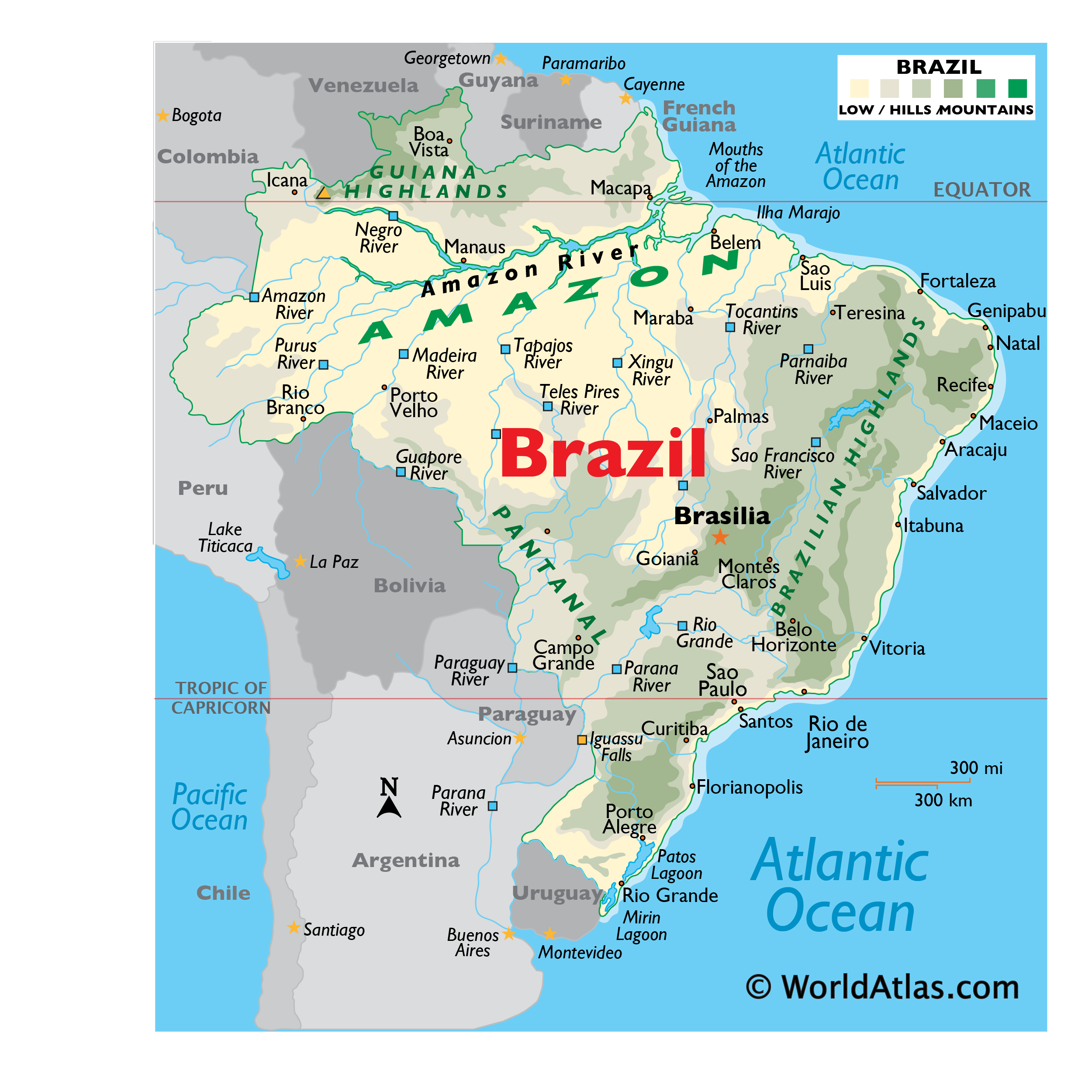
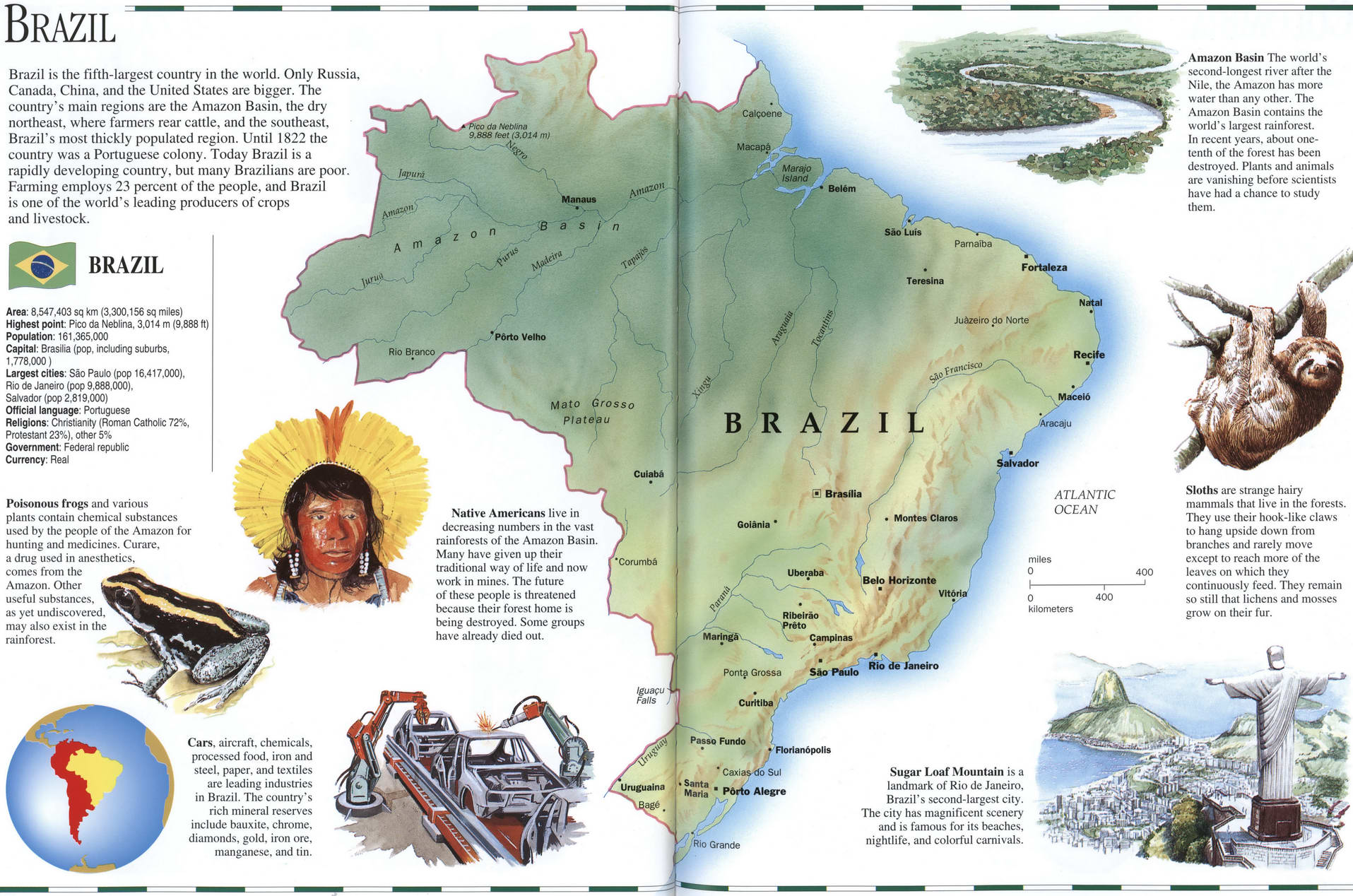
Brazil occupies a prominent position in the Southern Hemisphere, bordering the Atlantic Ocean to its east. Its geographical coordinates are approximately 10° S, 55° W, placing it squarely within the tropical and subtropical zones. The country’s vast size, spanning over 8.5 million square kilometers, makes it the fifth largest country in the world by land area.
Navigating Brazil’s Borders:
Brazil shares borders with ten other South American countries, highlighting its central role in the region:
- North: Colombia, Venezuela, Guyana, Suriname, and French Guiana.
- West: Peru, Bolivia, and Paraguay.
- South: Argentina and Uruguay.
These borders, both natural and artificial, have shaped Brazil’s history, its cultural exchanges, and its economic development.
The Geography of Diversity:
Brazil’s geographical position has gifted it with an extraordinary range of landscapes and ecosystems. The country boasts:
- The Amazon Rainforest: The largest rainforest in the world, covering nearly 60% of Brazil’s territory, is a vital carbon sink and home to incredible biodiversity.
- The Cerrado: A vast savanna region, characterized by unique flora and fauna, playing a crucial role in water regulation and agricultural production.
- The Pantanal: The world’s largest wetland, a haven for diverse wildlife and a critical habitat for migratory birds.
- The Atlantic Forest: A lush coastal forest, rich in biodiversity, facing significant threats from deforestation.
- The Brazilian Highlands: A vast plateau, encompassing diverse landscapes, including mountains, valleys, and grasslands, contributing to the country’s agricultural production.
The Importance of Brazil’s Location:
Brazil’s strategic geographical location has contributed to its global importance in various ways:
- Trade and Commerce: Brazil’s position on the Atlantic coast, with numerous ports, facilitates trade with Europe, Africa, and other parts of the Americas.
- Natural Resources: Its vast landmass holds abundant natural resources, including minerals, oil, and timber, making it a key player in the global economy.
- Biodiversity Hotspot: Brazil’s diverse ecosystems, including the Amazon rainforest, are crucial for maintaining global biodiversity and climate stability.
- Cultural Crossroads: Its location allows for a rich blend of cultures, influenced by indigenous populations, European colonizers, and African slaves, creating a unique cultural tapestry.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Q: What is the capital of Brazil?
A: The capital of Brazil is Brasília, a modern city designed in the 1950s and located in the heart of the country.
Q: What are the major cities in Brazil?
A: Brazil has several major cities, including São Paulo, Rio de Janeiro, Salvador, Belo Horizonte, and Fortaleza, each playing a significant role in the country’s economy and culture.
Q: What are the major languages spoken in Brazil?
A: The official language of Brazil is Portuguese, reflecting its historical ties to Portugal. However, many indigenous languages and dialects are also spoken throughout the country.
Q: What is the climate like in Brazil?
A: Brazil’s climate varies significantly depending on the region, ranging from tropical in the Amazon rainforest to subtropical in the southern regions.
Tips for Visiting Brazil:
- Plan your trip carefully: Consider the time of year, the region you wish to visit, and the activities you wish to enjoy.
- Learn basic Portuguese: Even a few phrases can be helpful for navigating the country.
- Respect local customs: Brazil has a vibrant culture, and respecting local customs is essential.
- Experience the diversity: Explore different regions to experience the unique landscapes, cultures, and cuisines.
- Be prepared for the weather: Pack for both hot and humid conditions, and be prepared for potential rain.
Conclusion:
Brazil’s unique geographical position, spanning vast landscapes and encompassing diverse cultures, has shaped its identity and influence on the world stage. Its strategic location, abundant natural resources, and vibrant cultural heritage make it a fascinating and important country to explore and understand. Brazil stands as a testament to the power of geography to influence not only physical landscapes but also human history, culture, and global impact.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Geographical Exploration of Brazil: A Nation Bridging Continents. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- A Comprehensive Guide To The Map Of Lakewood, California
- Thailand: A Jewel In The Heart Of Southeast Asia
- Navigating The Nation: A Guide To Free United States Map Vectors
- Navigating The Tapestry Of Arkansas: A Comprehensive Guide To Its Towns And Cities
- Mapping The Shifting Sands: A Look At 9th Century England
- A Journey Through Greene County, New York: Exploring The Land Of Catskill Mountains And Scenic Beauty
- The United States Of America In 1783: A Nation Forged In Boundaries
- Unraveling The Magic: A Comprehensive Guide To The Wizard Of Oz Map In User Experience Design
Leave a Reply